User login
Whether you’re a hospitalist who works only in a hospital, a hospitalist who works only in a post-acute care (PAC) setting, or a hospitalist who works in both types of facilities, knowing about current trends at PAC facilities and what the future may hold can help you excel in your current capacity and, ultimately, improve patient care.
The Hospitalist tapped experts in the post-acute space to tell us what they thought HM should know about working in PAC – which, in many ways, is quite different from the hospital setting. Here’s a compilation of their top eight must-knows.
1. PAC settings rely more on mid-level medical staff than hospitals do.
PAC facilities employ more mid-level providers, such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants, because they can support the level of medical complexity and decision making 95% of the time, says James D. Tollman, MD, FHM, president of Essex Inpatient Physicians in Boxford, Mass. Further, they are more heavily staffed by licensed practical nurses than are acute-care settings.
Usually, there is no physician or nurse practitioner presence at night. Clinicians rely on nursing staff’s assessment to make decisions regarding changes in patient status during off-hours, says Virginia Cummings, MD, director of long-term care, gerontology division, at Boston-based Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
2. Testing takes longer, and options are limited.
Access to some acute urgent resources such as laboratory testing, imaging tests, and pharmacy products is more challenging at PAC facilities because most of these resources are not on-site. Consequently, there is a time lag between ordering tests and new medications and implementing these orders.
“If a patient needs something performed diagnostically immediately, they usually have to be transported to the emergency room or a facility with the necessary testing equipment,” Dr. Tollman says.
However, Paul T. Liistro, managing partner, Arbors of Hop Brook Limited Partnership in Manchester, Conn., and Vernon Manor Health Care Center in Vernon, Conn., and administrator, Manchester Manor Health Care Center, notes that it’s possible for a laboratory service or mobile diagnostic unit to provide laboratory testing or certain imaging at a PAC facility. More-involved diagnostics, such as an MRI or a PET scan, typically require testing at a remote location.
3. Patient populations mainly include rehab and terminally ill patients.
Patients are typically sent to a PAC facility either to recover from an illness or injury or because they are chronically ill and have exhausted treatment options. Regarding the latter, “They are mostly there for palliation; we don’t perform daily tests or prescribe aggressive medications on these patients,” Dr. Nazir says.
Dr. Cummings explains that PAC clinicians go through “the dying process with the patient.”
“They may or may not have assistance from hospice organizations,” she says, “and when they don’t, [hospitalists] take on the role of palliative-care providers.”
Dr. Cummings has seen an increase in psychiatric patients entering PAC facilities.
“Many patients with chronic psychological problems are aging, and there are fewer inpatient psychiatric beds available to those with concurrent medical and psychiatric problems,” she says. Much of this work is now being done in PAC settings. 
4. You can build a relationship with your patient.
Because the pace of a PAC facility is slower and a patient typically stays in a PAC facility longer than at a hospital, there’s time for a hospitalist to have more in-depth conversations with patients and their families.
“Building a deeper relationship with a patient may give the hospitalist an opportunity to discover the cause of an acute problem,” Dr. Nazir says. “They can go in-depth into the psychosocial aspect of medicine and may be able to find out what led to the initial problem and the real root cause, which can help prevent future recurrences, such as repeat falls or forgetting to take a medication.”
5. Using EHRs can improve transitions.
Care transitions between a hospital and PAC facility can be compromised by a lack of information sharing, and they can affect the quality and safety of patient care, says Dori Cross, a doctoral candidate in health services organization and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor. Handoffs between providers require information continuity – information that is complete, timely, and in a usable format – to ensure appropriate medical decisions and to provide high-quality care during and after transition.
Electronic health records (EHRs) as well as health information exchanges (HIEs) allow providers to communicate and share patient information. For example, hospitals can send information electronically to PAC facilities (“push” exchange) or make information available online securely for PAC providers to log in and access (“pull” exchange). According to a 2014 survey data by the American Hospital Association, more than 50% of hospitals report sending structured summary-of-care records electronically to long-term care settings; a little less than half of those hospitals (23% of the total sample of hospitals) were also receiving information electronically from long-term care sites.1
“This bidirectional exchange, in particular, can make it easier to share information across provider organizations electronically and, in turn, improve care delivery,” says Ms. Cross, who authored an accepted paper on the subject in the Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Medicine.
6. Hospitalists can work with providers in PAC settings to improve transitions.
Despite improvements in the electronic transfer of medical information, gaps still exist and can cause problems. One chasm when discharging patients to a PAC facility, is when a hospital IT system is incapable of communicating with the PAC facility system. In this instance, Dr. Nazir says, the hospitalist “can help bridge the gap.”
“[We] can verbally relay relevant information to physicians at PAC facilities so they understand the patient’s status, needs, and expectations,” he says. “Furthermore, hospitalists and a PAC facility’s administration can brainstorm methods to improve the systems of care so the patient receives more effective and timely care.”
7. Hospitalists switching to the PAC setting should have formal training.
The two main obstacles for hospitalists who change from working in a hospital to a PAC facility are the lack of exposure to PAC work in training and the assumption that it requires the same skills sets of a typical hospitalist, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Los Angeles–based Agilon Health. The PAC setting has quite a number of differences compared with a hospital setting. For example, some regulations apply specifically to PAC facilities. In addition to formal training, hospitalists can benefit from using SHM’s Post-Acute Care Transitions Toolkit, having a mentor, or using resources from other organizations that function in this space such as The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine, Dr. Nazir says.
8. A variety of payors and payment models are in play.
Commercial insurers continue to be major payors for PAC, especially for individuals younger than 65 years. Medicare and Medicaid, administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, are the primary payors for patients aged 65 years and older.
“These scorecards are using a variety of criteria to rank providers, such as length of stay, cost, readmissions to hospitals, and quality.”
Because Medicare Part A covers many patients discharged to a PAC setting, any changes in payment incentives or benefit structures by the Medicare program will drive changes in PAC.
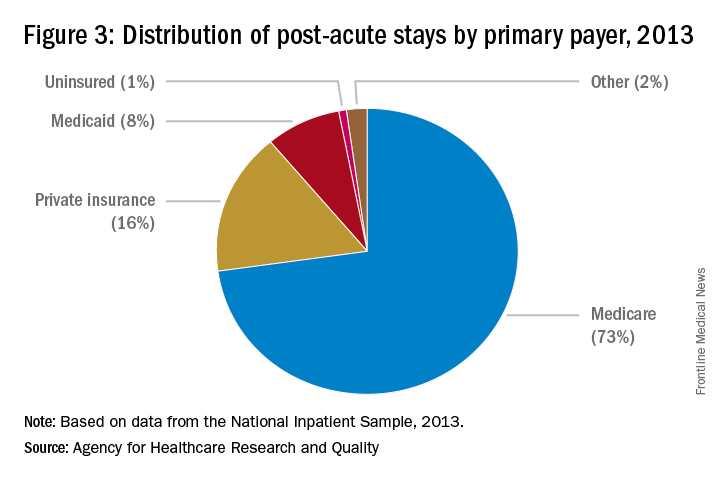
“For example, as Medicare implements payment adjustments for hospitals that have high rates of readmissions, hospitals have a new incentive to work closely with SNFs and other providers of PAC to ensure patients can avoid unnecessary readmissions,” says Tiffany A. Radcliff, PhD, a health economist and associate professor in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station.
Providers must follow the billing rules for each payor. The rules for Medicare payments are outlined on CMS’ website. Bundled payments for PAC under the Medicare Part A program are scheduled to be implemented by 2018.
Reference
Cross DA, Adler-Milstein J. Investing in post-acute care transitions: electronic information exchange between hospitals and long-term care facilities [published online ahead of print Sept. 14, 2016]. JAMDA. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.07.024.
Whether you’re a hospitalist who works only in a hospital, a hospitalist who works only in a post-acute care (PAC) setting, or a hospitalist who works in both types of facilities, knowing about current trends at PAC facilities and what the future may hold can help you excel in your current capacity and, ultimately, improve patient care.
The Hospitalist tapped experts in the post-acute space to tell us what they thought HM should know about working in PAC – which, in many ways, is quite different from the hospital setting. Here’s a compilation of their top eight must-knows.
1. PAC settings rely more on mid-level medical staff than hospitals do.
PAC facilities employ more mid-level providers, such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants, because they can support the level of medical complexity and decision making 95% of the time, says James D. Tollman, MD, FHM, president of Essex Inpatient Physicians in Boxford, Mass. Further, they are more heavily staffed by licensed practical nurses than are acute-care settings.
Usually, there is no physician or nurse practitioner presence at night. Clinicians rely on nursing staff’s assessment to make decisions regarding changes in patient status during off-hours, says Virginia Cummings, MD, director of long-term care, gerontology division, at Boston-based Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
2. Testing takes longer, and options are limited.
Access to some acute urgent resources such as laboratory testing, imaging tests, and pharmacy products is more challenging at PAC facilities because most of these resources are not on-site. Consequently, there is a time lag between ordering tests and new medications and implementing these orders.
“If a patient needs something performed diagnostically immediately, they usually have to be transported to the emergency room or a facility with the necessary testing equipment,” Dr. Tollman says.
However, Paul T. Liistro, managing partner, Arbors of Hop Brook Limited Partnership in Manchester, Conn., and Vernon Manor Health Care Center in Vernon, Conn., and administrator, Manchester Manor Health Care Center, notes that it’s possible for a laboratory service or mobile diagnostic unit to provide laboratory testing or certain imaging at a PAC facility. More-involved diagnostics, such as an MRI or a PET scan, typically require testing at a remote location.
3. Patient populations mainly include rehab and terminally ill patients.
Patients are typically sent to a PAC facility either to recover from an illness or injury or because they are chronically ill and have exhausted treatment options. Regarding the latter, “They are mostly there for palliation; we don’t perform daily tests or prescribe aggressive medications on these patients,” Dr. Nazir says.
Dr. Cummings explains that PAC clinicians go through “the dying process with the patient.”
“They may or may not have assistance from hospice organizations,” she says, “and when they don’t, [hospitalists] take on the role of palliative-care providers.”
Dr. Cummings has seen an increase in psychiatric patients entering PAC facilities.
“Many patients with chronic psychological problems are aging, and there are fewer inpatient psychiatric beds available to those with concurrent medical and psychiatric problems,” she says. Much of this work is now being done in PAC settings. 
4. You can build a relationship with your patient.
Because the pace of a PAC facility is slower and a patient typically stays in a PAC facility longer than at a hospital, there’s time for a hospitalist to have more in-depth conversations with patients and their families.
“Building a deeper relationship with a patient may give the hospitalist an opportunity to discover the cause of an acute problem,” Dr. Nazir says. “They can go in-depth into the psychosocial aspect of medicine and may be able to find out what led to the initial problem and the real root cause, which can help prevent future recurrences, such as repeat falls or forgetting to take a medication.”
5. Using EHRs can improve transitions.
Care transitions between a hospital and PAC facility can be compromised by a lack of information sharing, and they can affect the quality and safety of patient care, says Dori Cross, a doctoral candidate in health services organization and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor. Handoffs between providers require information continuity – information that is complete, timely, and in a usable format – to ensure appropriate medical decisions and to provide high-quality care during and after transition.
Electronic health records (EHRs) as well as health information exchanges (HIEs) allow providers to communicate and share patient information. For example, hospitals can send information electronically to PAC facilities (“push” exchange) or make information available online securely for PAC providers to log in and access (“pull” exchange). According to a 2014 survey data by the American Hospital Association, more than 50% of hospitals report sending structured summary-of-care records electronically to long-term care settings; a little less than half of those hospitals (23% of the total sample of hospitals) were also receiving information electronically from long-term care sites.1
“This bidirectional exchange, in particular, can make it easier to share information across provider organizations electronically and, in turn, improve care delivery,” says Ms. Cross, who authored an accepted paper on the subject in the Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Medicine.
6. Hospitalists can work with providers in PAC settings to improve transitions.
Despite improvements in the electronic transfer of medical information, gaps still exist and can cause problems. One chasm when discharging patients to a PAC facility, is when a hospital IT system is incapable of communicating with the PAC facility system. In this instance, Dr. Nazir says, the hospitalist “can help bridge the gap.”
“[We] can verbally relay relevant information to physicians at PAC facilities so they understand the patient’s status, needs, and expectations,” he says. “Furthermore, hospitalists and a PAC facility’s administration can brainstorm methods to improve the systems of care so the patient receives more effective and timely care.”
7. Hospitalists switching to the PAC setting should have formal training.
The two main obstacles for hospitalists who change from working in a hospital to a PAC facility are the lack of exposure to PAC work in training and the assumption that it requires the same skills sets of a typical hospitalist, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Los Angeles–based Agilon Health. The PAC setting has quite a number of differences compared with a hospital setting. For example, some regulations apply specifically to PAC facilities. In addition to formal training, hospitalists can benefit from using SHM’s Post-Acute Care Transitions Toolkit, having a mentor, or using resources from other organizations that function in this space such as The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine, Dr. Nazir says.
8. A variety of payors and payment models are in play.
Commercial insurers continue to be major payors for PAC, especially for individuals younger than 65 years. Medicare and Medicaid, administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, are the primary payors for patients aged 65 years and older.
“These scorecards are using a variety of criteria to rank providers, such as length of stay, cost, readmissions to hospitals, and quality.”
Because Medicare Part A covers many patients discharged to a PAC setting, any changes in payment incentives or benefit structures by the Medicare program will drive changes in PAC.

“For example, as Medicare implements payment adjustments for hospitals that have high rates of readmissions, hospitals have a new incentive to work closely with SNFs and other providers of PAC to ensure patients can avoid unnecessary readmissions,” says Tiffany A. Radcliff, PhD, a health economist and associate professor in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station.
Providers must follow the billing rules for each payor. The rules for Medicare payments are outlined on CMS’ website. Bundled payments for PAC under the Medicare Part A program are scheduled to be implemented by 2018.
Reference
Cross DA, Adler-Milstein J. Investing in post-acute care transitions: electronic information exchange between hospitals and long-term care facilities [published online ahead of print Sept. 14, 2016]. JAMDA. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.07.024.
Whether you’re a hospitalist who works only in a hospital, a hospitalist who works only in a post-acute care (PAC) setting, or a hospitalist who works in both types of facilities, knowing about current trends at PAC facilities and what the future may hold can help you excel in your current capacity and, ultimately, improve patient care.
The Hospitalist tapped experts in the post-acute space to tell us what they thought HM should know about working in PAC – which, in many ways, is quite different from the hospital setting. Here’s a compilation of their top eight must-knows.
1. PAC settings rely more on mid-level medical staff than hospitals do.
PAC facilities employ more mid-level providers, such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants, because they can support the level of medical complexity and decision making 95% of the time, says James D. Tollman, MD, FHM, president of Essex Inpatient Physicians in Boxford, Mass. Further, they are more heavily staffed by licensed practical nurses than are acute-care settings.
Usually, there is no physician or nurse practitioner presence at night. Clinicians rely on nursing staff’s assessment to make decisions regarding changes in patient status during off-hours, says Virginia Cummings, MD, director of long-term care, gerontology division, at Boston-based Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
2. Testing takes longer, and options are limited.
Access to some acute urgent resources such as laboratory testing, imaging tests, and pharmacy products is more challenging at PAC facilities because most of these resources are not on-site. Consequently, there is a time lag between ordering tests and new medications and implementing these orders.
“If a patient needs something performed diagnostically immediately, they usually have to be transported to the emergency room or a facility with the necessary testing equipment,” Dr. Tollman says.
However, Paul T. Liistro, managing partner, Arbors of Hop Brook Limited Partnership in Manchester, Conn., and Vernon Manor Health Care Center in Vernon, Conn., and administrator, Manchester Manor Health Care Center, notes that it’s possible for a laboratory service or mobile diagnostic unit to provide laboratory testing or certain imaging at a PAC facility. More-involved diagnostics, such as an MRI or a PET scan, typically require testing at a remote location.
3. Patient populations mainly include rehab and terminally ill patients.
Patients are typically sent to a PAC facility either to recover from an illness or injury or because they are chronically ill and have exhausted treatment options. Regarding the latter, “They are mostly there for palliation; we don’t perform daily tests or prescribe aggressive medications on these patients,” Dr. Nazir says.
Dr. Cummings explains that PAC clinicians go through “the dying process with the patient.”
“They may or may not have assistance from hospice organizations,” she says, “and when they don’t, [hospitalists] take on the role of palliative-care providers.”
Dr. Cummings has seen an increase in psychiatric patients entering PAC facilities.
“Many patients with chronic psychological problems are aging, and there are fewer inpatient psychiatric beds available to those with concurrent medical and psychiatric problems,” she says. Much of this work is now being done in PAC settings. 
4. You can build a relationship with your patient.
Because the pace of a PAC facility is slower and a patient typically stays in a PAC facility longer than at a hospital, there’s time for a hospitalist to have more in-depth conversations with patients and their families.
“Building a deeper relationship with a patient may give the hospitalist an opportunity to discover the cause of an acute problem,” Dr. Nazir says. “They can go in-depth into the psychosocial aspect of medicine and may be able to find out what led to the initial problem and the real root cause, which can help prevent future recurrences, such as repeat falls or forgetting to take a medication.”
5. Using EHRs can improve transitions.
Care transitions between a hospital and PAC facility can be compromised by a lack of information sharing, and they can affect the quality and safety of patient care, says Dori Cross, a doctoral candidate in health services organization and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor. Handoffs between providers require information continuity – information that is complete, timely, and in a usable format – to ensure appropriate medical decisions and to provide high-quality care during and after transition.
Electronic health records (EHRs) as well as health information exchanges (HIEs) allow providers to communicate and share patient information. For example, hospitals can send information electronically to PAC facilities (“push” exchange) or make information available online securely for PAC providers to log in and access (“pull” exchange). According to a 2014 survey data by the American Hospital Association, more than 50% of hospitals report sending structured summary-of-care records electronically to long-term care settings; a little less than half of those hospitals (23% of the total sample of hospitals) were also receiving information electronically from long-term care sites.1
“This bidirectional exchange, in particular, can make it easier to share information across provider organizations electronically and, in turn, improve care delivery,” says Ms. Cross, who authored an accepted paper on the subject in the Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Medicine.
6. Hospitalists can work with providers in PAC settings to improve transitions.
Despite improvements in the electronic transfer of medical information, gaps still exist and can cause problems. One chasm when discharging patients to a PAC facility, is when a hospital IT system is incapable of communicating with the PAC facility system. In this instance, Dr. Nazir says, the hospitalist “can help bridge the gap.”
“[We] can verbally relay relevant information to physicians at PAC facilities so they understand the patient’s status, needs, and expectations,” he says. “Furthermore, hospitalists and a PAC facility’s administration can brainstorm methods to improve the systems of care so the patient receives more effective and timely care.”
7. Hospitalists switching to the PAC setting should have formal training.
The two main obstacles for hospitalists who change from working in a hospital to a PAC facility are the lack of exposure to PAC work in training and the assumption that it requires the same skills sets of a typical hospitalist, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Los Angeles–based Agilon Health. The PAC setting has quite a number of differences compared with a hospital setting. For example, some regulations apply specifically to PAC facilities. In addition to formal training, hospitalists can benefit from using SHM’s Post-Acute Care Transitions Toolkit, having a mentor, or using resources from other organizations that function in this space such as The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine, Dr. Nazir says.
8. A variety of payors and payment models are in play.
Commercial insurers continue to be major payors for PAC, especially for individuals younger than 65 years. Medicare and Medicaid, administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, are the primary payors for patients aged 65 years and older.
“These scorecards are using a variety of criteria to rank providers, such as length of stay, cost, readmissions to hospitals, and quality.”
Because Medicare Part A covers many patients discharged to a PAC setting, any changes in payment incentives or benefit structures by the Medicare program will drive changes in PAC.

“For example, as Medicare implements payment adjustments for hospitals that have high rates of readmissions, hospitals have a new incentive to work closely with SNFs and other providers of PAC to ensure patients can avoid unnecessary readmissions,” says Tiffany A. Radcliff, PhD, a health economist and associate professor in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station.
Providers must follow the billing rules for each payor. The rules for Medicare payments are outlined on CMS’ website. Bundled payments for PAC under the Medicare Part A program are scheduled to be implemented by 2018.
Reference
Cross DA, Adler-Milstein J. Investing in post-acute care transitions: electronic information exchange between hospitals and long-term care facilities [published online ahead of print Sept. 14, 2016]. JAMDA. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.07.024.






