User login
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.
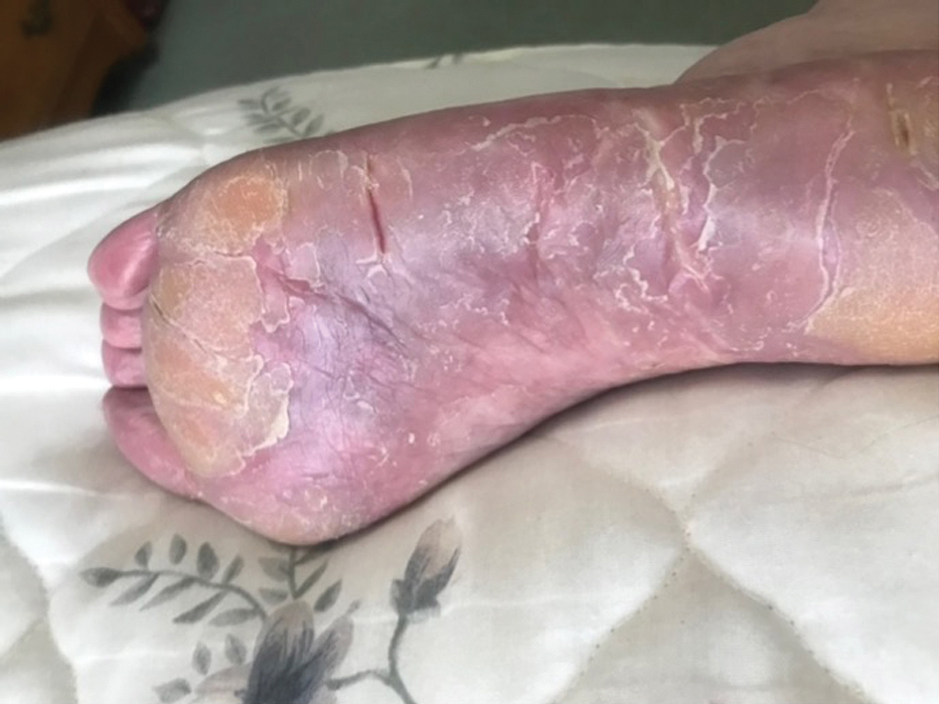
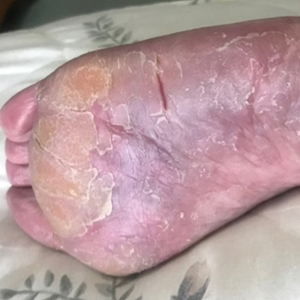
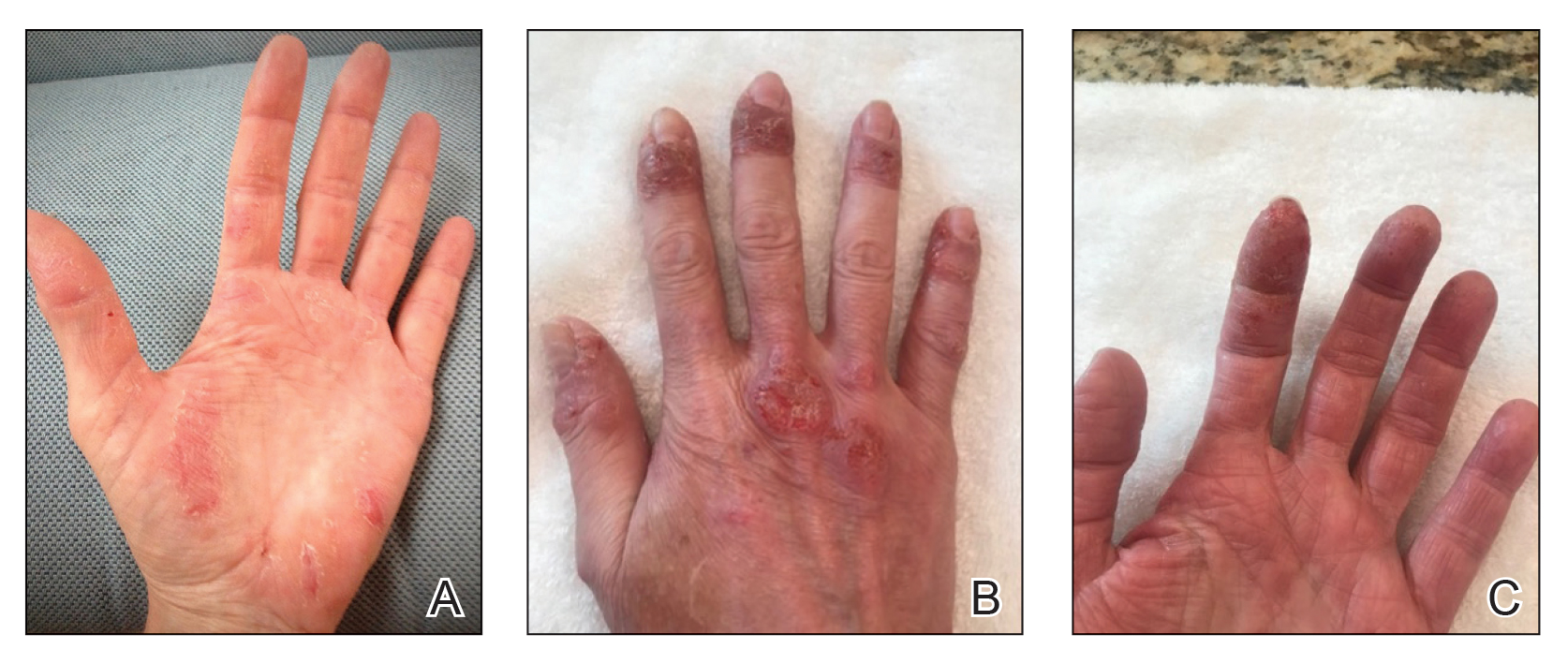
Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.
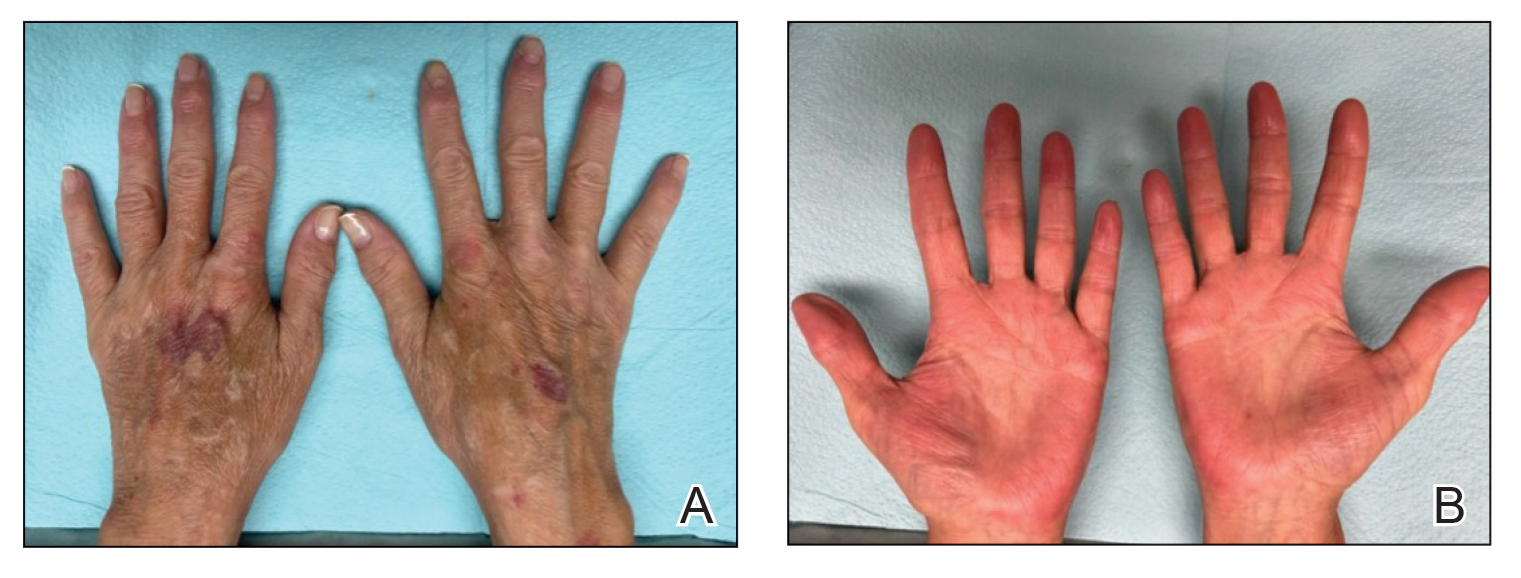
After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.
Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.

Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.

After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.

Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.

Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.

After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.

Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
Practice Points
- Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis can share clinical and histopathologic features, which represents their underlying immunopathologic spectrum.
- Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis can coexist in a single patient, which may be suspected from a clinical picture of treatment-resistant disease, a partial response to targeted therapies, or extensive hand involvement.