User login
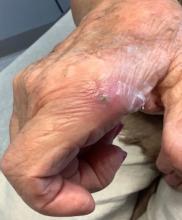
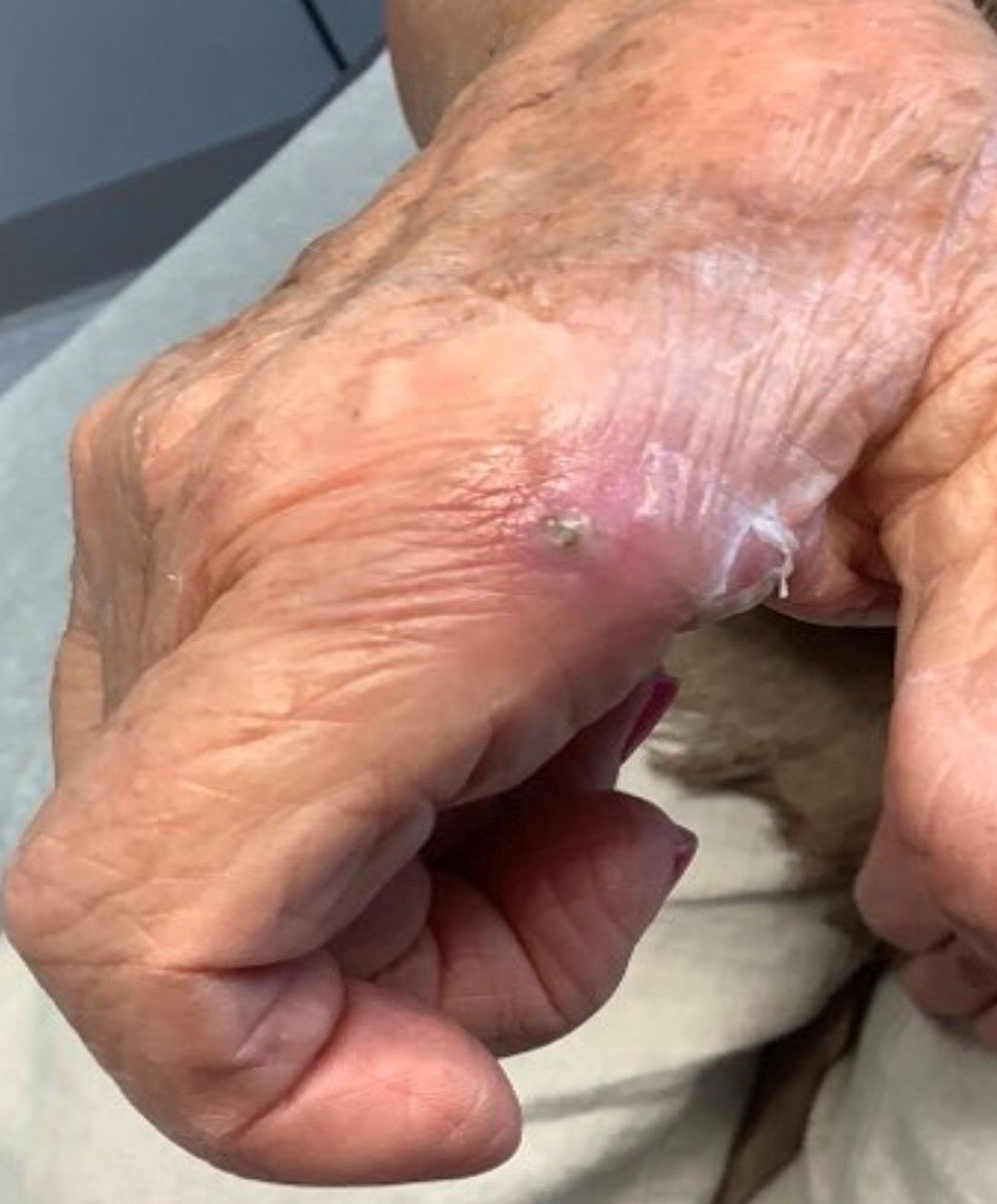
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
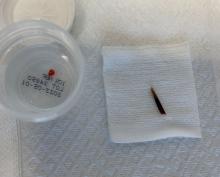
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).