User login
Investigators used coordinate and lesion network mapping to assess whether there was a shared brain network common to multiple psychiatric disorders. In a meta-analysis of almost 200 studies encompassing more than 15,000 individuals, they found that atrophy coordinates across these six psychiatric conditions all mapped to a common brain network.
Moreover, lesion damage to this network in patients with penetrating head trauma correlated with the number of psychiatric illnesses that the patients were diagnosed with post trauma.
The findings have “bigger-picture potential implications,” lead author Joseph Taylor, MD, PhD, medical director of transcranial magnetic stimulation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Boston, told this news organization.
“In psychiatry, we talk about symptoms and define our disorders based on symptom checklists, which are fairly reliable but don’t have neurobiological underpinnings,” said Dr. Taylor, who is also an associate psychiatrist in Brigham’s department of psychiatry.
By contrast, “in neurology, we ask: ‘Where is the lesion?’ Studying brain networks could potentially help us diagnose and treat people with psychiatric illness more effectively, just as we treat neurological disorders,” he added.
The findings were published online in Nature Human Behavior.
Beyond symptom checklists
Dr. Taylor noted that, in the field of psychiatry, “we often study disorders in isolation,” such as generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder.
“But what see clinically is that half of patients meet the criteria for more than one psychiatric disorder,” he said. “It can be difficult to diagnose and treat these patients, and there are worse treatment outcomes.”
There is also a “discrepancy” between how these disorders are studied (one at a time) and how patients are treated in clinic, Dr. Taylor noted. And there is increasing evidence that psychiatric disorders may share a common neurobiology.
This “highlights the possibility of potentially developing transdiagnostic treatments based on common neurobiology, not just symptom checklists,” Dr. Taylor said.
Prior work “has attempted to map abnormalities to common brain regions rather than to a common brain network,” the investigators wrote. Moreover, “prior studies have rarely tested specificity by comparing psychiatric disorders to other brain disorders.”
In the current study, the researchers used “morphometric brain lesion datasets coupled with a wiring diagram of the human brain to derive a convergent brain network for psychiatric illness.”
They analyzed four large published datasets. Dataset 1 was sourced from an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis (ALE) of whole-brain voxel-based studies that compared patients with psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, BD, depression, addiction, OCD, and anxiety to healthy controls (n = 193 studies; 15,892 individuals in total).
Dataset 2 was drawn from published neuroimaging studies involving patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative conditions (n = 72 studies). They reported coordinates regarding which patients with these disorders had more atrophy compared with control persons.
Dataset 3 was sourced from the Vietnam Head Injury study, which followed veterans with and those without penetrating head injuries (n = 194 veterans with injuries). Dataset 4 was sourced from published neurosurgical ablation coordinates for depression.
Shared neurobiology
Upon analyzing dataset 1, the researchers found decreased gray matter in the bilateral anterior insula, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, thalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and parietal operculum – findings that are “consistent with prior work.”
However, fewer than 35% of the studies contributed to any single cluster; and no cluster was specific to psychiatric versus neurodegenerative coordinates (drawn from dataset 2).
On the other hand, coordinate network mapping yielded “more statistically robust” (P < .001) results, which were found in 85% of the studies. “Psychiatric atrophy coordinates were functionally connected to the same network of brain regions,” the researchers reported.
This network was defined by two types of connectivity, positive and negative.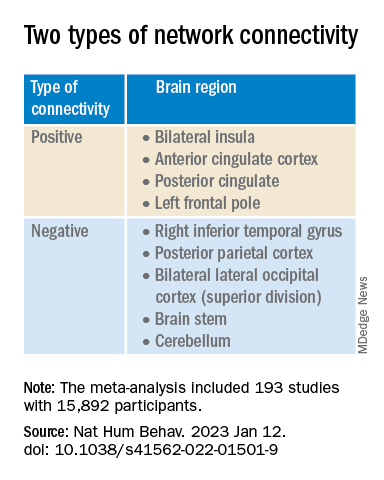
“The topography of this transdiagnostic network was independent of the statistical threshold and specific to psychiatric (vs. neurodegenerative) disorders, with the strongest peak occurring in the posterior parietal cortex (Brodmann Area 7) near the intraparietal sulcus,” the investigators wrote.
When lesions from dataset 3 were overlaid onto the ALE map and the transdiagnostic network in order to evaluate whether damage to either map correlated with number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnosis, results showed no evidence of a correlation between psychiatric comorbidity and damage on the ALE map (Pearson r, 0.02; P = .766).
However, when the same approach was applied to the transdiagnostic network, a statistically significant correlation was found between psychiatric comorbidity and lesion damage (Pearson r, –0.21; P = .01). A multiple regression model showed that the transdiagnostic, but not the ALE, network “independently predicted the number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnoses” (P = .003 vs. P = .1), the investigators reported.
All four neurosurgical ablative targets for psychiatric disorders found on analysis of dataset 4 “intersected” and aligned with the transdiagnostic network.
“The study does not immediately impact clinical practice, but it would be helpful for practicing clinicians to know that psychiatric disorders commonly co-occur and might share common neurobiology and a convergent brain network,” Dr. Taylor said.
“Future work based on our findings could potentially influence clinical trials and clinical practice, especially in the area of brain stimulation,” he added.
‘Exciting new targets’
In a comment, Desmond Oathes, PhD, associate director, Center for Neuromodulation and Stress, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the “next step in the science is to combine individual brain imaging, aka, ‘individualized connectomes,’ with these promising group maps to determine something meaningful at the individual patient level.”
Dr. Oathes, who is also a faculty clinician at the Center for the Treatment and Study of Anxiety and was not involved with the study, noted that an open question is whether the brain volume abnormalities/atrophy “can be changed with treatment and in what direction.”
A “strong take-home message from this paper is that brain volume measures from single coordinates are noisy as measures of psychiatric abnormality, whereas network effects seem to be especially sensitive for capturing these effects,” Dr. Oathes said.
The “abnormal networks across these disorders do not fit easily into well-known networks from healthy participants. However, they map well onto other databases relevant to psychiatric disorders and offer exciting new potential targets for prospective treatment studies,” he added.
The investigators received no specific funding for this work. Dr. Taylor reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oathes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators used coordinate and lesion network mapping to assess whether there was a shared brain network common to multiple psychiatric disorders. In a meta-analysis of almost 200 studies encompassing more than 15,000 individuals, they found that atrophy coordinates across these six psychiatric conditions all mapped to a common brain network.
Moreover, lesion damage to this network in patients with penetrating head trauma correlated with the number of psychiatric illnesses that the patients were diagnosed with post trauma.
The findings have “bigger-picture potential implications,” lead author Joseph Taylor, MD, PhD, medical director of transcranial magnetic stimulation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Boston, told this news organization.
“In psychiatry, we talk about symptoms and define our disorders based on symptom checklists, which are fairly reliable but don’t have neurobiological underpinnings,” said Dr. Taylor, who is also an associate psychiatrist in Brigham’s department of psychiatry.
By contrast, “in neurology, we ask: ‘Where is the lesion?’ Studying brain networks could potentially help us diagnose and treat people with psychiatric illness more effectively, just as we treat neurological disorders,” he added.
The findings were published online in Nature Human Behavior.
Beyond symptom checklists
Dr. Taylor noted that, in the field of psychiatry, “we often study disorders in isolation,” such as generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder.
“But what see clinically is that half of patients meet the criteria for more than one psychiatric disorder,” he said. “It can be difficult to diagnose and treat these patients, and there are worse treatment outcomes.”
There is also a “discrepancy” between how these disorders are studied (one at a time) and how patients are treated in clinic, Dr. Taylor noted. And there is increasing evidence that psychiatric disorders may share a common neurobiology.
This “highlights the possibility of potentially developing transdiagnostic treatments based on common neurobiology, not just symptom checklists,” Dr. Taylor said.
Prior work “has attempted to map abnormalities to common brain regions rather than to a common brain network,” the investigators wrote. Moreover, “prior studies have rarely tested specificity by comparing psychiatric disorders to other brain disorders.”
In the current study, the researchers used “morphometric brain lesion datasets coupled with a wiring diagram of the human brain to derive a convergent brain network for psychiatric illness.”
They analyzed four large published datasets. Dataset 1 was sourced from an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis (ALE) of whole-brain voxel-based studies that compared patients with psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, BD, depression, addiction, OCD, and anxiety to healthy controls (n = 193 studies; 15,892 individuals in total).
Dataset 2 was drawn from published neuroimaging studies involving patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative conditions (n = 72 studies). They reported coordinates regarding which patients with these disorders had more atrophy compared with control persons.
Dataset 3 was sourced from the Vietnam Head Injury study, which followed veterans with and those without penetrating head injuries (n = 194 veterans with injuries). Dataset 4 was sourced from published neurosurgical ablation coordinates for depression.
Shared neurobiology
Upon analyzing dataset 1, the researchers found decreased gray matter in the bilateral anterior insula, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, thalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and parietal operculum – findings that are “consistent with prior work.”
However, fewer than 35% of the studies contributed to any single cluster; and no cluster was specific to psychiatric versus neurodegenerative coordinates (drawn from dataset 2).
On the other hand, coordinate network mapping yielded “more statistically robust” (P < .001) results, which were found in 85% of the studies. “Psychiatric atrophy coordinates were functionally connected to the same network of brain regions,” the researchers reported.
This network was defined by two types of connectivity, positive and negative.
“The topography of this transdiagnostic network was independent of the statistical threshold and specific to psychiatric (vs. neurodegenerative) disorders, with the strongest peak occurring in the posterior parietal cortex (Brodmann Area 7) near the intraparietal sulcus,” the investigators wrote.
When lesions from dataset 3 were overlaid onto the ALE map and the transdiagnostic network in order to evaluate whether damage to either map correlated with number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnosis, results showed no evidence of a correlation between psychiatric comorbidity and damage on the ALE map (Pearson r, 0.02; P = .766).
However, when the same approach was applied to the transdiagnostic network, a statistically significant correlation was found between psychiatric comorbidity and lesion damage (Pearson r, –0.21; P = .01). A multiple regression model showed that the transdiagnostic, but not the ALE, network “independently predicted the number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnoses” (P = .003 vs. P = .1), the investigators reported.
All four neurosurgical ablative targets for psychiatric disorders found on analysis of dataset 4 “intersected” and aligned with the transdiagnostic network.
“The study does not immediately impact clinical practice, but it would be helpful for practicing clinicians to know that psychiatric disorders commonly co-occur and might share common neurobiology and a convergent brain network,” Dr. Taylor said.
“Future work based on our findings could potentially influence clinical trials and clinical practice, especially in the area of brain stimulation,” he added.
‘Exciting new targets’
In a comment, Desmond Oathes, PhD, associate director, Center for Neuromodulation and Stress, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the “next step in the science is to combine individual brain imaging, aka, ‘individualized connectomes,’ with these promising group maps to determine something meaningful at the individual patient level.”
Dr. Oathes, who is also a faculty clinician at the Center for the Treatment and Study of Anxiety and was not involved with the study, noted that an open question is whether the brain volume abnormalities/atrophy “can be changed with treatment and in what direction.”
A “strong take-home message from this paper is that brain volume measures from single coordinates are noisy as measures of psychiatric abnormality, whereas network effects seem to be especially sensitive for capturing these effects,” Dr. Oathes said.
The “abnormal networks across these disorders do not fit easily into well-known networks from healthy participants. However, they map well onto other databases relevant to psychiatric disorders and offer exciting new potential targets for prospective treatment studies,” he added.
The investigators received no specific funding for this work. Dr. Taylor reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oathes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators used coordinate and lesion network mapping to assess whether there was a shared brain network common to multiple psychiatric disorders. In a meta-analysis of almost 200 studies encompassing more than 15,000 individuals, they found that atrophy coordinates across these six psychiatric conditions all mapped to a common brain network.
Moreover, lesion damage to this network in patients with penetrating head trauma correlated with the number of psychiatric illnesses that the patients were diagnosed with post trauma.
The findings have “bigger-picture potential implications,” lead author Joseph Taylor, MD, PhD, medical director of transcranial magnetic stimulation at Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Boston, told this news organization.
“In psychiatry, we talk about symptoms and define our disorders based on symptom checklists, which are fairly reliable but don’t have neurobiological underpinnings,” said Dr. Taylor, who is also an associate psychiatrist in Brigham’s department of psychiatry.
By contrast, “in neurology, we ask: ‘Where is the lesion?’ Studying brain networks could potentially help us diagnose and treat people with psychiatric illness more effectively, just as we treat neurological disorders,” he added.
The findings were published online in Nature Human Behavior.
Beyond symptom checklists
Dr. Taylor noted that, in the field of psychiatry, “we often study disorders in isolation,” such as generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder.
“But what see clinically is that half of patients meet the criteria for more than one psychiatric disorder,” he said. “It can be difficult to diagnose and treat these patients, and there are worse treatment outcomes.”
There is also a “discrepancy” between how these disorders are studied (one at a time) and how patients are treated in clinic, Dr. Taylor noted. And there is increasing evidence that psychiatric disorders may share a common neurobiology.
This “highlights the possibility of potentially developing transdiagnostic treatments based on common neurobiology, not just symptom checklists,” Dr. Taylor said.
Prior work “has attempted to map abnormalities to common brain regions rather than to a common brain network,” the investigators wrote. Moreover, “prior studies have rarely tested specificity by comparing psychiatric disorders to other brain disorders.”
In the current study, the researchers used “morphometric brain lesion datasets coupled with a wiring diagram of the human brain to derive a convergent brain network for psychiatric illness.”
They analyzed four large published datasets. Dataset 1 was sourced from an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis (ALE) of whole-brain voxel-based studies that compared patients with psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, BD, depression, addiction, OCD, and anxiety to healthy controls (n = 193 studies; 15,892 individuals in total).
Dataset 2 was drawn from published neuroimaging studies involving patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative conditions (n = 72 studies). They reported coordinates regarding which patients with these disorders had more atrophy compared with control persons.
Dataset 3 was sourced from the Vietnam Head Injury study, which followed veterans with and those without penetrating head injuries (n = 194 veterans with injuries). Dataset 4 was sourced from published neurosurgical ablation coordinates for depression.
Shared neurobiology
Upon analyzing dataset 1, the researchers found decreased gray matter in the bilateral anterior insula, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, thalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and parietal operculum – findings that are “consistent with prior work.”
However, fewer than 35% of the studies contributed to any single cluster; and no cluster was specific to psychiatric versus neurodegenerative coordinates (drawn from dataset 2).
On the other hand, coordinate network mapping yielded “more statistically robust” (P < .001) results, which were found in 85% of the studies. “Psychiatric atrophy coordinates were functionally connected to the same network of brain regions,” the researchers reported.
This network was defined by two types of connectivity, positive and negative.
“The topography of this transdiagnostic network was independent of the statistical threshold and specific to psychiatric (vs. neurodegenerative) disorders, with the strongest peak occurring in the posterior parietal cortex (Brodmann Area 7) near the intraparietal sulcus,” the investigators wrote.
When lesions from dataset 3 were overlaid onto the ALE map and the transdiagnostic network in order to evaluate whether damage to either map correlated with number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnosis, results showed no evidence of a correlation between psychiatric comorbidity and damage on the ALE map (Pearson r, 0.02; P = .766).
However, when the same approach was applied to the transdiagnostic network, a statistically significant correlation was found between psychiatric comorbidity and lesion damage (Pearson r, –0.21; P = .01). A multiple regression model showed that the transdiagnostic, but not the ALE, network “independently predicted the number of post-lesion psychiatric diagnoses” (P = .003 vs. P = .1), the investigators reported.
All four neurosurgical ablative targets for psychiatric disorders found on analysis of dataset 4 “intersected” and aligned with the transdiagnostic network.
“The study does not immediately impact clinical practice, but it would be helpful for practicing clinicians to know that psychiatric disorders commonly co-occur and might share common neurobiology and a convergent brain network,” Dr. Taylor said.
“Future work based on our findings could potentially influence clinical trials and clinical practice, especially in the area of brain stimulation,” he added.
‘Exciting new targets’
In a comment, Desmond Oathes, PhD, associate director, Center for Neuromodulation and Stress, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the “next step in the science is to combine individual brain imaging, aka, ‘individualized connectomes,’ with these promising group maps to determine something meaningful at the individual patient level.”
Dr. Oathes, who is also a faculty clinician at the Center for the Treatment and Study of Anxiety and was not involved with the study, noted that an open question is whether the brain volume abnormalities/atrophy “can be changed with treatment and in what direction.”
A “strong take-home message from this paper is that brain volume measures from single coordinates are noisy as measures of psychiatric abnormality, whereas network effects seem to be especially sensitive for capturing these effects,” Dr. Oathes said.
The “abnormal networks across these disorders do not fit easily into well-known networks from healthy participants. However, they map well onto other databases relevant to psychiatric disorders and offer exciting new potential targets for prospective treatment studies,” he added.
The investigators received no specific funding for this work. Dr. Taylor reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oathes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE HUMAN BEHAVIOR


