User login
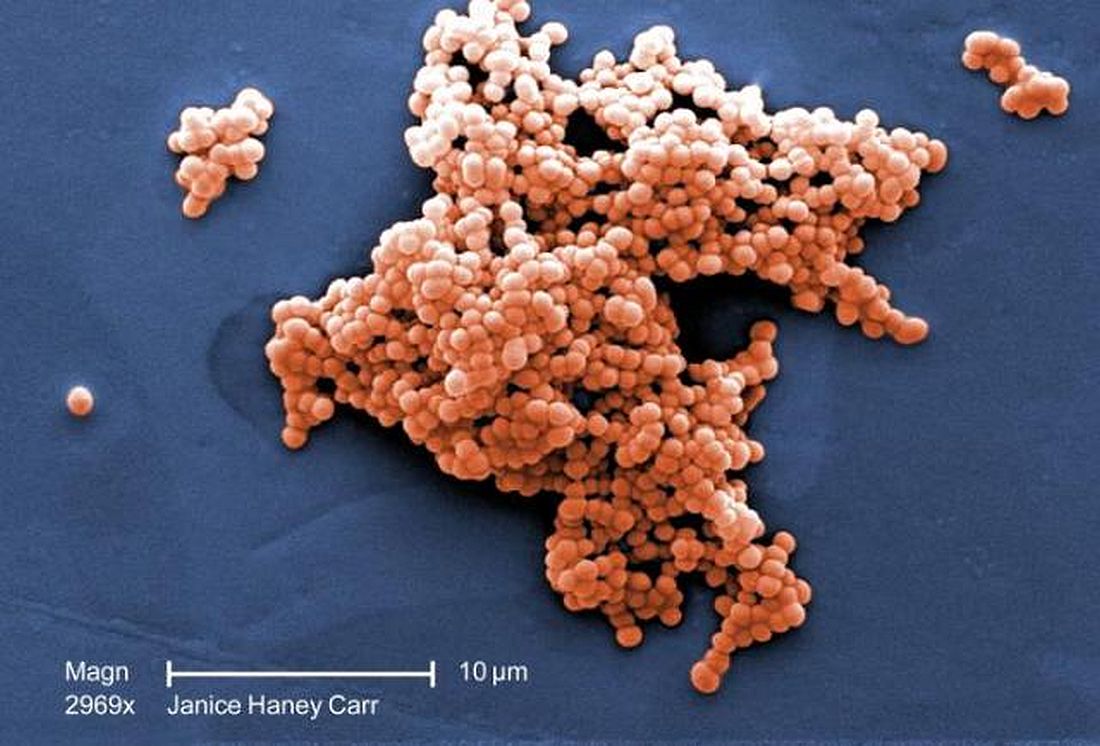
No major shifts appear to have occurred in the bacteria that cause meningitis in Canada, said Lynda Ouchenir, MD, University of Montreal, and her associates.
“There is a paucity of information on the characteristics of neonatal meningitis in the era of infant Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) and pneumococcal immunization, maternal group B Streptococcus (GBS) prophylaxis, and emerging antimicrobial resistance,” the researchers said. So, they undertook a retrospective study of infants with onset of bacterial meningitis in the first 90 days of life at seven Canadian hospitals to find out the major pathogens involved and best empirical antibiotics to use.
This substitution of a carbapenem for the cephalosporin was considered prudent if the birth hospitalization was complicated and if the cerebrospinal fluid Gram-stain or the blood culture was suggestive of Gram-negative meningitis, Dr. Ouchenir and her associates said.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017;140[1)]:e20170476).
No major shifts appear to have occurred in the bacteria that cause meningitis in Canada, said Lynda Ouchenir, MD, University of Montreal, and her associates.
“There is a paucity of information on the characteristics of neonatal meningitis in the era of infant Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) and pneumococcal immunization, maternal group B Streptococcus (GBS) prophylaxis, and emerging antimicrobial resistance,” the researchers said. So, they undertook a retrospective study of infants with onset of bacterial meningitis in the first 90 days of life at seven Canadian hospitals to find out the major pathogens involved and best empirical antibiotics to use.
This substitution of a carbapenem for the cephalosporin was considered prudent if the birth hospitalization was complicated and if the cerebrospinal fluid Gram-stain or the blood culture was suggestive of Gram-negative meningitis, Dr. Ouchenir and her associates said.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017;140[1)]:e20170476).
No major shifts appear to have occurred in the bacteria that cause meningitis in Canada, said Lynda Ouchenir, MD, University of Montreal, and her associates.
“There is a paucity of information on the characteristics of neonatal meningitis in the era of infant Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) and pneumococcal immunization, maternal group B Streptococcus (GBS) prophylaxis, and emerging antimicrobial resistance,” the researchers said. So, they undertook a retrospective study of infants with onset of bacterial meningitis in the first 90 days of life at seven Canadian hospitals to find out the major pathogens involved and best empirical antibiotics to use.
This substitution of a carbapenem for the cephalosporin was considered prudent if the birth hospitalization was complicated and if the cerebrospinal fluid Gram-stain or the blood culture was suggestive of Gram-negative meningitis, Dr. Ouchenir and her associates said.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017;140[1)]:e20170476).
FROM PEDIATRICS