User login
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.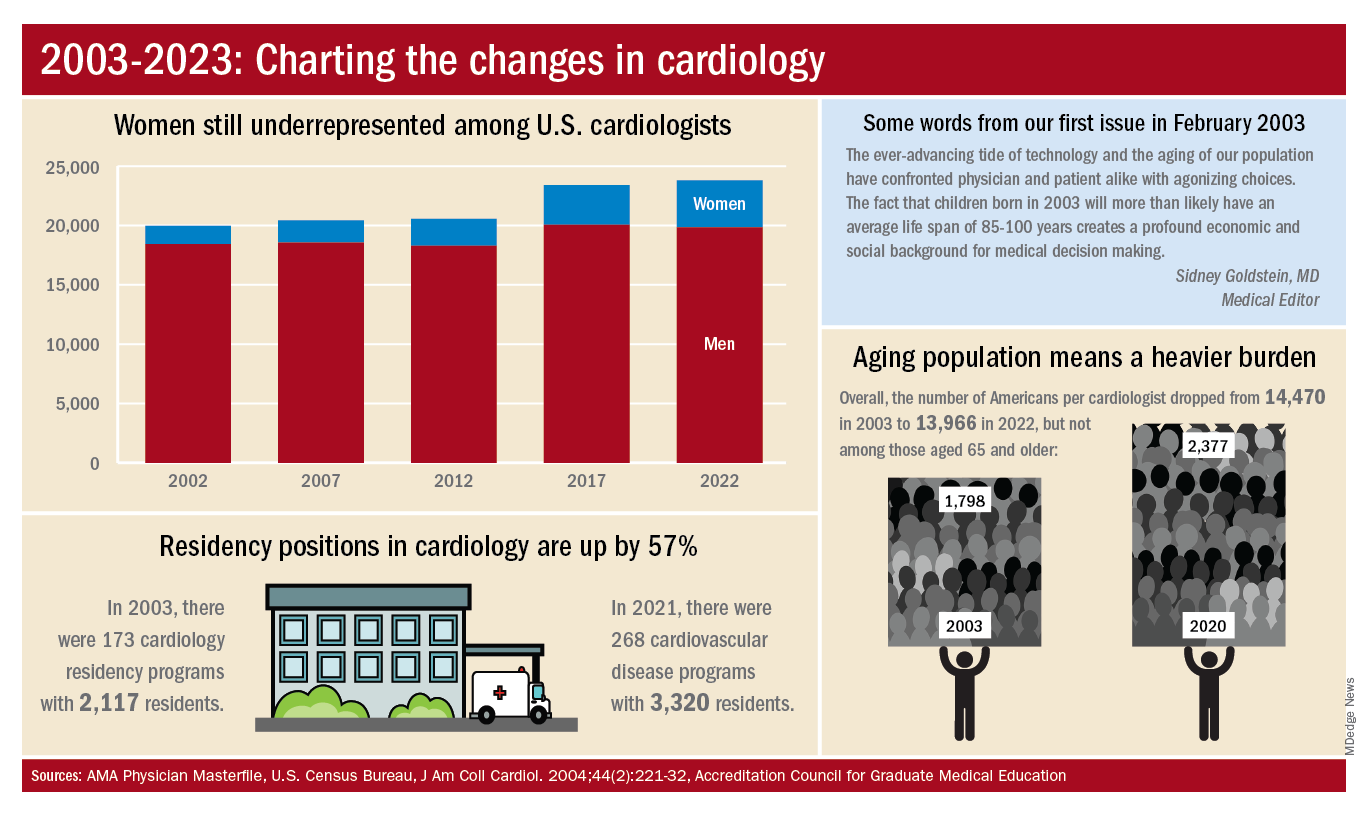
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.