User login
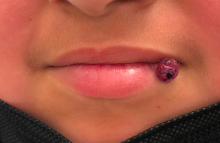
The patient’s history and examination are consistent with a diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. Specifically, the history of rapid growth, friable nature, associated bleeding, and hemorrhagic crusting point to pyogenic granuloma as the most likely diagnosis.
Pyogenic granuloma is an acquired benign vascular growth of the skin or mucous membranes.1 It most frequently occurs in children and young adults and most commonly affects the skin of the head, trunk, and extremities.2 Common mucosal sites include the gingiva, lips, and tongue.2 The etiology of pyogenic granuloma is unknown, though it is thought to be a process akin to the overgrowth of granulation tissue.3,4 Expression of angiogenic factors and subsequent vascular hyperplasia are also implicated as key players in the pathogenesis of pyogenic granuloma.1,4 In addition, several associated factors and inciting triggers have been proposed including trauma, infections, and hormonal fluctuations.3-5 However, the majority of patients do not report predisposing factors or a history of prior trauma at the site.3,6
Clinically, pyogenic granuloma usually presents as a painless, erythematous, dome-shaped friable papule or nodule that easily bleeds and may ulcerate. It typically undergoes a period of growth over weeks to months followed by stabilization. Occasionally, pyogenic granulomas will spontaneously involute, though most do not.7 Pyogenic granuloma may occur within an existing capillary malformation, such as a port wine stain, spontaneously or as a sequela of laser treatment.8,9 Diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma can typically be made clinically on the basis of history and exam. Dermoscopic evaluation of pyogenic granuloma will reveal a homogeneous papule with a surrounding white-brown collarette, and potentially white intersecting lines.10 Histopathologic evaluation may be necessary to differentiate lesions from conditions that may mimic pyogenic granuloma.
What’s on the differential?
The differential diagnosis for pyogenic granuloma consists of Spitz nevus, cherry hemangioma, amelanotic melanoma, and glomus tumor.
Spitz nevus
Spitz nevus (spindle and epithelial cell nevus) is a benign melanocytic lesion that classically appears as a sharply circumscribed, smooth, dome-shaped, pink-red, or brown papule or plaque. There is typically a history of rapid growth over several months followed by stabilization. It usually presents in childhood or adolescence and is most commonly located on the face and extremities. While there are similarities in the appearance of Spitz nevi and pyogenic granuloma, Spitz nevi are not usually friable nor associated with bleeding as in our patient. Furthermore, on dermoscopy, Spitz nevus typically exhibits a starburst pattern with regularly distributed dotted vessels, or a peripheral globular pattern with reticular depigmentation. The definitive diagnosis of Spitz nevi relies on histopathologic evaluation, which is critical for discriminating Spitz nevi from melanoma.
Cherry hemangioma
Cherry angiomas are the most common type of acquired benign vascular proliferation. They present as small, bright red or violaceous macules or papules. However, they typically appear in early to midadulthood and increase in number with age. The age of our patient and solitary presentation of the lesion make this diagnosis unlikely. In addition, cherry angiomas are not usually associated with bleeding. It is important to note that, depending on the age of the patient, pyogenic granuloma may also be confused with infantile hemangioma. Infantile hemangiomas may become bright red papules, nodules, or plaques that appear in early infancy. They characteristically involute, which does not typically happen with pyogenic granuloma.
Amelanotic melanoma
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon variant of melanoma with little to no pigmentation. It may appear as a skin-colored to light-brown, pink, or red macule, papule, or nodule. The lesion may be asymmetric with irregular and well-defined borders. The variable and uncharacteristic appearance of this melanoma variant makes it diagnostically challenging and it is often confused with benign lesions including pyogenic granuloma. Dermoscopy can help distinguish amelanotic melanoma from other benign conditions, and will reveal areas of pink to white, polymorphous vessels and crystalline structures. However, ultimately biopsy and histopathological evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Glomus tumor
Glomus tumors are rare, benign neoplasms originating from cells of the glomus body that presents as a red-purple, vascular papule or nodule. They are usually found in areas rich in glomus bodies, such as the subungual regions, fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Glomus tumors are typically associated with tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity. They do not bleed or ulcerate. While pyogenic granuloma may be confused for glomus tumor when present on the fingers or extremities, the location of the lesion in our patient is not consistent with a diagnosis of glomus tumor.
Management and disease course
Management with procedural or topical interventions is usually pursued for pyogenic granuloma because of frequent bleeding and ulceration of lesions. The most common approach is simple excision by a scoop or shave technique, with or without curettage and most commonly with electrocautery of the base. Other options include full-thickness excision, destruction with laser therapy, cryotherapy, or topical treatments (for example, timolol).11 Lesion recurrence can occur with both surgical and nonsurgical management.11 Regardless of management technique, it is useful to obtain histopathologic evaluation of tissue for accurate diagnosis.
Our patient underwent surgical destruction of her lower-lip lesion with shave excision followed by electrocautery. The surgical specimen was sent for pathology, which confirmed the diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. The patient experienced no complications from the procedure and did not have recurrence of the lesion.
Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Ms. Sui nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Lin RL and Janniger CK. Cutis. 2004 Oct;74(4):229-33.
2. Harris MN et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Jun;42(6):1012-6.
3. Pagliai KA and Cohen BA. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):10-3.
4. Kamal R et al. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012 Jan;16(1):79-82.
5. Requena L and Sangueza OP. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Dec;37(6):887-919.
6. Patrice SJ et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991 Dec;8(4):267-76.
7. Luba MC et al. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Feb 15;67(4):729-38.
8. Swerlick RA and Cooper PH. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 May;8(5):627-30.
9. Sheehan DJ and Lesher JL Jr. Cutis. 2004 Mar;73(3):175-80.
10. Zaballos P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Jun;154(6):1108-11.
11. Lee J et al. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011 Sep;64(9):1216-20. .
The patient’s history and examination are consistent with a diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. Specifically, the history of rapid growth, friable nature, associated bleeding, and hemorrhagic crusting point to pyogenic granuloma as the most likely diagnosis.
Pyogenic granuloma is an acquired benign vascular growth of the skin or mucous membranes.1 It most frequently occurs in children and young adults and most commonly affects the skin of the head, trunk, and extremities.2 Common mucosal sites include the gingiva, lips, and tongue.2 The etiology of pyogenic granuloma is unknown, though it is thought to be a process akin to the overgrowth of granulation tissue.3,4 Expression of angiogenic factors and subsequent vascular hyperplasia are also implicated as key players in the pathogenesis of pyogenic granuloma.1,4 In addition, several associated factors and inciting triggers have been proposed including trauma, infections, and hormonal fluctuations.3-5 However, the majority of patients do not report predisposing factors or a history of prior trauma at the site.3,6
Clinically, pyogenic granuloma usually presents as a painless, erythematous, dome-shaped friable papule or nodule that easily bleeds and may ulcerate. It typically undergoes a period of growth over weeks to months followed by stabilization. Occasionally, pyogenic granulomas will spontaneously involute, though most do not.7 Pyogenic granuloma may occur within an existing capillary malformation, such as a port wine stain, spontaneously or as a sequela of laser treatment.8,9 Diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma can typically be made clinically on the basis of history and exam. Dermoscopic evaluation of pyogenic granuloma will reveal a homogeneous papule with a surrounding white-brown collarette, and potentially white intersecting lines.10 Histopathologic evaluation may be necessary to differentiate lesions from conditions that may mimic pyogenic granuloma.
What’s on the differential?
The differential diagnosis for pyogenic granuloma consists of Spitz nevus, cherry hemangioma, amelanotic melanoma, and glomus tumor.
Spitz nevus
Spitz nevus (spindle and epithelial cell nevus) is a benign melanocytic lesion that classically appears as a sharply circumscribed, smooth, dome-shaped, pink-red, or brown papule or plaque. There is typically a history of rapid growth over several months followed by stabilization. It usually presents in childhood or adolescence and is most commonly located on the face and extremities. While there are similarities in the appearance of Spitz nevi and pyogenic granuloma, Spitz nevi are not usually friable nor associated with bleeding as in our patient. Furthermore, on dermoscopy, Spitz nevus typically exhibits a starburst pattern with regularly distributed dotted vessels, or a peripheral globular pattern with reticular depigmentation. The definitive diagnosis of Spitz nevi relies on histopathologic evaluation, which is critical for discriminating Spitz nevi from melanoma.
Cherry hemangioma
Cherry angiomas are the most common type of acquired benign vascular proliferation. They present as small, bright red or violaceous macules or papules. However, they typically appear in early to midadulthood and increase in number with age. The age of our patient and solitary presentation of the lesion make this diagnosis unlikely. In addition, cherry angiomas are not usually associated with bleeding. It is important to note that, depending on the age of the patient, pyogenic granuloma may also be confused with infantile hemangioma. Infantile hemangiomas may become bright red papules, nodules, or plaques that appear in early infancy. They characteristically involute, which does not typically happen with pyogenic granuloma.
Amelanotic melanoma
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon variant of melanoma with little to no pigmentation. It may appear as a skin-colored to light-brown, pink, or red macule, papule, or nodule. The lesion may be asymmetric with irregular and well-defined borders. The variable and uncharacteristic appearance of this melanoma variant makes it diagnostically challenging and it is often confused with benign lesions including pyogenic granuloma. Dermoscopy can help distinguish amelanotic melanoma from other benign conditions, and will reveal areas of pink to white, polymorphous vessels and crystalline structures. However, ultimately biopsy and histopathological evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Glomus tumor
Glomus tumors are rare, benign neoplasms originating from cells of the glomus body that presents as a red-purple, vascular papule or nodule. They are usually found in areas rich in glomus bodies, such as the subungual regions, fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Glomus tumors are typically associated with tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity. They do not bleed or ulcerate. While pyogenic granuloma may be confused for glomus tumor when present on the fingers or extremities, the location of the lesion in our patient is not consistent with a diagnosis of glomus tumor.
Management and disease course
Management with procedural or topical interventions is usually pursued for pyogenic granuloma because of frequent bleeding and ulceration of lesions. The most common approach is simple excision by a scoop or shave technique, with or without curettage and most commonly with electrocautery of the base. Other options include full-thickness excision, destruction with laser therapy, cryotherapy, or topical treatments (for example, timolol).11 Lesion recurrence can occur with both surgical and nonsurgical management.11 Regardless of management technique, it is useful to obtain histopathologic evaluation of tissue for accurate diagnosis.
Our patient underwent surgical destruction of her lower-lip lesion with shave excision followed by electrocautery. The surgical specimen was sent for pathology, which confirmed the diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. The patient experienced no complications from the procedure and did not have recurrence of the lesion.
Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Ms. Sui nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Lin RL and Janniger CK. Cutis. 2004 Oct;74(4):229-33.
2. Harris MN et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Jun;42(6):1012-6.
3. Pagliai KA and Cohen BA. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):10-3.
4. Kamal R et al. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012 Jan;16(1):79-82.
5. Requena L and Sangueza OP. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Dec;37(6):887-919.
6. Patrice SJ et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991 Dec;8(4):267-76.
7. Luba MC et al. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Feb 15;67(4):729-38.
8. Swerlick RA and Cooper PH. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 May;8(5):627-30.
9. Sheehan DJ and Lesher JL Jr. Cutis. 2004 Mar;73(3):175-80.
10. Zaballos P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Jun;154(6):1108-11.
11. Lee J et al. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011 Sep;64(9):1216-20. .
The patient’s history and examination are consistent with a diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. Specifically, the history of rapid growth, friable nature, associated bleeding, and hemorrhagic crusting point to pyogenic granuloma as the most likely diagnosis.
Pyogenic granuloma is an acquired benign vascular growth of the skin or mucous membranes.1 It most frequently occurs in children and young adults and most commonly affects the skin of the head, trunk, and extremities.2 Common mucosal sites include the gingiva, lips, and tongue.2 The etiology of pyogenic granuloma is unknown, though it is thought to be a process akin to the overgrowth of granulation tissue.3,4 Expression of angiogenic factors and subsequent vascular hyperplasia are also implicated as key players in the pathogenesis of pyogenic granuloma.1,4 In addition, several associated factors and inciting triggers have been proposed including trauma, infections, and hormonal fluctuations.3-5 However, the majority of patients do not report predisposing factors or a history of prior trauma at the site.3,6
Clinically, pyogenic granuloma usually presents as a painless, erythematous, dome-shaped friable papule or nodule that easily bleeds and may ulcerate. It typically undergoes a period of growth over weeks to months followed by stabilization. Occasionally, pyogenic granulomas will spontaneously involute, though most do not.7 Pyogenic granuloma may occur within an existing capillary malformation, such as a port wine stain, spontaneously or as a sequela of laser treatment.8,9 Diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma can typically be made clinically on the basis of history and exam. Dermoscopic evaluation of pyogenic granuloma will reveal a homogeneous papule with a surrounding white-brown collarette, and potentially white intersecting lines.10 Histopathologic evaluation may be necessary to differentiate lesions from conditions that may mimic pyogenic granuloma.
What’s on the differential?
The differential diagnosis for pyogenic granuloma consists of Spitz nevus, cherry hemangioma, amelanotic melanoma, and glomus tumor.
Spitz nevus
Spitz nevus (spindle and epithelial cell nevus) is a benign melanocytic lesion that classically appears as a sharply circumscribed, smooth, dome-shaped, pink-red, or brown papule or plaque. There is typically a history of rapid growth over several months followed by stabilization. It usually presents in childhood or adolescence and is most commonly located on the face and extremities. While there are similarities in the appearance of Spitz nevi and pyogenic granuloma, Spitz nevi are not usually friable nor associated with bleeding as in our patient. Furthermore, on dermoscopy, Spitz nevus typically exhibits a starburst pattern with regularly distributed dotted vessels, or a peripheral globular pattern with reticular depigmentation. The definitive diagnosis of Spitz nevi relies on histopathologic evaluation, which is critical for discriminating Spitz nevi from melanoma.
Cherry hemangioma
Cherry angiomas are the most common type of acquired benign vascular proliferation. They present as small, bright red or violaceous macules or papules. However, they typically appear in early to midadulthood and increase in number with age. The age of our patient and solitary presentation of the lesion make this diagnosis unlikely. In addition, cherry angiomas are not usually associated with bleeding. It is important to note that, depending on the age of the patient, pyogenic granuloma may also be confused with infantile hemangioma. Infantile hemangiomas may become bright red papules, nodules, or plaques that appear in early infancy. They characteristically involute, which does not typically happen with pyogenic granuloma.
Amelanotic melanoma
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon variant of melanoma with little to no pigmentation. It may appear as a skin-colored to light-brown, pink, or red macule, papule, or nodule. The lesion may be asymmetric with irregular and well-defined borders. The variable and uncharacteristic appearance of this melanoma variant makes it diagnostically challenging and it is often confused with benign lesions including pyogenic granuloma. Dermoscopy can help distinguish amelanotic melanoma from other benign conditions, and will reveal areas of pink to white, polymorphous vessels and crystalline structures. However, ultimately biopsy and histopathological evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Glomus tumor
Glomus tumors are rare, benign neoplasms originating from cells of the glomus body that presents as a red-purple, vascular papule or nodule. They are usually found in areas rich in glomus bodies, such as the subungual regions, fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Glomus tumors are typically associated with tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity. They do not bleed or ulcerate. While pyogenic granuloma may be confused for glomus tumor when present on the fingers or extremities, the location of the lesion in our patient is not consistent with a diagnosis of glomus tumor.
Management and disease course
Management with procedural or topical interventions is usually pursued for pyogenic granuloma because of frequent bleeding and ulceration of lesions. The most common approach is simple excision by a scoop or shave technique, with or without curettage and most commonly with electrocautery of the base. Other options include full-thickness excision, destruction with laser therapy, cryotherapy, or topical treatments (for example, timolol).11 Lesion recurrence can occur with both surgical and nonsurgical management.11 Regardless of management technique, it is useful to obtain histopathologic evaluation of tissue for accurate diagnosis.
Our patient underwent surgical destruction of her lower-lip lesion with shave excision followed by electrocautery. The surgical specimen was sent for pathology, which confirmed the diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma. The patient experienced no complications from the procedure and did not have recurrence of the lesion.
Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Ms. Sui nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Lin RL and Janniger CK. Cutis. 2004 Oct;74(4):229-33.
2. Harris MN et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Jun;42(6):1012-6.
3. Pagliai KA and Cohen BA. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):10-3.
4. Kamal R et al. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012 Jan;16(1):79-82.
5. Requena L and Sangueza OP. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Dec;37(6):887-919.
6. Patrice SJ et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991 Dec;8(4):267-76.
7. Luba MC et al. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Feb 15;67(4):729-38.
8. Swerlick RA and Cooper PH. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 May;8(5):627-30.
9. Sheehan DJ and Lesher JL Jr. Cutis. 2004 Mar;73(3):175-80.
10. Zaballos P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Jun;154(6):1108-11.
11. Lee J et al. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011 Sep;64(9):1216-20. .