User login
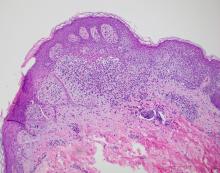
A biopsy of the edge of one of lesions on the torso was performed. Histopathology demonstrated hyperkeratosis of the stratum corneum with focal thickening of the granular cell layer, basal layer degeneration of the epidermis, and a band-like subepidermal lymphocytic infiltrate with Civatte bodies consistent with lichen planus. There was some reduction in the elastic fibers on the papillary dermis.
Given the morphology of the lesions and the histopathologic presentation, he was diagnosed with annular atrophic lichen planus (AALP). Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, nails, hair, and mucosa. Lichen planus is seen in less than 1% of the population, occurring mainly in middle-aged adults and rarely seen in children. Though, there appears to be no clear racial predilection, a small study in the United States showed a higher incidence of lichen planus in Black children. Lesions with classic characteristics are pruritic, polygonal, violaceous, flat-topped papules and plaques.
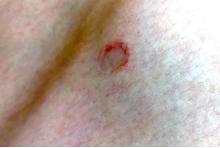
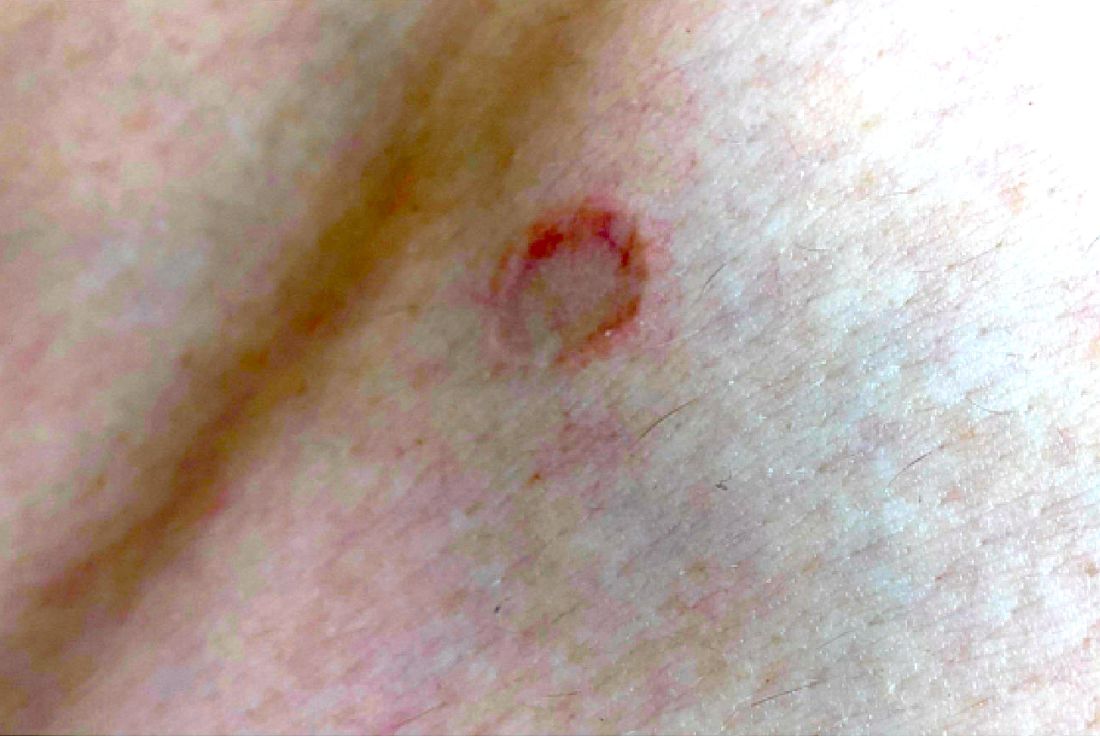
There are different subtypes of lichen planus, which include papular or classic form, hypertrophic, vesiculobullous, actinic, annular, atrophic, annular atrophic, linear, follicular, lichen planus pigmentosus, lichen pigmentosa pigmentosus-inversus, lichen planus–lupus erythematosus overlap syndrome, and lichen planus pemphigoides. The annular atrophic form is the least common of all, and there are few reports in the pediatric population. AALP presents as annular papules and plaques with atrophic centers that resolve within a few months leaving postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation and, in some patients, permanent atrophic scarring.
In histopathology, the lesions show the classic characteristics of lichen planus including vacuolar interface changes and necrotic keratinocytes, hypergranulosis, band-like infiltrate in the dermis, melanin incontinence, and Civatte bodies. In AALP, the center of the lesion shows an atrophic epidermis, and there is also a characteristic partial reduction to complete destruction of elastic fibers in the papillary dermis in the center of the lesion and sometimes in the periphery as well, which helps differentiate AALP from other forms of lichen planus.
The differential diagnosis for AALP includes tinea corporis, which can present with annular lesions, but they are usually scaly and rarely resolve on their own. Pityriasis rosea lesions can also look very similar to AALP lesions, but the difference is the presence of an inner collaret of scale and a lack of atrophy in pityriasis rosea. Pityriasis rosea is a rash that can be triggered by viral infections, medications, and vaccines and self-resolves within 10-12 weeks. Secondary syphilis can also be annular and resemble lesions of AALP. Syphilis patients are usually sexually active and may have lesions present on the palms and soles, which were not seen in our patient.
Granuloma annulare should also be included in the differential diagnosis of AALP. Granuloma annulare lesions present as annular papules or plaques with raised borders and a slightly hyperpigmented center that may appear more depressed compared to the edges of the lesion, though not atrophic as seen in AALP. Pityriasis lichenoides chronica is an inflammatory condition of the skin in which patients present with erythematous to brown papules in different stages which may have a mica-like scale, usually not seen on AALP. Sometimes a skin biopsy will be needed to differentiate between these conditions.
It is very important to make a timely diagnosis of AALP and treat the lesions early as it may leave long-lasting dyspigmentation and scarring. Though AAPL lesions can be resistant to treatment with topical medications, there are reports of improvement with superpotent topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. In recalcitrant cases, systemic therapy with isotretinoin, acitretin, methotrexate, systemic corticosteroids, dapsone, and hydroxychloroquine can be considered. Our patient was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% with good response.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Bowers S and Warshaw EM. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):557-72; quiz 573-6.
Gorouhi F et al. Scientific World Journal. 2014 Jan 30;2014:742826.
Santhosh P and George M. Int J Dermatol. 2022.61:1213-7.
Sears S et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:1283-7.
Weston G and Payette M. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015 Sep 16;1(3):140-9.
A biopsy of the edge of one of lesions on the torso was performed. Histopathology demonstrated hyperkeratosis of the stratum corneum with focal thickening of the granular cell layer, basal layer degeneration of the epidermis, and a band-like subepidermal lymphocytic infiltrate with Civatte bodies consistent with lichen planus. There was some reduction in the elastic fibers on the papillary dermis.
Given the morphology of the lesions and the histopathologic presentation, he was diagnosed with annular atrophic lichen planus (AALP). Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, nails, hair, and mucosa. Lichen planus is seen in less than 1% of the population, occurring mainly in middle-aged adults and rarely seen in children. Though, there appears to be no clear racial predilection, a small study in the United States showed a higher incidence of lichen planus in Black children. Lesions with classic characteristics are pruritic, polygonal, violaceous, flat-topped papules and plaques.
There are different subtypes of lichen planus, which include papular or classic form, hypertrophic, vesiculobullous, actinic, annular, atrophic, annular atrophic, linear, follicular, lichen planus pigmentosus, lichen pigmentosa pigmentosus-inversus, lichen planus–lupus erythematosus overlap syndrome, and lichen planus pemphigoides. The annular atrophic form is the least common of all, and there are few reports in the pediatric population. AALP presents as annular papules and plaques with atrophic centers that resolve within a few months leaving postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation and, in some patients, permanent atrophic scarring.
In histopathology, the lesions show the classic characteristics of lichen planus including vacuolar interface changes and necrotic keratinocytes, hypergranulosis, band-like infiltrate in the dermis, melanin incontinence, and Civatte bodies. In AALP, the center of the lesion shows an atrophic epidermis, and there is also a characteristic partial reduction to complete destruction of elastic fibers in the papillary dermis in the center of the lesion and sometimes in the periphery as well, which helps differentiate AALP from other forms of lichen planus.
The differential diagnosis for AALP includes tinea corporis, which can present with annular lesions, but they are usually scaly and rarely resolve on their own. Pityriasis rosea lesions can also look very similar to AALP lesions, but the difference is the presence of an inner collaret of scale and a lack of atrophy in pityriasis rosea. Pityriasis rosea is a rash that can be triggered by viral infections, medications, and vaccines and self-resolves within 10-12 weeks. Secondary syphilis can also be annular and resemble lesions of AALP. Syphilis patients are usually sexually active and may have lesions present on the palms and soles, which were not seen in our patient.
Granuloma annulare should also be included in the differential diagnosis of AALP. Granuloma annulare lesions present as annular papules or plaques with raised borders and a slightly hyperpigmented center that may appear more depressed compared to the edges of the lesion, though not atrophic as seen in AALP. Pityriasis lichenoides chronica is an inflammatory condition of the skin in which patients present with erythematous to brown papules in different stages which may have a mica-like scale, usually not seen on AALP. Sometimes a skin biopsy will be needed to differentiate between these conditions.
It is very important to make a timely diagnosis of AALP and treat the lesions early as it may leave long-lasting dyspigmentation and scarring. Though AAPL lesions can be resistant to treatment with topical medications, there are reports of improvement with superpotent topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. In recalcitrant cases, systemic therapy with isotretinoin, acitretin, methotrexate, systemic corticosteroids, dapsone, and hydroxychloroquine can be considered. Our patient was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% with good response.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Bowers S and Warshaw EM. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):557-72; quiz 573-6.
Gorouhi F et al. Scientific World Journal. 2014 Jan 30;2014:742826.
Santhosh P and George M. Int J Dermatol. 2022.61:1213-7.
Sears S et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:1283-7.
Weston G and Payette M. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015 Sep 16;1(3):140-9.
A biopsy of the edge of one of lesions on the torso was performed. Histopathology demonstrated hyperkeratosis of the stratum corneum with focal thickening of the granular cell layer, basal layer degeneration of the epidermis, and a band-like subepidermal lymphocytic infiltrate with Civatte bodies consistent with lichen planus. There was some reduction in the elastic fibers on the papillary dermis.
Given the morphology of the lesions and the histopathologic presentation, he was diagnosed with annular atrophic lichen planus (AALP). Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, nails, hair, and mucosa. Lichen planus is seen in less than 1% of the population, occurring mainly in middle-aged adults and rarely seen in children. Though, there appears to be no clear racial predilection, a small study in the United States showed a higher incidence of lichen planus in Black children. Lesions with classic characteristics are pruritic, polygonal, violaceous, flat-topped papules and plaques.
There are different subtypes of lichen planus, which include papular or classic form, hypertrophic, vesiculobullous, actinic, annular, atrophic, annular atrophic, linear, follicular, lichen planus pigmentosus, lichen pigmentosa pigmentosus-inversus, lichen planus–lupus erythematosus overlap syndrome, and lichen planus pemphigoides. The annular atrophic form is the least common of all, and there are few reports in the pediatric population. AALP presents as annular papules and plaques with atrophic centers that resolve within a few months leaving postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation and, in some patients, permanent atrophic scarring.
In histopathology, the lesions show the classic characteristics of lichen planus including vacuolar interface changes and necrotic keratinocytes, hypergranulosis, band-like infiltrate in the dermis, melanin incontinence, and Civatte bodies. In AALP, the center of the lesion shows an atrophic epidermis, and there is also a characteristic partial reduction to complete destruction of elastic fibers in the papillary dermis in the center of the lesion and sometimes in the periphery as well, which helps differentiate AALP from other forms of lichen planus.
The differential diagnosis for AALP includes tinea corporis, which can present with annular lesions, but they are usually scaly and rarely resolve on their own. Pityriasis rosea lesions can also look very similar to AALP lesions, but the difference is the presence of an inner collaret of scale and a lack of atrophy in pityriasis rosea. Pityriasis rosea is a rash that can be triggered by viral infections, medications, and vaccines and self-resolves within 10-12 weeks. Secondary syphilis can also be annular and resemble lesions of AALP. Syphilis patients are usually sexually active and may have lesions present on the palms and soles, which were not seen in our patient.
Granuloma annulare should also be included in the differential diagnosis of AALP. Granuloma annulare lesions present as annular papules or plaques with raised borders and a slightly hyperpigmented center that may appear more depressed compared to the edges of the lesion, though not atrophic as seen in AALP. Pityriasis lichenoides chronica is an inflammatory condition of the skin in which patients present with erythematous to brown papules in different stages which may have a mica-like scale, usually not seen on AALP. Sometimes a skin biopsy will be needed to differentiate between these conditions.
It is very important to make a timely diagnosis of AALP and treat the lesions early as it may leave long-lasting dyspigmentation and scarring. Though AAPL lesions can be resistant to treatment with topical medications, there are reports of improvement with superpotent topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. In recalcitrant cases, systemic therapy with isotretinoin, acitretin, methotrexate, systemic corticosteroids, dapsone, and hydroxychloroquine can be considered. Our patient was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% with good response.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Bowers S and Warshaw EM. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):557-72; quiz 573-6.
Gorouhi F et al. Scientific World Journal. 2014 Jan 30;2014:742826.
Santhosh P and George M. Int J Dermatol. 2022.61:1213-7.
Sears S et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:1283-7.
Weston G and Payette M. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015 Sep 16;1(3):140-9.
A 17-year-old healthy male was referred by his pediatrician for evaluation of a rash on the skin which has been present on and off for a year. During the initial presentation, the lesions were clustered on the back, were slightly itchy, and resolved after 3 months. Several new lesions have developed on the neck, torso, and extremities, leaving hypopigmented marks on the skin. He has previously been treated with topical antifungal creams, oral fluconazole, and triamcinolone ointment without resolution of the lesions.
He is not involved in any contact sports, he has not traveled outside the country, and is not taking any other medications. He is not sexually active. He also has a diagnosis of mild acne that he is currently treating with over-the-counter medications.
On physical exam he had several annular plaques with central atrophic centers and no scale. He also had some hypo- and hyperpigmented macules at the sites of prior skin lesions