User login
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
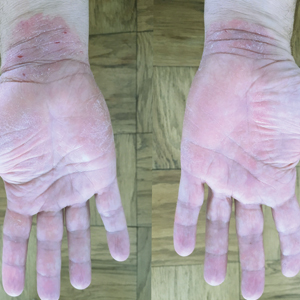
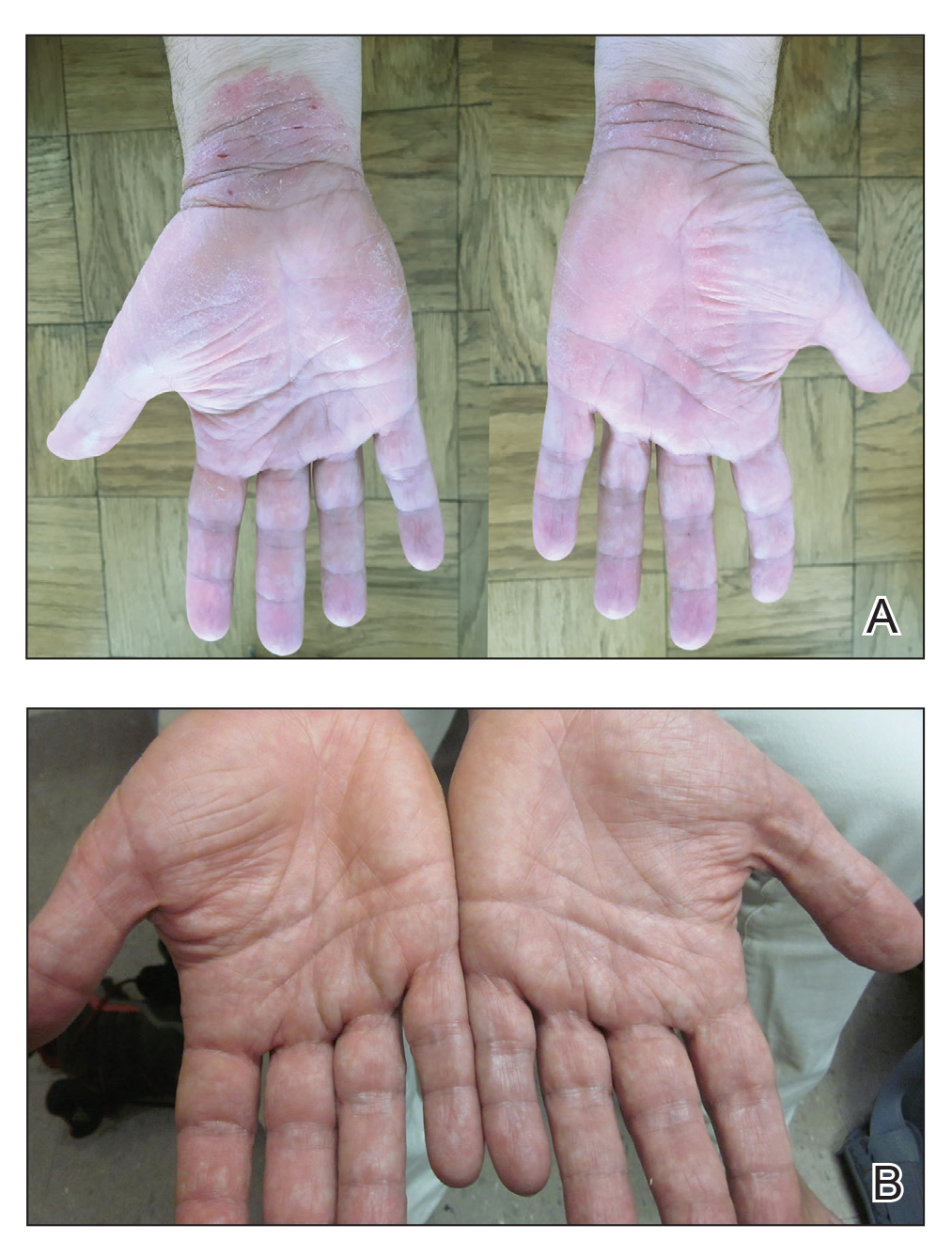
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).

Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).


Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).


Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
Practice Points
- Palmoplantar psoriasis is challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.
- Combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches may minimize side effects and loss of efficacy as well as enhance treatment responses.
- Apremilast and acitretin combination therapy led to 90% skin improvement in a case of severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis.