User login
A pregnancy loss at any gestational age is devastating. Women and/or couples may, unfairly, self-blame as they desperately seek substantive answers. Their support systems, including health care providers, offer some, albeit fleeting, comfort. Conception is merely the start of an emotionally arduous first trimester that often results in a learned helplessness. This month, we focus on the comprehensive evaluation and the medical evidence–based approach to recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
RPL is defined by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine as two or more clinical pregnancy losses of less than 20 weeks’ gestation with a prevalence of approximately 5%. Embryo aneuploidy is the most common reason for a spontaneous miscarriage, occurring in 50%-70% of losses. The risk of spontaneous miscarriage during the reproductive years follows a J-shaped pattern. The lowest percentage is in women aged 25-29 years (9.8%), with a nadir at age 27 (9.5%), then an increasingly steep rise after age 35 to a peak at age 45 and over (53.6%). The loss rate is closer to 50% of all fertilizations since many spontaneous miscarriages occur at 2-4 weeks, before a pregnancy can be clinically diagnosed. The frequency of embryo aneuploidy significantly decreases and embryo euploidy increases with successive numbers of spontaneous miscarriages.
After three or more spontaneous miscarriages, nulliparous women appear to have a higher rate of subsequent pregnancy loss, compared with parous women (BMJ. 2000;320:1708). We recommend an evaluation following two losses given the lack of evidence for a difference in diagnostic yield following two versus three miscarriages and particularly because of the emotional effects of impact of RPL.
RPL causes, percentages of contribution, and evaluation
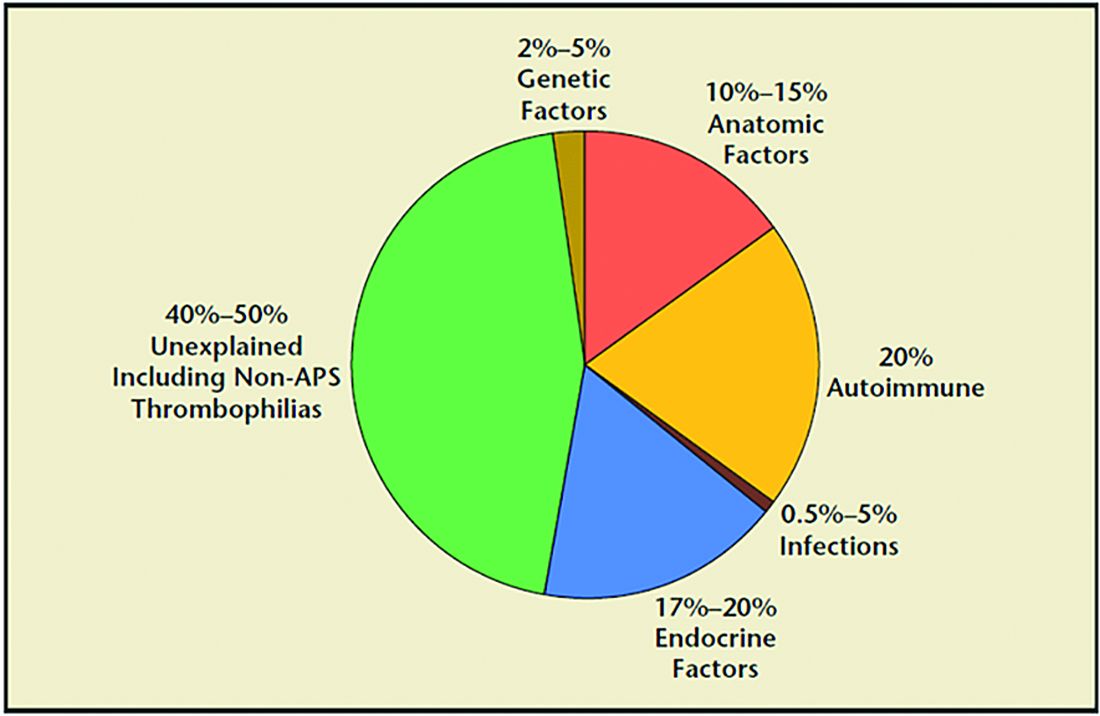
1. Genetic (2%-5%). Because of the risk of an embryo with an unbalanced chromosomal rearrangement inherited from a translocation present in either of the couple, a blood karyotype of the couple is essential despite a history of one or more successful live births. While in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) can successfully diagnose affected embryos to avoid their intrauterine transfer, overall live birth rates are similar when comparing natural conception attempts with PGT-SR, although the latter may reduce miscarriages.
2. Anatomic (10%-15%). Hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingogram, or saline ultrasound can be used to image the uterine cavity to evaluate for polyps, fibroids, scarring, or a congenital septum – all of which can be surgically corrected. Chronic endometritis has been found in 27% of patients with recurrent miscarriage (and in 14% with recurrent implantation failure), therefore testing by biopsy is reasonable. An elevated level of homocysteine has been reported to impair DNA methylation and gene expression, causing defective chorionic villous vascularization in spontaneous miscarriage tissues. We recommend folic acid supplementation and the avoidance of testing for MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase). Of note, the recent TRUST study showed no significant benefit from metroplasty in comparison with expectant management in 12 months of observation resulting in a live birth rate of 31% versus 35%, respectively.
3. Acquired thrombophilias (20%). Medical evidence supports testing for the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS), i.e., RPL with either the presence of lupus anticoagulant (LAC), anticardiolipin antibodies, or anti-beta2 glycoprotein for IgG and IgM. Persistent LAC or elevations of antibodies greater than 40 GPL or greater than the 99th percentile for more than 12 weeks justifies the use of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). APS has been shown to cause RPL, thrombosis, and/or autoimmune thrombocytopenia. There is no definitive evidence to support testing for MTHFR or any other thrombophilias for first trimester RPL. APS has up to a 90% fetal loss rate without therapeutic intervention. Treatment includes low-dose aspirin (81 mg daily) and LMWH. These medications are thought to help prevent thrombosis in the placenta, helping to maintain pregnancies.
4. Hormonal (17%-20%). The most common hormonal disorders increasing the risk for miscarriage is thyroid dysfunction (both hyper- and hypothyroid), prolactin elevations, and lack of glucose control. While the concern for a luteal phase (LPD) prevails, there is no accepted definition or treatment. There is recent evidence that antibodies to thyroid peroxidase may increase miscarriage and that low-dose thyroid replacement may reduce this risk. One other important area is the polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). This hormonal abnormality affects 6%-20% of all reproductive aged women and may increase miscarriage.
5. Unexplained (40%-50%). The most frustrating but most common reason for RPL. Nevertheless, close monitoring and supportive care throughout the first trimester has been demonstrated in medical studies to improve outcome.
Seven surprising facts about recurrent miscarriage
1. Folic acid 4 mg daily may decrease embryo chromosomal abnormalities and miscarriage.
Folic acid in doses of at least 0.4 mg daily have long been advocated to reduce spina bifida and neural tube defects. It is optimal to begin folic acid for several months prior to conception attempts. There is evidence it may help treat RPL by reducing the chance for chromosomal errors.
2. A randomized trial did not demonstrate an improved live birth rate using progesterone in the first trimester. However, women enrolled may not have begun progesterone until 6 weeks of pregnancy, begging the question if earlier progesterone would have demonstrated improvement.
Dydrogesterone, a progestogen that is highly selective for the progesterone receptor, lacks estrogenic, androgenic, anabolic, and corticoid properties. Although not available in the United States, dydrogesterone appears to reduce the rate of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage (two or more losses). Also, progesterone support has been shown to reduce loss in threatened miscarriage – 17 OHPC 500 mg IM weekly in the first trimester.
3. No benefit of aspirin and/or heparin to treat unexplained RM.
The use of aspirin and/or heparin-like medication has convincingly been shown to not improve live birth rates in RPL.
4. Inherited thrombophilias are NOT associated with RM and should not be tested.
Screening for factor V (Leiden mutation), factor II (Prothrombin G20210A), and MTHFR have not been shown to cause RM and no treatment, such as aspirin and/or heparin-like medications, improves the live birth rate.
5. Close monitoring and empathetic care improves outcomes.
For unknown reasons, clinics providing close monitoring, emotional support, and education to patients with unexplained RM report higher live birth rates, compared with patients not receiving this level of care.
6. Behavior changes reduce miscarriage.
Elevations in body mass index (BMI) and cigarette smoking both increase the risk of miscarriage. As a result, a healthy BMI and eliminating tobacco use reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. Excessive caffeine use (more than two equivalent cups of caffeine in coffee per day) also may increase spontaneous miscarriage.
7. Fertility medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) do not improve outcomes.
While patients and, often, health care providers, feel compelled to proceed with fertility treatment, ovulation induction medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or PGT-A have not been shown to improve the chance for a live birth. PGT-A did not reduce the risk of miscarriage in women with recurrent pregnancy loss.
In summary, following two or more pregnancy losses, I recommend obtaining chromosomal testing of the couple, viewing the uterine cavity, blood testing for thyroid, prolactin, and glucose control, and acquired thrombophilias (as above). Fortunately, when the cause is unexplained, the woman has a 70%-80% chance of a spontaneous live birth over the next 10 years from diagnosis. By further understanding, knowing how to diagnose, and, finally, treating the cause of RPL we can hopefully prevent the heartbreak women and couples endure.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A pregnancy loss at any gestational age is devastating. Women and/or couples may, unfairly, self-blame as they desperately seek substantive answers. Their support systems, including health care providers, offer some, albeit fleeting, comfort. Conception is merely the start of an emotionally arduous first trimester that often results in a learned helplessness. This month, we focus on the comprehensive evaluation and the medical evidence–based approach to recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
RPL is defined by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine as two or more clinical pregnancy losses of less than 20 weeks’ gestation with a prevalence of approximately 5%. Embryo aneuploidy is the most common reason for a spontaneous miscarriage, occurring in 50%-70% of losses. The risk of spontaneous miscarriage during the reproductive years follows a J-shaped pattern. The lowest percentage is in women aged 25-29 years (9.8%), with a nadir at age 27 (9.5%), then an increasingly steep rise after age 35 to a peak at age 45 and over (53.6%). The loss rate is closer to 50% of all fertilizations since many spontaneous miscarriages occur at 2-4 weeks, before a pregnancy can be clinically diagnosed. The frequency of embryo aneuploidy significantly decreases and embryo euploidy increases with successive numbers of spontaneous miscarriages.
After three or more spontaneous miscarriages, nulliparous women appear to have a higher rate of subsequent pregnancy loss, compared with parous women (BMJ. 2000;320:1708). We recommend an evaluation following two losses given the lack of evidence for a difference in diagnostic yield following two versus three miscarriages and particularly because of the emotional effects of impact of RPL.
RPL causes, percentages of contribution, and evaluation
1. Genetic (2%-5%). Because of the risk of an embryo with an unbalanced chromosomal rearrangement inherited from a translocation present in either of the couple, a blood karyotype of the couple is essential despite a history of one or more successful live births. While in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) can successfully diagnose affected embryos to avoid their intrauterine transfer, overall live birth rates are similar when comparing natural conception attempts with PGT-SR, although the latter may reduce miscarriages.
2. Anatomic (10%-15%). Hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingogram, or saline ultrasound can be used to image the uterine cavity to evaluate for polyps, fibroids, scarring, or a congenital septum – all of which can be surgically corrected. Chronic endometritis has been found in 27% of patients with recurrent miscarriage (and in 14% with recurrent implantation failure), therefore testing by biopsy is reasonable. An elevated level of homocysteine has been reported to impair DNA methylation and gene expression, causing defective chorionic villous vascularization in spontaneous miscarriage tissues. We recommend folic acid supplementation and the avoidance of testing for MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase). Of note, the recent TRUST study showed no significant benefit from metroplasty in comparison with expectant management in 12 months of observation resulting in a live birth rate of 31% versus 35%, respectively.
3. Acquired thrombophilias (20%). Medical evidence supports testing for the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS), i.e., RPL with either the presence of lupus anticoagulant (LAC), anticardiolipin antibodies, or anti-beta2 glycoprotein for IgG and IgM. Persistent LAC or elevations of antibodies greater than 40 GPL or greater than the 99th percentile for more than 12 weeks justifies the use of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). APS has been shown to cause RPL, thrombosis, and/or autoimmune thrombocytopenia. There is no definitive evidence to support testing for MTHFR or any other thrombophilias for first trimester RPL. APS has up to a 90% fetal loss rate without therapeutic intervention. Treatment includes low-dose aspirin (81 mg daily) and LMWH. These medications are thought to help prevent thrombosis in the placenta, helping to maintain pregnancies.
4. Hormonal (17%-20%). The most common hormonal disorders increasing the risk for miscarriage is thyroid dysfunction (both hyper- and hypothyroid), prolactin elevations, and lack of glucose control. While the concern for a luteal phase (LPD) prevails, there is no accepted definition or treatment. There is recent evidence that antibodies to thyroid peroxidase may increase miscarriage and that low-dose thyroid replacement may reduce this risk. One other important area is the polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). This hormonal abnormality affects 6%-20% of all reproductive aged women and may increase miscarriage.
5. Unexplained (40%-50%). The most frustrating but most common reason for RPL. Nevertheless, close monitoring and supportive care throughout the first trimester has been demonstrated in medical studies to improve outcome.

Seven surprising facts about recurrent miscarriage
1. Folic acid 4 mg daily may decrease embryo chromosomal abnormalities and miscarriage.
Folic acid in doses of at least 0.4 mg daily have long been advocated to reduce spina bifida and neural tube defects. It is optimal to begin folic acid for several months prior to conception attempts. There is evidence it may help treat RPL by reducing the chance for chromosomal errors.
2. A randomized trial did not demonstrate an improved live birth rate using progesterone in the first trimester. However, women enrolled may not have begun progesterone until 6 weeks of pregnancy, begging the question if earlier progesterone would have demonstrated improvement.
Dydrogesterone, a progestogen that is highly selective for the progesterone receptor, lacks estrogenic, androgenic, anabolic, and corticoid properties. Although not available in the United States, dydrogesterone appears to reduce the rate of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage (two or more losses). Also, progesterone support has been shown to reduce loss in threatened miscarriage – 17 OHPC 500 mg IM weekly in the first trimester.
3. No benefit of aspirin and/or heparin to treat unexplained RM.
The use of aspirin and/or heparin-like medication has convincingly been shown to not improve live birth rates in RPL.
4. Inherited thrombophilias are NOT associated with RM and should not be tested.
Screening for factor V (Leiden mutation), factor II (Prothrombin G20210A), and MTHFR have not been shown to cause RM and no treatment, such as aspirin and/or heparin-like medications, improves the live birth rate.
5. Close monitoring and empathetic care improves outcomes.
For unknown reasons, clinics providing close monitoring, emotional support, and education to patients with unexplained RM report higher live birth rates, compared with patients not receiving this level of care.
6. Behavior changes reduce miscarriage.
Elevations in body mass index (BMI) and cigarette smoking both increase the risk of miscarriage. As a result, a healthy BMI and eliminating tobacco use reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. Excessive caffeine use (more than two equivalent cups of caffeine in coffee per day) also may increase spontaneous miscarriage.
7. Fertility medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) do not improve outcomes.
While patients and, often, health care providers, feel compelled to proceed with fertility treatment, ovulation induction medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or PGT-A have not been shown to improve the chance for a live birth. PGT-A did not reduce the risk of miscarriage in women with recurrent pregnancy loss.
In summary, following two or more pregnancy losses, I recommend obtaining chromosomal testing of the couple, viewing the uterine cavity, blood testing for thyroid, prolactin, and glucose control, and acquired thrombophilias (as above). Fortunately, when the cause is unexplained, the woman has a 70%-80% chance of a spontaneous live birth over the next 10 years from diagnosis. By further understanding, knowing how to diagnose, and, finally, treating the cause of RPL we can hopefully prevent the heartbreak women and couples endure.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A pregnancy loss at any gestational age is devastating. Women and/or couples may, unfairly, self-blame as they desperately seek substantive answers. Their support systems, including health care providers, offer some, albeit fleeting, comfort. Conception is merely the start of an emotionally arduous first trimester that often results in a learned helplessness. This month, we focus on the comprehensive evaluation and the medical evidence–based approach to recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
RPL is defined by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine as two or more clinical pregnancy losses of less than 20 weeks’ gestation with a prevalence of approximately 5%. Embryo aneuploidy is the most common reason for a spontaneous miscarriage, occurring in 50%-70% of losses. The risk of spontaneous miscarriage during the reproductive years follows a J-shaped pattern. The lowest percentage is in women aged 25-29 years (9.8%), with a nadir at age 27 (9.5%), then an increasingly steep rise after age 35 to a peak at age 45 and over (53.6%). The loss rate is closer to 50% of all fertilizations since many spontaneous miscarriages occur at 2-4 weeks, before a pregnancy can be clinically diagnosed. The frequency of embryo aneuploidy significantly decreases and embryo euploidy increases with successive numbers of spontaneous miscarriages.
After three or more spontaneous miscarriages, nulliparous women appear to have a higher rate of subsequent pregnancy loss, compared with parous women (BMJ. 2000;320:1708). We recommend an evaluation following two losses given the lack of evidence for a difference in diagnostic yield following two versus three miscarriages and particularly because of the emotional effects of impact of RPL.
RPL causes, percentages of contribution, and evaluation
1. Genetic (2%-5%). Because of the risk of an embryo with an unbalanced chromosomal rearrangement inherited from a translocation present in either of the couple, a blood karyotype of the couple is essential despite a history of one or more successful live births. While in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) can successfully diagnose affected embryos to avoid their intrauterine transfer, overall live birth rates are similar when comparing natural conception attempts with PGT-SR, although the latter may reduce miscarriages.
2. Anatomic (10%-15%). Hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingogram, or saline ultrasound can be used to image the uterine cavity to evaluate for polyps, fibroids, scarring, or a congenital septum – all of which can be surgically corrected. Chronic endometritis has been found in 27% of patients with recurrent miscarriage (and in 14% with recurrent implantation failure), therefore testing by biopsy is reasonable. An elevated level of homocysteine has been reported to impair DNA methylation and gene expression, causing defective chorionic villous vascularization in spontaneous miscarriage tissues. We recommend folic acid supplementation and the avoidance of testing for MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase). Of note, the recent TRUST study showed no significant benefit from metroplasty in comparison with expectant management in 12 months of observation resulting in a live birth rate of 31% versus 35%, respectively.
3. Acquired thrombophilias (20%). Medical evidence supports testing for the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS), i.e., RPL with either the presence of lupus anticoagulant (LAC), anticardiolipin antibodies, or anti-beta2 glycoprotein for IgG and IgM. Persistent LAC or elevations of antibodies greater than 40 GPL or greater than the 99th percentile for more than 12 weeks justifies the use of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). APS has been shown to cause RPL, thrombosis, and/or autoimmune thrombocytopenia. There is no definitive evidence to support testing for MTHFR or any other thrombophilias for first trimester RPL. APS has up to a 90% fetal loss rate without therapeutic intervention. Treatment includes low-dose aspirin (81 mg daily) and LMWH. These medications are thought to help prevent thrombosis in the placenta, helping to maintain pregnancies.
4. Hormonal (17%-20%). The most common hormonal disorders increasing the risk for miscarriage is thyroid dysfunction (both hyper- and hypothyroid), prolactin elevations, and lack of glucose control. While the concern for a luteal phase (LPD) prevails, there is no accepted definition or treatment. There is recent evidence that antibodies to thyroid peroxidase may increase miscarriage and that low-dose thyroid replacement may reduce this risk. One other important area is the polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). This hormonal abnormality affects 6%-20% of all reproductive aged women and may increase miscarriage.
5. Unexplained (40%-50%). The most frustrating but most common reason for RPL. Nevertheless, close monitoring and supportive care throughout the first trimester has been demonstrated in medical studies to improve outcome.

Seven surprising facts about recurrent miscarriage
1. Folic acid 4 mg daily may decrease embryo chromosomal abnormalities and miscarriage.
Folic acid in doses of at least 0.4 mg daily have long been advocated to reduce spina bifida and neural tube defects. It is optimal to begin folic acid for several months prior to conception attempts. There is evidence it may help treat RPL by reducing the chance for chromosomal errors.
2. A randomized trial did not demonstrate an improved live birth rate using progesterone in the first trimester. However, women enrolled may not have begun progesterone until 6 weeks of pregnancy, begging the question if earlier progesterone would have demonstrated improvement.
Dydrogesterone, a progestogen that is highly selective for the progesterone receptor, lacks estrogenic, androgenic, anabolic, and corticoid properties. Although not available in the United States, dydrogesterone appears to reduce the rate of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage (two or more losses). Also, progesterone support has been shown to reduce loss in threatened miscarriage – 17 OHPC 500 mg IM weekly in the first trimester.
3. No benefit of aspirin and/or heparin to treat unexplained RM.
The use of aspirin and/or heparin-like medication has convincingly been shown to not improve live birth rates in RPL.
4. Inherited thrombophilias are NOT associated with RM and should not be tested.
Screening for factor V (Leiden mutation), factor II (Prothrombin G20210A), and MTHFR have not been shown to cause RM and no treatment, such as aspirin and/or heparin-like medications, improves the live birth rate.
5. Close monitoring and empathetic care improves outcomes.
For unknown reasons, clinics providing close monitoring, emotional support, and education to patients with unexplained RM report higher live birth rates, compared with patients not receiving this level of care.
6. Behavior changes reduce miscarriage.
Elevations in body mass index (BMI) and cigarette smoking both increase the risk of miscarriage. As a result, a healthy BMI and eliminating tobacco use reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. Excessive caffeine use (more than two equivalent cups of caffeine in coffee per day) also may increase spontaneous miscarriage.
7. Fertility medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) do not improve outcomes.
While patients and, often, health care providers, feel compelled to proceed with fertility treatment, ovulation induction medications, intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, or PGT-A have not been shown to improve the chance for a live birth. PGT-A did not reduce the risk of miscarriage in women with recurrent pregnancy loss.
In summary, following two or more pregnancy losses, I recommend obtaining chromosomal testing of the couple, viewing the uterine cavity, blood testing for thyroid, prolactin, and glucose control, and acquired thrombophilias (as above). Fortunately, when the cause is unexplained, the woman has a 70%-80% chance of a spontaneous live birth over the next 10 years from diagnosis. By further understanding, knowing how to diagnose, and, finally, treating the cause of RPL we can hopefully prevent the heartbreak women and couples endure.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.

