User login
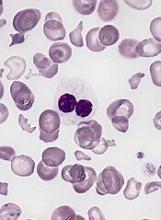
MADRID—Interim results of a phase 1 study suggest flotetuzumab, a CD123 and CD3 bispecific antibody, may be a feasible treatment option for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or intermediate/high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Researchers said flotetuzumab demonstrated acceptable tolerability in the dose-escalation portion of the study, with infusion-related reactions (IRRs) and cytokine release syndrome (CRS) being the most common adverse events (AEs).
In addition, flotetuzumab exhibited anti-leukemic activity in 8 of 14 response-evaluable patients, with 6 patients achieving a response.
Norbert Vey, MD, of Institut Paoli-Calmettes in Marseille, France, presented these results at the ESMO 2017 Congress (abstract 995O*). The study is sponsored by MacroGenics, Inc., the company developing flotetuzumab.
Flotetuzumab (MGD006) recognizes CD123 and CD3. The primary mechanism of flotetuzumab is thought to be its ability to redirect T cells to kill CD123-expressing cells. To achieve this, the molecule combines a portion of an antibody recognizing CD3 (an activating molecule expressed by T cells) with an arm that recognizes CD123 on the target cancer cells.
In this ongoing phase 1 study of flotetuzumab, researchers have enrolled 47 patients with a median age of 64 (range, 29-84). About 89% of these patients had AML (n=42), and the rest (n=5) had MDS.
Twenty-four percent had relapsed AML (n=10), 55% had refractory AML (n=23), and 21% had failed treatment with hypomethylating agents (n=9). One patient had intermediate-1-risk MDS, 2 had intermediate-2-risk, and 2 had high-risk MDS.
Treatment
The study began with single patients receiving flotetuzumab at escalating doses—3 ng/kg/day, 10 ng/kg/day, 30 ng/kg/day, and 100 ng/kg/day.
Then, patients received a range of doses on 2 different schedules for cycle 1. One group received treatment 7 days a week. The other had a 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
All patients received a lead-in dose during the first week of cycle 1. They received 30 ng/kg/day for 3 days, then 100 ng/kg/day for 4 days.
For the rest of cycle 1, patients in the 4 days/3 days group received doses of 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg. Patients in the daily dosing group received doses of 300 ng/kg, 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg.
For cycle 2 and beyond, all patients were on the 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
Safety
The maximum tolerated dose and schedule was 500 ng/kg/day for 7 days.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurring at the 700 ng/kg/day dose included grade 2 IRRs/CRS in 2 patients and grade 3 myalgia in 1 patient. There was 1 drug-related central nervous system AE that led to treatment discontinuation.
IRRs/CRS occurred in 77% of patients, with 13% of patients having grade 3 events and 8.5% of patients discontinuing treatment due to IRRs/CRS.
The researchers said they found ways to decrease the incidence and severity of CRS. One is early intervention with tocilizumab. The other is a 2-step lead-in dose during week 1. So patients first receive 30 ng/kg, then 100 ng/kg, and then their target dose.
Other grade 3 AEs occurring in this trial include febrile neutropenia (11%), anemia (11%), and decreases in platelets (13%), white blood cells (11%), and lymphocytes (13%).
Efficacy
The researchers said they observed encouraging anti-leukemic activity in patients treated at 500 ng/kg/day or greater.
As of the data cut-off, 14 patients treated at this dose were evaluable for response. Eight (57%) patients had anti-leukemic activity, with 6 (43%) of these patients experiencing an objective response.
One patient achieved a complete response (CR), 2 had a CR with incomplete count recovery, and 1 had a molecular CR.
In most responders, anti-leukemic activity was observed after a single cycle of therapy.
MacroGenics is currently enrolling patients in dose-expansion cohorts. The company plans to present updated results from this trial at another scientific conference later this year. ![]()
*Slides from this presentation are available on the MacroGenics website at http://ir.macrogenics.com/events.cfm.
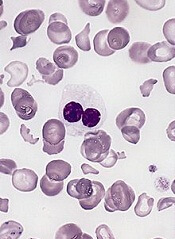
MADRID—Interim results of a phase 1 study suggest flotetuzumab, a CD123 and CD3 bispecific antibody, may be a feasible treatment option for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or intermediate/high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Researchers said flotetuzumab demonstrated acceptable tolerability in the dose-escalation portion of the study, with infusion-related reactions (IRRs) and cytokine release syndrome (CRS) being the most common adverse events (AEs).
In addition, flotetuzumab exhibited anti-leukemic activity in 8 of 14 response-evaluable patients, with 6 patients achieving a response.
Norbert Vey, MD, of Institut Paoli-Calmettes in Marseille, France, presented these results at the ESMO 2017 Congress (abstract 995O*). The study is sponsored by MacroGenics, Inc., the company developing flotetuzumab.
Flotetuzumab (MGD006) recognizes CD123 and CD3. The primary mechanism of flotetuzumab is thought to be its ability to redirect T cells to kill CD123-expressing cells. To achieve this, the molecule combines a portion of an antibody recognizing CD3 (an activating molecule expressed by T cells) with an arm that recognizes CD123 on the target cancer cells.
In this ongoing phase 1 study of flotetuzumab, researchers have enrolled 47 patients with a median age of 64 (range, 29-84). About 89% of these patients had AML (n=42), and the rest (n=5) had MDS.
Twenty-four percent had relapsed AML (n=10), 55% had refractory AML (n=23), and 21% had failed treatment with hypomethylating agents (n=9). One patient had intermediate-1-risk MDS, 2 had intermediate-2-risk, and 2 had high-risk MDS.
Treatment
The study began with single patients receiving flotetuzumab at escalating doses—3 ng/kg/day, 10 ng/kg/day, 30 ng/kg/day, and 100 ng/kg/day.
Then, patients received a range of doses on 2 different schedules for cycle 1. One group received treatment 7 days a week. The other had a 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
All patients received a lead-in dose during the first week of cycle 1. They received 30 ng/kg/day for 3 days, then 100 ng/kg/day for 4 days.
For the rest of cycle 1, patients in the 4 days/3 days group received doses of 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg. Patients in the daily dosing group received doses of 300 ng/kg, 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg.
For cycle 2 and beyond, all patients were on the 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
Safety
The maximum tolerated dose and schedule was 500 ng/kg/day for 7 days.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurring at the 700 ng/kg/day dose included grade 2 IRRs/CRS in 2 patients and grade 3 myalgia in 1 patient. There was 1 drug-related central nervous system AE that led to treatment discontinuation.
IRRs/CRS occurred in 77% of patients, with 13% of patients having grade 3 events and 8.5% of patients discontinuing treatment due to IRRs/CRS.
The researchers said they found ways to decrease the incidence and severity of CRS. One is early intervention with tocilizumab. The other is a 2-step lead-in dose during week 1. So patients first receive 30 ng/kg, then 100 ng/kg, and then their target dose.
Other grade 3 AEs occurring in this trial include febrile neutropenia (11%), anemia (11%), and decreases in platelets (13%), white blood cells (11%), and lymphocytes (13%).
Efficacy
The researchers said they observed encouraging anti-leukemic activity in patients treated at 500 ng/kg/day or greater.
As of the data cut-off, 14 patients treated at this dose were evaluable for response. Eight (57%) patients had anti-leukemic activity, with 6 (43%) of these patients experiencing an objective response.
One patient achieved a complete response (CR), 2 had a CR with incomplete count recovery, and 1 had a molecular CR.
In most responders, anti-leukemic activity was observed after a single cycle of therapy.
MacroGenics is currently enrolling patients in dose-expansion cohorts. The company plans to present updated results from this trial at another scientific conference later this year. ![]()
*Slides from this presentation are available on the MacroGenics website at http://ir.macrogenics.com/events.cfm.
MADRID—Interim results of a phase 1 study suggest flotetuzumab, a CD123 and CD3 bispecific antibody, may be a feasible treatment option for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or intermediate/high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Researchers said flotetuzumab demonstrated acceptable tolerability in the dose-escalation portion of the study, with infusion-related reactions (IRRs) and cytokine release syndrome (CRS) being the most common adverse events (AEs).
In addition, flotetuzumab exhibited anti-leukemic activity in 8 of 14 response-evaluable patients, with 6 patients achieving a response.
Norbert Vey, MD, of Institut Paoli-Calmettes in Marseille, France, presented these results at the ESMO 2017 Congress (abstract 995O*). The study is sponsored by MacroGenics, Inc., the company developing flotetuzumab.
Flotetuzumab (MGD006) recognizes CD123 and CD3. The primary mechanism of flotetuzumab is thought to be its ability to redirect T cells to kill CD123-expressing cells. To achieve this, the molecule combines a portion of an antibody recognizing CD3 (an activating molecule expressed by T cells) with an arm that recognizes CD123 on the target cancer cells.
In this ongoing phase 1 study of flotetuzumab, researchers have enrolled 47 patients with a median age of 64 (range, 29-84). About 89% of these patients had AML (n=42), and the rest (n=5) had MDS.
Twenty-four percent had relapsed AML (n=10), 55% had refractory AML (n=23), and 21% had failed treatment with hypomethylating agents (n=9). One patient had intermediate-1-risk MDS, 2 had intermediate-2-risk, and 2 had high-risk MDS.
Treatment
The study began with single patients receiving flotetuzumab at escalating doses—3 ng/kg/day, 10 ng/kg/day, 30 ng/kg/day, and 100 ng/kg/day.
Then, patients received a range of doses on 2 different schedules for cycle 1. One group received treatment 7 days a week. The other had a 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
All patients received a lead-in dose during the first week of cycle 1. They received 30 ng/kg/day for 3 days, then 100 ng/kg/day for 4 days.
For the rest of cycle 1, patients in the 4 days/3 days group received doses of 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg. Patients in the daily dosing group received doses of 300 ng/kg, 500 ng/kg, 700 ng/kg, 900 ng/kg, or 1000 ng/kg.
For cycle 2 and beyond, all patients were on the 4-days-on/3-days-off schedule.
Safety
The maximum tolerated dose and schedule was 500 ng/kg/day for 7 days.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurring at the 700 ng/kg/day dose included grade 2 IRRs/CRS in 2 patients and grade 3 myalgia in 1 patient. There was 1 drug-related central nervous system AE that led to treatment discontinuation.
IRRs/CRS occurred in 77% of patients, with 13% of patients having grade 3 events and 8.5% of patients discontinuing treatment due to IRRs/CRS.
The researchers said they found ways to decrease the incidence and severity of CRS. One is early intervention with tocilizumab. The other is a 2-step lead-in dose during week 1. So patients first receive 30 ng/kg, then 100 ng/kg, and then their target dose.
Other grade 3 AEs occurring in this trial include febrile neutropenia (11%), anemia (11%), and decreases in platelets (13%), white blood cells (11%), and lymphocytes (13%).
Efficacy
The researchers said they observed encouraging anti-leukemic activity in patients treated at 500 ng/kg/day or greater.
As of the data cut-off, 14 patients treated at this dose were evaluable for response. Eight (57%) patients had anti-leukemic activity, with 6 (43%) of these patients experiencing an objective response.
One patient achieved a complete response (CR), 2 had a CR with incomplete count recovery, and 1 had a molecular CR.
In most responders, anti-leukemic activity was observed after a single cycle of therapy.
MacroGenics is currently enrolling patients in dose-expansion cohorts. The company plans to present updated results from this trial at another scientific conference later this year. ![]()
*Slides from this presentation are available on the MacroGenics website at http://ir.macrogenics.com/events.cfm.