User login
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — At the same time, there is new recognition that systemic inflammation can occur with rosacea, and targeting treatment to the phenotype continues to gain steam as a way to help people with this difficult-to-manage condition.
“Anyone here think they’ve got rosacea under control? No, I wish — not yet,” Diane Dr. Thiboutot, MD, said at the annual ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Botulinum Toxin Benefits
With that in mind, Dr. Thiboutot highlighted emerging therapies for treating rosacea. “Last year, there were a couple of reports … looking at the use of botulinum toxin injections for patients with rosacea,” said Dr. Thiboutot, professor of dermatology and vice chair for research in the Department of Dermatology at Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania.
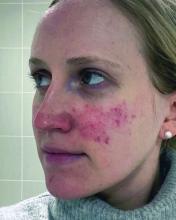
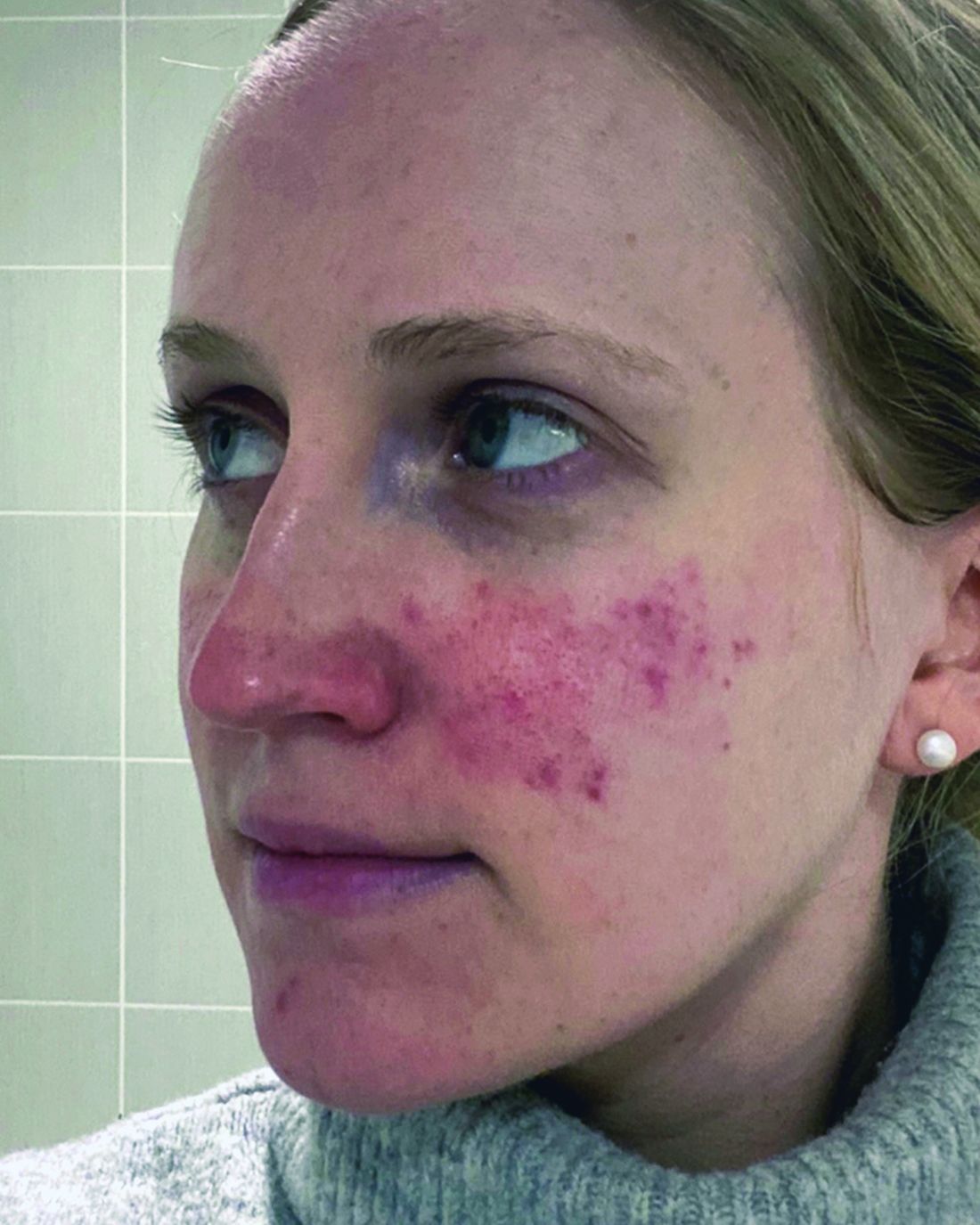
One report describes the case of a woman with rosacea who had severe recurrent episodes of erythema and flushing. She also experienced occasional papules and pustules and had been recalcitrant to multiple treatments for rosacea, according to the report published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology in June 2023. The patient was treated with a total of 150-180 units of botulinum toxin administered as 3-6 units spaced 1 cm apart every 2-4 months. She was “eventually maintained every 6 months with excellent improvement,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
In another case, a man with refractory vascular and papulopustular rosacea was treated with half of a unit of botulinum toxin spaced every 0.5 cm. Images taken at baseline, 1 month, and 3 months after treatment demonstrated improvements, as reported in June 2023.
Regarding botulinum toxin for rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said, “it’s a very interesting thing to think about.”
Susan Weinkle, MD, ODAC conference cochair, session moderator, and collaborative associate professor of dermatology at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, agreed. “I do think it holds some interesting potential,” she said. “How good are your hands? Because administering 0.5-unit injections evenly is a little bit challenging.”
However, one approach that might help is “if we could be a little more innovative like they are in Europe.” Physicians in Europe can use a metered syringe, one where they dial in the exact amount per injection, which allows them to be consistent, she added.
With rosacea erythema, Dr. Thiboutot noted, a spotted effect can result if injections are not administered uniformly.
Potential Role for Paroxetine
The antidepressant paroxetine, a potent selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, could be an effective treatment for refractory erythema of rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said. It is approved for treating depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and social phobia. The agent has also shown effectiveness in alleviating hot flashes associated with vascular dysregulation in menopause.
Uptake in serotonin and changes in receptors are closely related to vascular dilation and constriction, Dr. Thiboutot added, so paroxetine “may be beneficial in treating vascular dysfunction” including in people with rosacea. Evidence to support this potential approach comes from the primary results of a randomized controlled trial published in June 2023. Based on the results, the researchers concluded that paroxetine “appears to be an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment for refractory erythema in rosacea.”
In the trial, almost 43% of people treated with paroxetine met the primary endpoint for improving recalcitrant erythema at week 12 compared with almost 21% who took a placebo, a statistically significant difference.
Heparan Sulfate Analog in a Cream
Evidence suggests that a low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate analog is another agent that holds potential for treating rosacea. For example, a 2023 randomized controlled trial evaluated the immune response in rosacea, focusing on a specific cathelicidin peptide called LL-37 that activates an inflammasome in rosacea. Low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate holds the potential to inhibit LL-37 activity, as LL-37 is inhibited by binding to heparan sulfate, a cell surface glycosaminoglycan.
The study of 16 people assessed the ability of the analog to modulate this response; they were also treated with the pulsed dye laser. Participants who applied a dermal repair cream that contained this ingredient experienced a one-grade reduction in erythema at weeks 4 and 8 compared with a control group applying a moisturizer.
A Growing Case for Systemic Inflammation
In the meantime, treating rosacea with more traditional therapies remains challenging.
But there’s hope. Success has been reported in the few years since an expert panel recommended treating based on phenotype — a treat-what-you-see approach, Dr. Thiboutot said.
“We don’t have a single treatment that is one-size-fits-all. We have to individualize our treatment [based] more on what we are seeing and what the patient is experiencing.”
Eventually, therapies to treat systemic inflammation could provide benefits as well. As with hidradenitis suppurativa and psoriasis, “there’s evidence of systemic inflammation in some of our rosacea patients,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
For example, researchers compared blood taken from people with and without rosacea and found increased levels of some inflammatory markers among participants with the condition.
The retrospective study published in June 2023 in Scientific Reports included 100 patients with rosacea and 58 controls. The investigators found significantly higher elevations in the SII index, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the patients with rosacea.
“There was no significant link between the severity of rosacea and the ESR, CRP, or SII index values, Dr. Thiboutot added. “This study suggests inflammation beyond the skin in rosacea patients.”
For more guidance on treating rosacea through standard management options, including how to tailor therapy to each individual, she recommended the 2019 Update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. “It’s a nice quick way to see, based on expert opinion, the most effective treatments and what the evidence base is,” said Dr. Thiboutot, lead author of the paper, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in February 2020.
Dr. Thiboutot reported no relevant financial relationships.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — At the same time, there is new recognition that systemic inflammation can occur with rosacea, and targeting treatment to the phenotype continues to gain steam as a way to help people with this difficult-to-manage condition.
“Anyone here think they’ve got rosacea under control? No, I wish — not yet,” Diane Dr. Thiboutot, MD, said at the annual ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Botulinum Toxin Benefits
With that in mind, Dr. Thiboutot highlighted emerging therapies for treating rosacea. “Last year, there were a couple of reports … looking at the use of botulinum toxin injections for patients with rosacea,” said Dr. Thiboutot, professor of dermatology and vice chair for research in the Department of Dermatology at Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania.
One report describes the case of a woman with rosacea who had severe recurrent episodes of erythema and flushing. She also experienced occasional papules and pustules and had been recalcitrant to multiple treatments for rosacea, according to the report published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology in June 2023. The patient was treated with a total of 150-180 units of botulinum toxin administered as 3-6 units spaced 1 cm apart every 2-4 months. She was “eventually maintained every 6 months with excellent improvement,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
In another case, a man with refractory vascular and papulopustular rosacea was treated with half of a unit of botulinum toxin spaced every 0.5 cm. Images taken at baseline, 1 month, and 3 months after treatment demonstrated improvements, as reported in June 2023.
Regarding botulinum toxin for rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said, “it’s a very interesting thing to think about.”
Susan Weinkle, MD, ODAC conference cochair, session moderator, and collaborative associate professor of dermatology at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, agreed. “I do think it holds some interesting potential,” she said. “How good are your hands? Because administering 0.5-unit injections evenly is a little bit challenging.”
However, one approach that might help is “if we could be a little more innovative like they are in Europe.” Physicians in Europe can use a metered syringe, one where they dial in the exact amount per injection, which allows them to be consistent, she added.
With rosacea erythema, Dr. Thiboutot noted, a spotted effect can result if injections are not administered uniformly.
Potential Role for Paroxetine
The antidepressant paroxetine, a potent selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, could be an effective treatment for refractory erythema of rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said. It is approved for treating depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and social phobia. The agent has also shown effectiveness in alleviating hot flashes associated with vascular dysregulation in menopause.
Uptake in serotonin and changes in receptors are closely related to vascular dilation and constriction, Dr. Thiboutot added, so paroxetine “may be beneficial in treating vascular dysfunction” including in people with rosacea. Evidence to support this potential approach comes from the primary results of a randomized controlled trial published in June 2023. Based on the results, the researchers concluded that paroxetine “appears to be an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment for refractory erythema in rosacea.”
In the trial, almost 43% of people treated with paroxetine met the primary endpoint for improving recalcitrant erythema at week 12 compared with almost 21% who took a placebo, a statistically significant difference.
Heparan Sulfate Analog in a Cream
Evidence suggests that a low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate analog is another agent that holds potential for treating rosacea. For example, a 2023 randomized controlled trial evaluated the immune response in rosacea, focusing on a specific cathelicidin peptide called LL-37 that activates an inflammasome in rosacea. Low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate holds the potential to inhibit LL-37 activity, as LL-37 is inhibited by binding to heparan sulfate, a cell surface glycosaminoglycan.
The study of 16 people assessed the ability of the analog to modulate this response; they were also treated with the pulsed dye laser. Participants who applied a dermal repair cream that contained this ingredient experienced a one-grade reduction in erythema at weeks 4 and 8 compared with a control group applying a moisturizer.
A Growing Case for Systemic Inflammation
In the meantime, treating rosacea with more traditional therapies remains challenging.
But there’s hope. Success has been reported in the few years since an expert panel recommended treating based on phenotype — a treat-what-you-see approach, Dr. Thiboutot said.
“We don’t have a single treatment that is one-size-fits-all. We have to individualize our treatment [based] more on what we are seeing and what the patient is experiencing.”
Eventually, therapies to treat systemic inflammation could provide benefits as well. As with hidradenitis suppurativa and psoriasis, “there’s evidence of systemic inflammation in some of our rosacea patients,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
For example, researchers compared blood taken from people with and without rosacea and found increased levels of some inflammatory markers among participants with the condition.
The retrospective study published in June 2023 in Scientific Reports included 100 patients with rosacea and 58 controls. The investigators found significantly higher elevations in the SII index, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the patients with rosacea.
“There was no significant link between the severity of rosacea and the ESR, CRP, or SII index values, Dr. Thiboutot added. “This study suggests inflammation beyond the skin in rosacea patients.”
For more guidance on treating rosacea through standard management options, including how to tailor therapy to each individual, she recommended the 2019 Update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. “It’s a nice quick way to see, based on expert opinion, the most effective treatments and what the evidence base is,” said Dr. Thiboutot, lead author of the paper, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in February 2020.
Dr. Thiboutot reported no relevant financial relationships.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — At the same time, there is new recognition that systemic inflammation can occur with rosacea, and targeting treatment to the phenotype continues to gain steam as a way to help people with this difficult-to-manage condition.
“Anyone here think they’ve got rosacea under control? No, I wish — not yet,” Diane Dr. Thiboutot, MD, said at the annual ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Botulinum Toxin Benefits
With that in mind, Dr. Thiboutot highlighted emerging therapies for treating rosacea. “Last year, there were a couple of reports … looking at the use of botulinum toxin injections for patients with rosacea,” said Dr. Thiboutot, professor of dermatology and vice chair for research in the Department of Dermatology at Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania.
One report describes the case of a woman with rosacea who had severe recurrent episodes of erythema and flushing. She also experienced occasional papules and pustules and had been recalcitrant to multiple treatments for rosacea, according to the report published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology in June 2023. The patient was treated with a total of 150-180 units of botulinum toxin administered as 3-6 units spaced 1 cm apart every 2-4 months. She was “eventually maintained every 6 months with excellent improvement,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
In another case, a man with refractory vascular and papulopustular rosacea was treated with half of a unit of botulinum toxin spaced every 0.5 cm. Images taken at baseline, 1 month, and 3 months after treatment demonstrated improvements, as reported in June 2023.
Regarding botulinum toxin for rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said, “it’s a very interesting thing to think about.”
Susan Weinkle, MD, ODAC conference cochair, session moderator, and collaborative associate professor of dermatology at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, agreed. “I do think it holds some interesting potential,” she said. “How good are your hands? Because administering 0.5-unit injections evenly is a little bit challenging.”
However, one approach that might help is “if we could be a little more innovative like they are in Europe.” Physicians in Europe can use a metered syringe, one where they dial in the exact amount per injection, which allows them to be consistent, she added.
With rosacea erythema, Dr. Thiboutot noted, a spotted effect can result if injections are not administered uniformly.
Potential Role for Paroxetine
The antidepressant paroxetine, a potent selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, could be an effective treatment for refractory erythema of rosacea, Dr. Thiboutot said. It is approved for treating depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and social phobia. The agent has also shown effectiveness in alleviating hot flashes associated with vascular dysregulation in menopause.
Uptake in serotonin and changes in receptors are closely related to vascular dilation and constriction, Dr. Thiboutot added, so paroxetine “may be beneficial in treating vascular dysfunction” including in people with rosacea. Evidence to support this potential approach comes from the primary results of a randomized controlled trial published in June 2023. Based on the results, the researchers concluded that paroxetine “appears to be an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment for refractory erythema in rosacea.”
In the trial, almost 43% of people treated with paroxetine met the primary endpoint for improving recalcitrant erythema at week 12 compared with almost 21% who took a placebo, a statistically significant difference.
Heparan Sulfate Analog in a Cream
Evidence suggests that a low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate analog is another agent that holds potential for treating rosacea. For example, a 2023 randomized controlled trial evaluated the immune response in rosacea, focusing on a specific cathelicidin peptide called LL-37 that activates an inflammasome in rosacea. Low-molecular-weight heparan sulfate holds the potential to inhibit LL-37 activity, as LL-37 is inhibited by binding to heparan sulfate, a cell surface glycosaminoglycan.
The study of 16 people assessed the ability of the analog to modulate this response; they were also treated with the pulsed dye laser. Participants who applied a dermal repair cream that contained this ingredient experienced a one-grade reduction in erythema at weeks 4 and 8 compared with a control group applying a moisturizer.
A Growing Case for Systemic Inflammation
In the meantime, treating rosacea with more traditional therapies remains challenging.
But there’s hope. Success has been reported in the few years since an expert panel recommended treating based on phenotype — a treat-what-you-see approach, Dr. Thiboutot said.
“We don’t have a single treatment that is one-size-fits-all. We have to individualize our treatment [based] more on what we are seeing and what the patient is experiencing.”
Eventually, therapies to treat systemic inflammation could provide benefits as well. As with hidradenitis suppurativa and psoriasis, “there’s evidence of systemic inflammation in some of our rosacea patients,” Dr. Thiboutot said.
For example, researchers compared blood taken from people with and without rosacea and found increased levels of some inflammatory markers among participants with the condition.
The retrospective study published in June 2023 in Scientific Reports included 100 patients with rosacea and 58 controls. The investigators found significantly higher elevations in the SII index, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the patients with rosacea.
“There was no significant link between the severity of rosacea and the ESR, CRP, or SII index values, Dr. Thiboutot added. “This study suggests inflammation beyond the skin in rosacea patients.”
For more guidance on treating rosacea through standard management options, including how to tailor therapy to each individual, she recommended the 2019 Update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. “It’s a nice quick way to see, based on expert opinion, the most effective treatments and what the evidence base is,” said Dr. Thiboutot, lead author of the paper, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in February 2020.
Dr. Thiboutot reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ODAC 2024