User login
New COVID-19 cases and hospital admissions in children continue to decline, while the slow pace of vaccinations has not deterred manufacturers from seeking new emergency authorizations.
Since reaching a post-Omicron peak of 112,000 in late May, the number of weekly cases has fluctuated, with no stretch of increases or decreases lasting more than 4 weeks or the weekly count rising above 97,000 or falling lower than the current 55,000, according to state-level data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.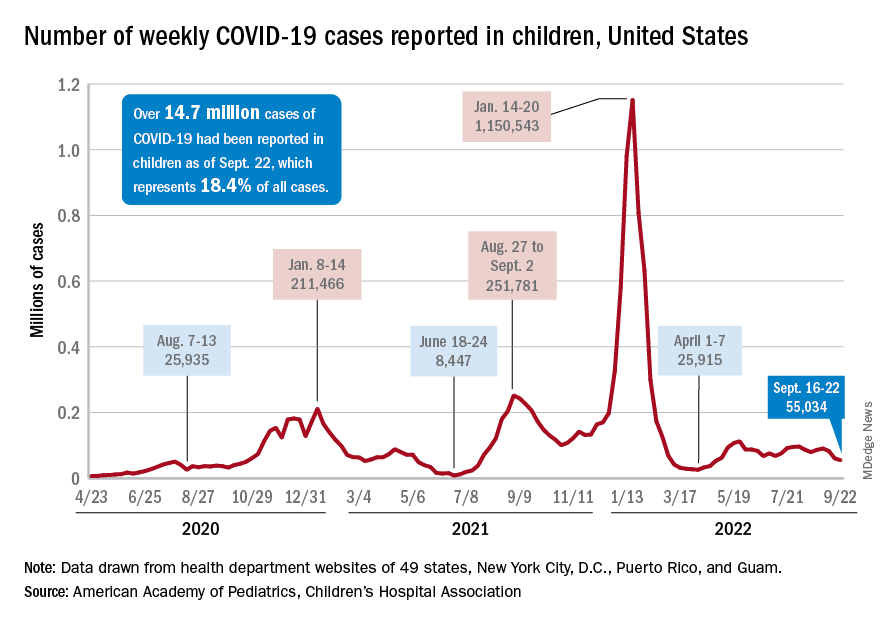
New admissions with confirmed COVID for children aged 0-17 years, which did not follow that pattern and instead continued to rise through the spring and early summer, have been largely decreasing in recent weeks and had fallen to 0.27 per 100,000 population as of Sept. 21 after peaking at 0.46 per 100,000 in late July, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. A similar decline has been seen for emergency department visits since late August.
The biggest vaccination news of the week came from Moderna and Pfizer and BioNTech, which are each seeking emergency authorization from the Food and Drug Administration for bivalent vaccine boosters that target both the original COVID strain and the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of Omicron.
“Pfizer’s booster would be for children 5 to 11 who have completed a primary vaccination series [and] Moderna’s updated boosters would be for children ages 6 to 17 who have completed a primary vaccination series,” WebMD said.
Although almost 61% of children aged 12-17 years are already fully vaccinated, that is not the case among those aged 5-11, of whom only 31.4% have completed the initial vaccine regimen. Since becoming eligible in June, just 1.9% of children under 5 years of age have been fully vaccinated and 6.3% have received at least one dose, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The latest data put the already boosted child populations at 28.8% for 12- to 17-year-olds and 14.8% in those aged 5-11.
About 51,000 children under age 5 years received their initial COVID vaccination during the week of Sept. 15-21, and the trend for that measure is one of gradual decline since July. Among the older children that same week, there were 28,000 initial vaccinations in the 5- to 11-year-olds and 18,000 for those aged 12-17, and activity in both age groups has largely stagnated since the spring, according to a separate AAP report based on CDC data.
New COVID-19 cases and hospital admissions in children continue to decline, while the slow pace of vaccinations has not deterred manufacturers from seeking new emergency authorizations.
Since reaching a post-Omicron peak of 112,000 in late May, the number of weekly cases has fluctuated, with no stretch of increases or decreases lasting more than 4 weeks or the weekly count rising above 97,000 or falling lower than the current 55,000, according to state-level data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New admissions with confirmed COVID for children aged 0-17 years, which did not follow that pattern and instead continued to rise through the spring and early summer, have been largely decreasing in recent weeks and had fallen to 0.27 per 100,000 population as of Sept. 21 after peaking at 0.46 per 100,000 in late July, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. A similar decline has been seen for emergency department visits since late August.
The biggest vaccination news of the week came from Moderna and Pfizer and BioNTech, which are each seeking emergency authorization from the Food and Drug Administration for bivalent vaccine boosters that target both the original COVID strain and the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of Omicron.
“Pfizer’s booster would be for children 5 to 11 who have completed a primary vaccination series [and] Moderna’s updated boosters would be for children ages 6 to 17 who have completed a primary vaccination series,” WebMD said.
Although almost 61% of children aged 12-17 years are already fully vaccinated, that is not the case among those aged 5-11, of whom only 31.4% have completed the initial vaccine regimen. Since becoming eligible in June, just 1.9% of children under 5 years of age have been fully vaccinated and 6.3% have received at least one dose, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The latest data put the already boosted child populations at 28.8% for 12- to 17-year-olds and 14.8% in those aged 5-11.
About 51,000 children under age 5 years received their initial COVID vaccination during the week of Sept. 15-21, and the trend for that measure is one of gradual decline since July. Among the older children that same week, there were 28,000 initial vaccinations in the 5- to 11-year-olds and 18,000 for those aged 12-17, and activity in both age groups has largely stagnated since the spring, according to a separate AAP report based on CDC data.
New COVID-19 cases and hospital admissions in children continue to decline, while the slow pace of vaccinations has not deterred manufacturers from seeking new emergency authorizations.
Since reaching a post-Omicron peak of 112,000 in late May, the number of weekly cases has fluctuated, with no stretch of increases or decreases lasting more than 4 weeks or the weekly count rising above 97,000 or falling lower than the current 55,000, according to state-level data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New admissions with confirmed COVID for children aged 0-17 years, which did not follow that pattern and instead continued to rise through the spring and early summer, have been largely decreasing in recent weeks and had fallen to 0.27 per 100,000 population as of Sept. 21 after peaking at 0.46 per 100,000 in late July, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. A similar decline has been seen for emergency department visits since late August.
The biggest vaccination news of the week came from Moderna and Pfizer and BioNTech, which are each seeking emergency authorization from the Food and Drug Administration for bivalent vaccine boosters that target both the original COVID strain and the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of Omicron.
“Pfizer’s booster would be for children 5 to 11 who have completed a primary vaccination series [and] Moderna’s updated boosters would be for children ages 6 to 17 who have completed a primary vaccination series,” WebMD said.
Although almost 61% of children aged 12-17 years are already fully vaccinated, that is not the case among those aged 5-11, of whom only 31.4% have completed the initial vaccine regimen. Since becoming eligible in June, just 1.9% of children under 5 years of age have been fully vaccinated and 6.3% have received at least one dose, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The latest data put the already boosted child populations at 28.8% for 12- to 17-year-olds and 14.8% in those aged 5-11.
About 51,000 children under age 5 years received their initial COVID vaccination during the week of Sept. 15-21, and the trend for that measure is one of gradual decline since July. Among the older children that same week, there were 28,000 initial vaccinations in the 5- to 11-year-olds and 18,000 for those aged 12-17, and activity in both age groups has largely stagnated since the spring, according to a separate AAP report based on CDC data.