User login
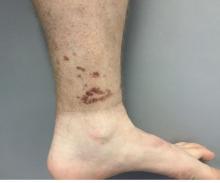
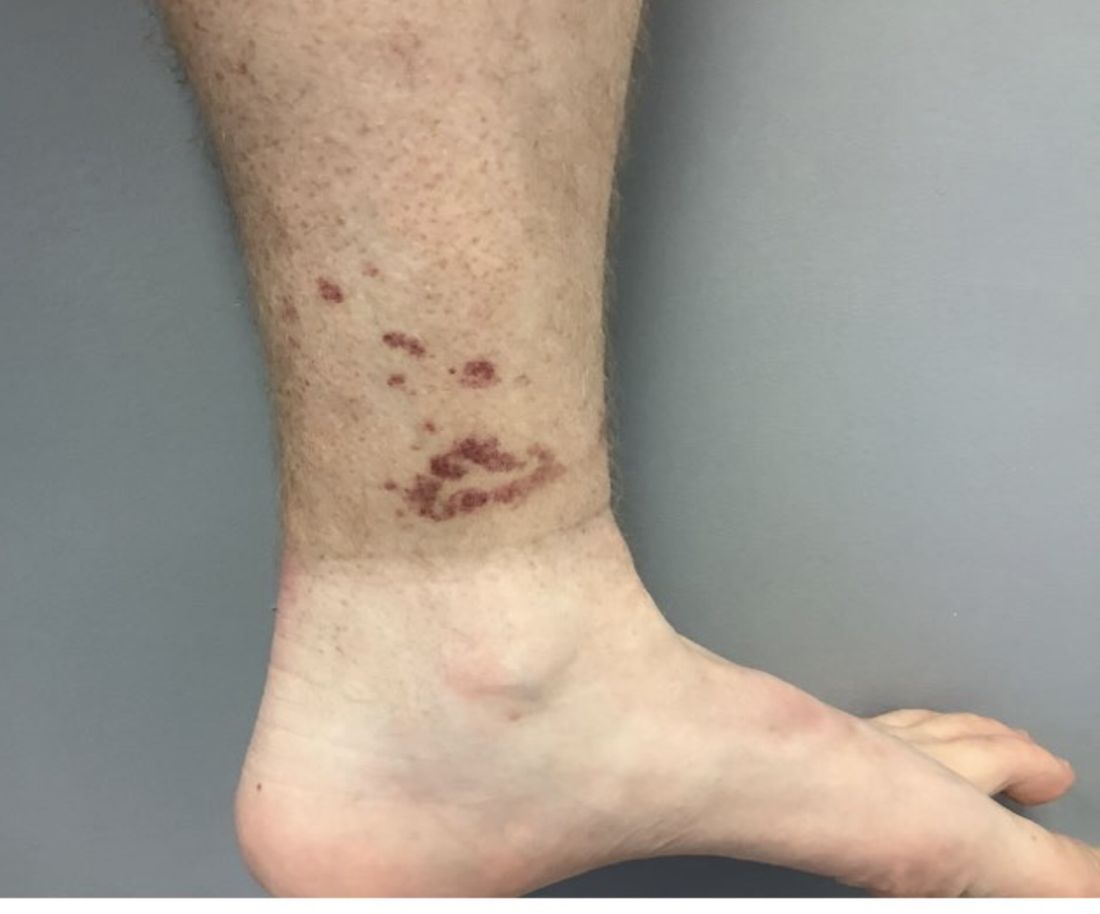
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. .” A form of EIV has been described in the literature as “Disney dermatitis.” It is often seen in healthy adults after a long day of walking at the parks. Other forms of exercise, such as jogging, hiking, or swimming, may also cause the condition.
Clinically, EIV affects the lower legs and presents as purpuric macules. Edema may be present. Lesions may be asymptomatic or may present with pruritus or burning. Diagnosis is often made clinically. Skin biopsies for H&E and DIF (direct immunofluorescence) can help distinguish the type of vasculitis that is present. Laboratory tests may be needed to exclude other causes of vasculitis. Episodes may be recurrent.
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also called anaphylactoid purpura, is a subtype of small-vessel vasculitis where IgA immunoglobulin is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis is children (usually ages 4-8). In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved. Schamberg’s disease, or capillaritis, is also called pigmented purpura. In this benign condition, leakage from capillaries results in erythematous to brown patches on the lower extremities. A true vasculitis is not seen. The brown discoloration is due to hemosiderin deposition. Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition in which abnormal immunoglobulin complexes deposit in tissues and vessels. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present in small vessels. Palpable purpura and livedo may be seen clinically, and systemic symptoms may be present.
Treatment of EIV is largely supportive as lesions will resolve on their own over 3-4 weeks. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may result. Temporary cessation of exercise and compression stockings can help speed up the resolution of lesions. Systemic medications used in the treatment of severe vasculitis, such as systemic steroids, dapsone, and colchicine, are not needed in EIV.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. .” A form of EIV has been described in the literature as “Disney dermatitis.” It is often seen in healthy adults after a long day of walking at the parks. Other forms of exercise, such as jogging, hiking, or swimming, may also cause the condition.
Clinically, EIV affects the lower legs and presents as purpuric macules. Edema may be present. Lesions may be asymptomatic or may present with pruritus or burning. Diagnosis is often made clinically. Skin biopsies for H&E and DIF (direct immunofluorescence) can help distinguish the type of vasculitis that is present. Laboratory tests may be needed to exclude other causes of vasculitis. Episodes may be recurrent.
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also called anaphylactoid purpura, is a subtype of small-vessel vasculitis where IgA immunoglobulin is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis is children (usually ages 4-8). In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved. Schamberg’s disease, or capillaritis, is also called pigmented purpura. In this benign condition, leakage from capillaries results in erythematous to brown patches on the lower extremities. A true vasculitis is not seen. The brown discoloration is due to hemosiderin deposition. Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition in which abnormal immunoglobulin complexes deposit in tissues and vessels. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present in small vessels. Palpable purpura and livedo may be seen clinically, and systemic symptoms may be present.
Treatment of EIV is largely supportive as lesions will resolve on their own over 3-4 weeks. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may result. Temporary cessation of exercise and compression stockings can help speed up the resolution of lesions. Systemic medications used in the treatment of severe vasculitis, such as systemic steroids, dapsone, and colchicine, are not needed in EIV.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. .” A form of EIV has been described in the literature as “Disney dermatitis.” It is often seen in healthy adults after a long day of walking at the parks. Other forms of exercise, such as jogging, hiking, or swimming, may also cause the condition.
Clinically, EIV affects the lower legs and presents as purpuric macules. Edema may be present. Lesions may be asymptomatic or may present with pruritus or burning. Diagnosis is often made clinically. Skin biopsies for H&E and DIF (direct immunofluorescence) can help distinguish the type of vasculitis that is present. Laboratory tests may be needed to exclude other causes of vasculitis. Episodes may be recurrent.
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also called anaphylactoid purpura, is a subtype of small-vessel vasculitis where IgA immunoglobulin is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis is children (usually ages 4-8). In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved. Schamberg’s disease, or capillaritis, is also called pigmented purpura. In this benign condition, leakage from capillaries results in erythematous to brown patches on the lower extremities. A true vasculitis is not seen. The brown discoloration is due to hemosiderin deposition. Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition in which abnormal immunoglobulin complexes deposit in tissues and vessels. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present in small vessels. Palpable purpura and livedo may be seen clinically, and systemic symptoms may be present.
Treatment of EIV is largely supportive as lesions will resolve on their own over 3-4 weeks. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may result. Temporary cessation of exercise and compression stockings can help speed up the resolution of lesions. Systemic medications used in the treatment of severe vasculitis, such as systemic steroids, dapsone, and colchicine, are not needed in EIV.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.