User login
Concurrent Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Successfully Treated With Dual Biologic Therapy
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.
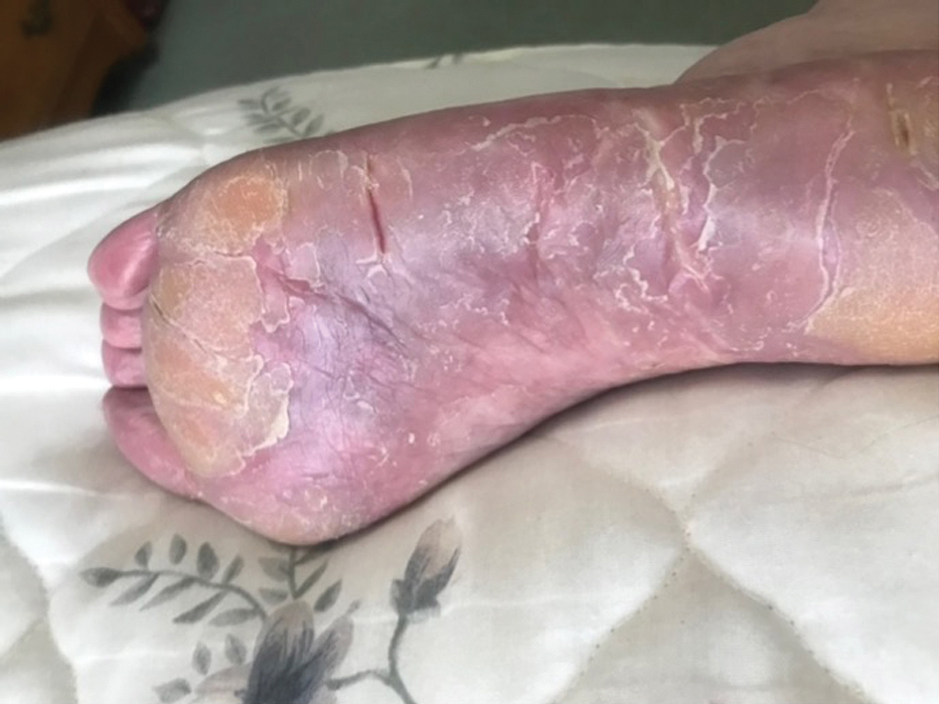
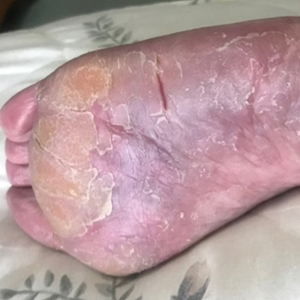
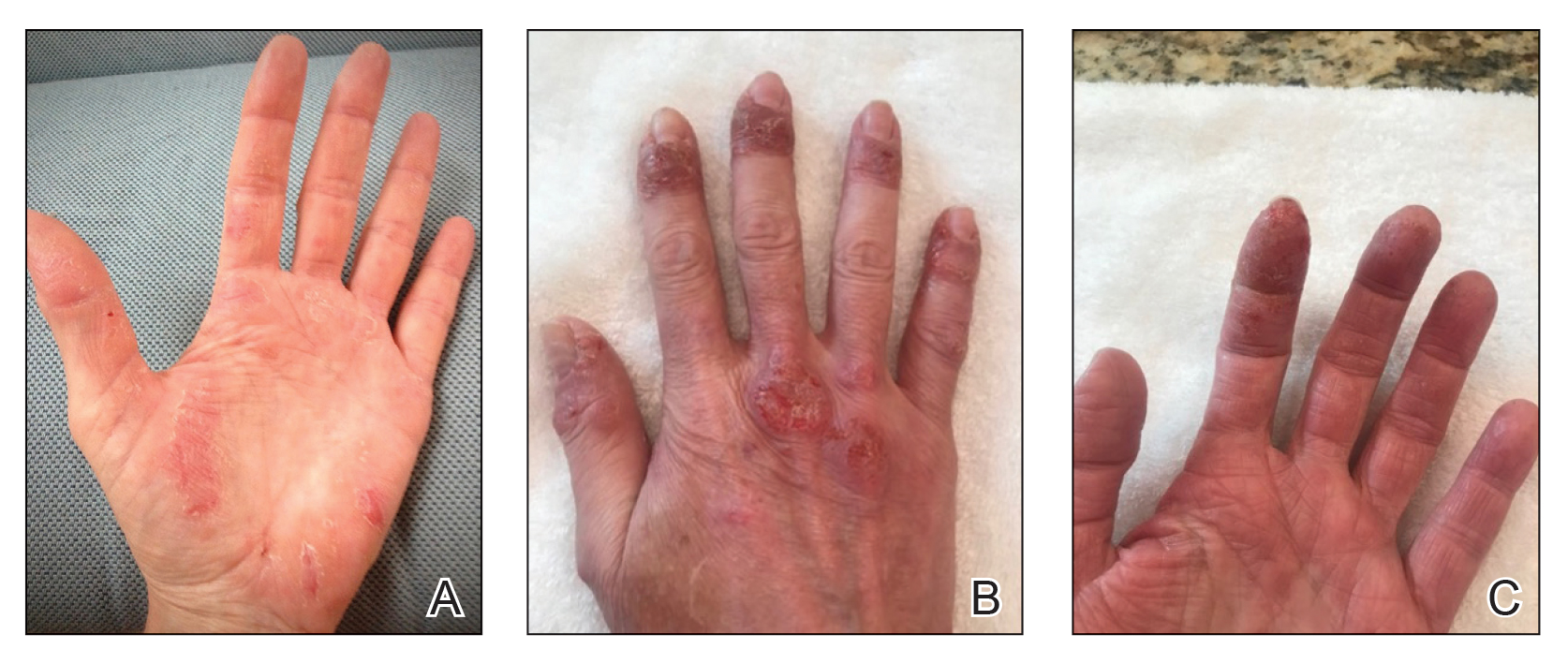
Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.
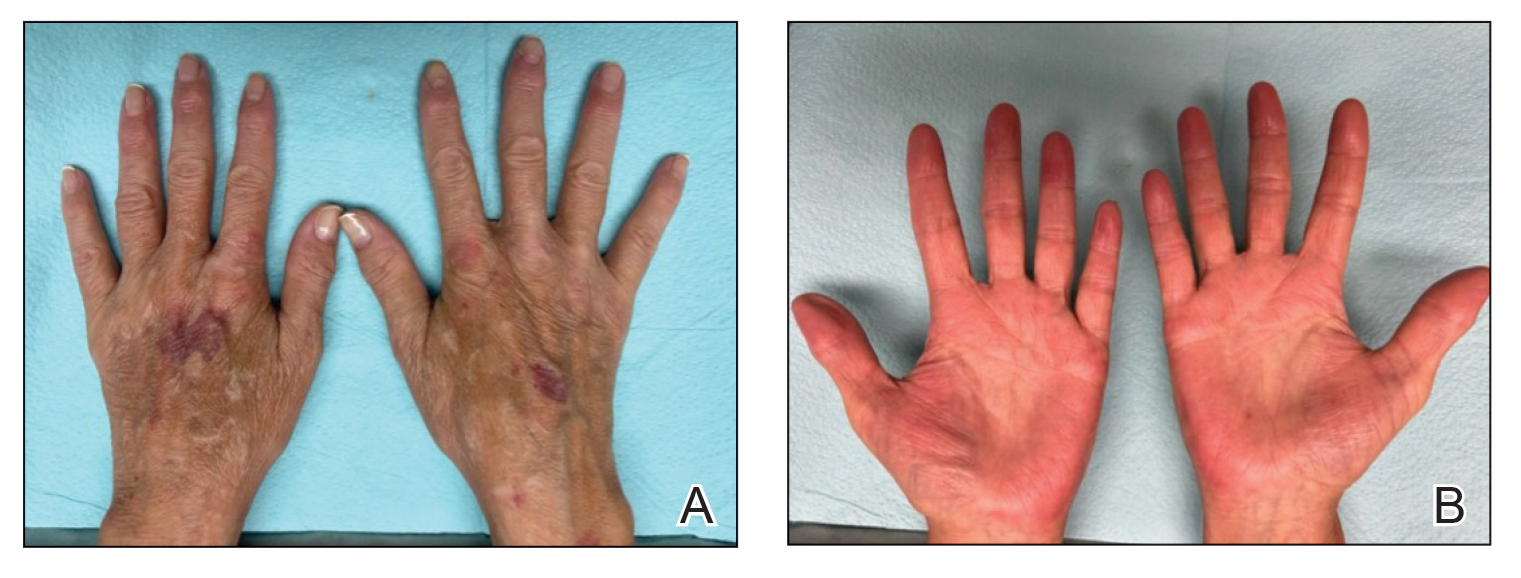
After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.
Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.

Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.

After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.

Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis are common skin diseases in which dysfunction of the epidermal barrier leads to skin inflammation and altered expression of proinflammatory cytokines.1 There often is overlap in the clinical and histopathologic features of AD and psoriasis, which can make diagnosis a challenge. Persistent late-stage AD can present with psoriasiform lichenified changes, and psoriasis lesions in the acute stage can have an eczematous appearance.2 Histologically, chronic psoriasis lesions share many overlapping features with AD, and some subsets of AD with IL-17 predominance (ie, intrinsic, pediatric, presentation in Asian patients) exhibit a psoriasiform appearance.3,4
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are considered 2 distinct conditions because AD is a helper T cell (TH2)–driven disease with subsequent overproduction of IL-4 and IL-13 and psoriasis is a TH17 cell–driven disease with overproduction of IL-173; however, the shared features of AD and psoriasis represent an underlying immunopathological spectrum2,5,6 in which one condition can develop following treatment of the other condition (immunological shift in pathways), both conditions can occur at different times in a patient’s life with alternating cycles of disease flares, or both conditions can coexist as an overlapping syndrome.1,2 A retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 estimated the prevalence of concomitant AD and psoriasis in the United States at 1.3%, with AD following the diagnosis of psoriasis in 67% of cases.1 Concurrent AD and psoriasis—when both diseases flaresimultaneously—is the rarest scenario.2,5
Treatment modalities for AD include topical corticosteroids, which act on immune cells to suppress the release of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as dupilumab, which offers targeted blockade of involved cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. Psoriasis can be treated with multiple immune modulators, including topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as systemic medications that reduce T-cell activation and inflammatory cytokines through targeting of IFN-γ, IL-2, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23.7,8
We present the case of a patient with long-standing concurrent, treatment-resistant AD and psoriasis who was successfully treated with dual biologic therapy with guselkumab and dupilumab.
Case Report
A 62-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with red itchy scales and painful fissures on the palms, hands, and soles of more than 12 years’ duration. Her medical history included an allergy to amoxicillin-clavulanate as well as an allergy to both dog and cat dander on prick testing. Her family history included dyshidrotic eczema in her mother. A complete blood cell count with differential was within reference range. A shave biopsy of the right dorsal hand performed at the onset of symptoms at an outside facility revealed hyperkeratotic acanthotic epidermis with a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Results of patch testing indicated contact hypersensitivity to the botanical rosin colophonium (or colophony); carba mix (1, 3-diphenylguanidine, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate, and zinc diethydithiocarbamate); thiuram mix (tetramethylthiuram disulfide, tetramethylthiuram monosulfide, and tetraethylthiuram disulfide); n,n-diphenylguanidine; and tixocortol-21-pivalate. Our patient was given guidance on avoiding these agents, as it was suspected that exposure may be exacerbating the psoriasis. The psoriasis was treated with topical corticosteroids, keratolytics, and calcineurin inhibitors, all of which offered minimal or no relief. Trials of systemic agents, including methotrexate (discontinued because transaminitis developed), etanercept, adalimumab, and apremilast for 6 to 10 months did not provide improvement.

Two years prior to the current presentation, our patient had been treated with the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab, which provided moderate improvement. When she presented to our clinic, physical examination while she was taking guselkumab demonstrated prurigo with excoriations of the extremities, hyperkeratosis with scaling and fissures of the soles, erythematous scaly plaques on the palms and dorsal surface of the hands, and mild onycholysis of the nails (Figures 1 and 2). Because we were concerned about concomitant intrinsic AD, dupilumab was initiated in conjunction with guselkumab. A second biopsy was considered but deferred in favor of clinical monitoring.

After 1 year of dual biologic therapy, the patient experienced near-complete resolution of symptoms. The psoriasis completely resolved from an initial body surface area of 5%, and the AD body surface area decreased from 30% to 2% (Figure 3). The patient reported no adverse effects from treatment.

Comment
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis involve complex immunopathology and a spectrum of cytokines that might explain the overlap in their clinical and histopathologic presentations.
Atopic dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis involves TH1, TH2, TH9, TH17, and TH22 cells; TH2 cells release IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, all of which are key cytokines in the inflammatory pathway of AD.9,10 Activation of the helper T-cell subset and the release of cytokines differ slightly based on the subcategory of AD and the stage of exacerbation. In addition to TH2-cell activation, TH1 cells and TH22 cells—which release IL-12 and IL-22, respectively—are active in both intrinsic and extrinsic AD. TH17 cells and TH9 cells—which release IL-17 and IL-9, respectively—are more prominent in the intrinsic pathway than in the extrinsic pathway.9 Intrinsic AD is recognized by a lack of eosinophilia, female predominance, and delayed onset compared to extrinsic AD; there also is a lack of history of atopy.1 Extrinsic AD is characterized by eosinophilia as well as a personal and family history of atopy.11 Our patient—a female with onset in older adulthood, lack of eosinophilia, and a family history of atopy—displayed features of both intrinsic and extrinsic AD.
Psoriasis—The immunopathology of psoriasis involves stimulation of dendritic cells, which activate TH17 cells through IL-23. TH17 cells then release IL-17 and IL-22. Therefore, both AD and psoriasis involve activation of TH22 and TH1 cells, with increased IL-17 and IL-22 production.3,10,12 IL-17 and IL-22 induce epidermal hyperplasia; IL-22 also contributes to skin barrier dysfunction.12 Therefore, it might be reasonable to consider psoriasis and AD as diseases that exist across a T-cell axis spectrum, thereby accounting for some overlap in disease characteristics.3
Dual Biologic Therapy—Dupilumab blocks the IL-4 receptor α subunit, a receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, which are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of AD.10 Guselkumab inhibits IL-23, thus blocking the inflammatory cascade of TH17 cell activation and release of IL-17 and IL-22 in the psoriasis pathway.13 Although an immunopathological spectrum exists between the 2 diseases, the continued presence of AD symptoms after blocking the IL-23 cascade suggests that additional blockade of TH2 cells is required to control AD in patients with true concurrent disease.
Accurate diagnosis of AD and/or psoriasis is important when considering targeted treatment of these conditions with biologics. The use of dual biologics is limited by a paucity of data regarding the safety of these agents when given in combination. A recent meta-analysis of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease demonstrated acceptable safety results with a pooled adverse reaction rate of 31%.14
Anchoring Bias—Anchoring bias can occur when a clinician’s decisions are influenced by a particular event or reference point, which might cause them to disregard subsequent evidence. Our case illustrates the importance of critically assessing the response to treatment and being mindful of the potential influence of anchoring bias on the differential diagnosis. Although overcoming biases in conditions with clinical overlap can be challenging, it is important to consider coexisting AD and psoriasis in patients with extensive hand involvement when multiple treatments have failed and only a partial response to targeted pathways has been achieved. In our case, the patient also had contact hypersensitivity to tixocortol-21-pivalate, which indicates hypersensitivity to many prescription topical corticosteroids, oral prednisone, and over-the-counter hydrocortisone; however, topical corticosteroids continued to be prescribed for her, which might have contributed to the lack of improvement and even exacerbated the rash.
Future Considerations—A consideration for the future in this case is discontinuing guselkumab to observe whether symptoms recur. We discussed this option with the patient, but she opted to continue treatment with dupilumab and guselkumab because of the symptom resolution.
Conclusion
Concomitant disease can present as an overlapping pattern in the same area, whereas other regions might have geographically isolated disease. Our patient’s overlap of symptoms, the failure of multiple treatments, and the partial improvement she experienced on guselkumab made diagnosis and management challenging; however, dual biologic therapy was successful.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
- Barry K, Zancanaro P, Casseres R, et al. Concomitant atopic dermatitis and psoriasis—a retrospective review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:716-720. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1702147
- Bozek A, Zajac M, Krupka M. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis as overlapping syndromes. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527859. doi:10.1155/2020/7527859
- Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: two different immune diseases or one spectrum? Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;48:68-73. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.008
- De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Reumatismo. 2007;59(suppl 1):46-48. doi:10.4081/reumatismo.2007.1s.46
- Docampo A, MJ, I, et al. Response to letter to the editor: ‘psoriasis dermatitis: an overlap condition of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in children.’ J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:E410-E412. doi:10.1111/jdv.15716
- Johnson MC, Bowers NL, Strowd LC. Concurrent atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris: implications for targeted biologic therapy. Cutis. 2022;109:110-112. doi:10.12788/cutis.0453
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ, et al. New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3086. doi:10.3390/ijms19103086
- Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, et al. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1053-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
- Czarnowicki T, He H, Krueger JG, et al. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.032
- Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:7488. doi:10.3390/ijms21207488
- Gordon KB, Armstrong AW, Foley P, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum IL-23-regulated IL-17 and IL-22 in psoriasis: VOYAGE 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2437-2446.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
- Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and safety of dual biologic therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414.
Practice Points
- Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis can share clinical and histopathologic features, which represents their underlying immunopathologic spectrum.
- Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis can coexist in a single patient, which may be suspected from a clinical picture of treatment-resistant disease, a partial response to targeted therapies, or extensive hand involvement.
Commentary: Are "significant" results necessarily clinically meaningful? October 2023
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
Commentary: Newer Drugs for AD Plus Dupilumab and Other Issues, September 2023
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
Commentary: Abrocitinib, Malignancy Risk, and S aureus in AD, August 2023
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
Commentary: Topical treatments, dupilumab, and long-term treatment of AD, July 2023
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
Commentary: Topical treatments, dupilumab, and long-term treatment of AD, July 2023
There is a tremendous amount of atopic dermatitis (AD) research underway. This month, we have several interesting articles to present.
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
I love articles like this one from Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
There is a tremendous amount of atopic dermatitis (AD) research underway. This month, we have several interesting articles to present.
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
I love articles like this one from Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
There is a tremendous amount of atopic dermatitis (AD) research underway. This month, we have several interesting articles to present.
Silverberg and colleagues described a very well-designed, vehicle-controlled, randomized 8-week study of a topical formulation of a purified strain of Nitrosomonas eutropha, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium. In theory, this bacterium may reduce Staphylococcus aureus. The study compared two concentrations of the bacterium vs vehicle delivered as a spray twice per day. Study participants were adults with AD affecting 10%-40% of body surface area.
The study found "meaningful" improvements in itch and objective signs of disease, with clear separation between both doses of the bacterial spray compared with vehicle. At week 4, about 23% of participants treated with the bacterium were clear or almost clear (with a 2-point improvement) compared with 12% in the vehicle group (for comparison, in a phase 2 study comparing topical ruxolitinib with 0.1% triamcinolone cream, there was a 25% clear or almost clear rate [with 2-point improvement] in the triamcinolone-treated individuals).
Though an "all-natural" bacterial approach to managing AD may be appealing to some, it sounded like magic to me. But this well-done study makes it seem like the bacterial approach could be more promising than I had thought. This study also reported about twice as many adverse events (including gastrointestinal issues) with the bacterium-treated participants compared with those who received vehicle, adding to my belief that the bacterial product has efficacy. Whether any other topical will be more effective and safer than is topical triamcinolone remains to be seen. I'm still pessimistic about topicals because of patients' poor adherence to topical treatment, but perhaps an easy-to-use spray that isn't associated with patients' fear of "steroids" will be helpful.
I love articles like this one from Chen and colleagues. They analyzed data on hundreds of thousands of patients with and without AD. Adults with AD had a "significantly increased risk" of developing venous thromboembolism compared with adults without AD. The huge sample size of their study seems compelling. That huge sample size allows detection of effects so small that they may be clinically insignificant.
They report that patients with AD had a venous thromboembolism at a rate of 1.05/1000 patients-years; the rate was 0.82 for patients without AD. From that, we can calculate that there would be an additional 23 patients with venous thromboembolism for every 100,000 patient-years or about one more venous thromboembolism in the AD group in every 4000 patient-years. Though the finding was statistically significant, I don't think it is clinically meaningful.
The authors correctly conclude that "vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients with AD who present with relevant symptoms (eg, unexplained dyspnea, chest tightness, and limb swelling)." But it is probably also true that vascular examination and consultation with the emergency department, cardiologists, or pulmonologists are indicated for patients without AD who present with those symptoms. I think the authors might have been on solid ground if they had concluded that there was a statistically significant but clinically insignificant increased risk for venous thromboembolism in patients with AD.
Eichenfeld and colleagues examined the use of topical crisaborole once per day as a maintenance treatment for patients with mild to moderate AD. The study compared patients given topical crisaborole with those randomly assigned to vehicle. The active treatment was effective because topical crisaborole treated patients had longer times to the first flare following treatment and fewer flares over the 1 year of treatment. The differences were not huge, but I think they were clinically meaningful. I'm guessing that the topical crisaborole maintenance treatment would have been even more effective had it been used regularly. The study did not, as far as I could tell, assess how well the treatment was used.
An interesting aspect of this study is that it began with nearly 500 participants who started on twice daily topical crisaborole. The 270 patients who responded to the treatment (achieving clear or almost clear with at least a 2-point improvement) were enrolled in the 1-year maintenance phase. Thus, the participants in the maintenance phase were preselected for patients who respond to topical crisaborole. We don't know why they were responders (I, of course, expect it is because they selected for patients who are better than others are at using a topical treatment), but it may be best not to try to generalize these results and assume this form of maintenance treatment would work equally well in a population who achieve initial success with an oral therapy regimen (for example, a quick course of oral prednisone).
Dupilumab was a revolutionary treatment for AD. I didn't think that I'd ever see a more effective treatment. It's so safe too! It has been a first-line treatment for AD since its introduction. Now, we also have oral Janus kinase inhibitor options. Blauvelt and colleagues examined what happens when patients who have been on dupilumab are switched to a high dose (30 mg/d) of upadacitinib (the standard starting dose of upadacitinib is 15 mg/d). Though dupilumab is very effective, upadacitinib is more so. After 4 weeks of switching to upadacitinib, nearly half the patients were completely clear of AD compared with only 16.0% after 24 weeks of dupilumab! The authors point out, optimistically, that "No new safety risks were observed." Though there were no cancers, gastrointestinal perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events, or venous thromboembolic events, there were cases of eczema herpeticum and zoster in patients treated with upadacitinib. Having upadacitinib available for patients who fail dupilumab is a clear benefit; the role of upadacitinib before dupilumab seems less clear.
Patients doing great on dupilumab for AD may be wondering: Do I still need to take it every 2 weeks? Spekhorst and colleagues may have the answer. They describe the response to tapering dupilumab in patients who had been on the drug for at least 1 year with well-controlled disease for at least 6 months. Patients in the study then continued dupilumab with the longest possible dosing interval while maintaining control of their AD.
Generally, patients maintained good control of their AD, with only a small increase in mean disease severity and in concomitant use of topical steroids. For the patients who attempted prolongation, 83% successfully continued dupilumab treatment with a prolonged interval. Not at all surprisingly, the authors calculated that prolonging the interval between dosing led to large savings in cost.
One of the nice features of dupilumab treatment is that loss of response over time seems unusual. Perhaps there is a low propensity for forming antidrug antibodies when dupilumab is used in the standard every 2-week dosing regimen. I don't know whether antidrug antibodies would be more likely with the intermittent dosing regimen. But now that we have other good systemic treatment options for AD, losing dupilumab efficacy would not be as critical a problem as it used to be. I also want to point out that patients' adherence to injection treatment, though better than adherence to topicals, is far from perfect. It's likely that many patients have already been prolonging the interval between taking their treatments. If you want to know, just ask them. The way I like to phrase the question is: "Are you keeping the extra injectors you've accumulated refrigerated like you are supposed to?"
Commentary: AD, RA, Probiotics, and a New JAK inhibitor, June 2023
The most common adverse events were acne, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) level elevations, and nasopharyngitis. I'm confident that none of my patients will have CPK elevations detected, because I won't be testing for it. I suspect that CPK elevations come from people being more physically active when their skin clears up.
I have the sense that our comfort with Janus kinase (JAK) inhibition will grow rapidly as we use the drug for patients with vitiligo, alopecia areata, resistant atopic dermatitis, and other diseases. Many of us are comfortable with methotrexate, dapsone, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate; our comfort with JAK inhibitors for our patients who need it will almost surely follow.
Williams and colleagues did a meta-analysis looking at the relationship between AD and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They claim that “patients with AD had significantly increased odds of comorbid RA.” This claim should not be taken at face value. What they found was that the observed rate of RA was higher in patients with AD than in controls, and the difference was not something you would see by chance very often. But that does not make something significant. To truly be significant, you'd expect it to be clinically meaningful. The relationship they found — even if not due to chance or to some unmeasured bias — wasn't clinically relevant, in my opinion. RA is a relatively rare phenomenon. If it is barely more common in patients with AD than in controls, it is still rare in AD patients. We don't need to screen for RA in AD patients. We don't need to do anything with this apparent association.
The bottom line is to be wary when you see an article that reports a “significant” finding, especially when it is based on a higher relative risk, like an odds ratio. What we need to know is what the absolute magnitude of the risk is. We need to know how many patients with AD you'd have to see before you'd see one more case of RA due to AD. Williams and colleagues' study doesn't report the information we need as clinicians.
Fijan and colleagues did a meta-analysis to assess the effects of single-strain probiotic lactobacilli on atopic dermatitis. The found a “significant” (meaning, statistically significant) reduction with the lactobacilli treatment compared with placebo. They used the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as the outcome. There was a mean 4.5-unit improvement.
For comparison, Wollenberg and colleagues1 reported the SCORAD improvement seen with dupilumab: 49- and 46-unit improvements in children and adolescents, respectively.
While I'm sure that patients would love a safe, effective, “all natural” probiotic option for atopic dermatitis, I'm not optimistic that this gut magic is going to work.
Additional Reference
- Wollenberg A, Marcoux D, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORing Atopic Dermatitis outcomes in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2022;102:adv00726. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v102.854
The most common adverse events were acne, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) level elevations, and nasopharyngitis. I'm confident that none of my patients will have CPK elevations detected, because I won't be testing for it. I suspect that CPK elevations come from people being more physically active when their skin clears up.
I have the sense that our comfort with Janus kinase (JAK) inhibition will grow rapidly as we use the drug for patients with vitiligo, alopecia areata, resistant atopic dermatitis, and other diseases. Many of us are comfortable with methotrexate, dapsone, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate; our comfort with JAK inhibitors for our patients who need it will almost surely follow.
Williams and colleagues did a meta-analysis looking at the relationship between AD and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They claim that “patients with AD had significantly increased odds of comorbid RA.” This claim should not be taken at face value. What they found was that the observed rate of RA was higher in patients with AD than in controls, and the difference was not something you would see by chance very often. But that does not make something significant. To truly be significant, you'd expect it to be clinically meaningful. The relationship they found — even if not due to chance or to some unmeasured bias — wasn't clinically relevant, in my opinion. RA is a relatively rare phenomenon. If it is barely more common in patients with AD than in controls, it is still rare in AD patients. We don't need to screen for RA in AD patients. We don't need to do anything with this apparent association.
The bottom line is to be wary when you see an article that reports a “significant” finding, especially when it is based on a higher relative risk, like an odds ratio. What we need to know is what the absolute magnitude of the risk is. We need to know how many patients with AD you'd have to see before you'd see one more case of RA due to AD. Williams and colleagues' study doesn't report the information we need as clinicians.
Fijan and colleagues did a meta-analysis to assess the effects of single-strain probiotic lactobacilli on atopic dermatitis. The found a “significant” (meaning, statistically significant) reduction with the lactobacilli treatment compared with placebo. They used the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as the outcome. There was a mean 4.5-unit improvement.
For comparison, Wollenberg and colleagues1 reported the SCORAD improvement seen with dupilumab: 49- and 46-unit improvements in children and adolescents, respectively.
While I'm sure that patients would love a safe, effective, “all natural” probiotic option for atopic dermatitis, I'm not optimistic that this gut magic is going to work.
Additional Reference
- Wollenberg A, Marcoux D, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORing Atopic Dermatitis outcomes in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2022;102:adv00726. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v102.854
The most common adverse events were acne, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) level elevations, and nasopharyngitis. I'm confident that none of my patients will have CPK elevations detected, because I won't be testing for it. I suspect that CPK elevations come from people being more physically active when their skin clears up.
I have the sense that our comfort with Janus kinase (JAK) inhibition will grow rapidly as we use the drug for patients with vitiligo, alopecia areata, resistant atopic dermatitis, and other diseases. Many of us are comfortable with methotrexate, dapsone, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate; our comfort with JAK inhibitors for our patients who need it will almost surely follow.
Williams and colleagues did a meta-analysis looking at the relationship between AD and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They claim that “patients with AD had significantly increased odds of comorbid RA.” This claim should not be taken at face value. What they found was that the observed rate of RA was higher in patients with AD than in controls, and the difference was not something you would see by chance very often. But that does not make something significant. To truly be significant, you'd expect it to be clinically meaningful. The relationship they found — even if not due to chance or to some unmeasured bias — wasn't clinically relevant, in my opinion. RA is a relatively rare phenomenon. If it is barely more common in patients with AD than in controls, it is still rare in AD patients. We don't need to screen for RA in AD patients. We don't need to do anything with this apparent association.
The bottom line is to be wary when you see an article that reports a “significant” finding, especially when it is based on a higher relative risk, like an odds ratio. What we need to know is what the absolute magnitude of the risk is. We need to know how many patients with AD you'd have to see before you'd see one more case of RA due to AD. Williams and colleagues' study doesn't report the information we need as clinicians.
Fijan and colleagues did a meta-analysis to assess the effects of single-strain probiotic lactobacilli on atopic dermatitis. The found a “significant” (meaning, statistically significant) reduction with the lactobacilli treatment compared with placebo. They used the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as the outcome. There was a mean 4.5-unit improvement.
For comparison, Wollenberg and colleagues1 reported the SCORAD improvement seen with dupilumab: 49- and 46-unit improvements in children and adolescents, respectively.
While I'm sure that patients would love a safe, effective, “all natural” probiotic option for atopic dermatitis, I'm not optimistic that this gut magic is going to work.
Additional Reference
- Wollenberg A, Marcoux D, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORing Atopic Dermatitis outcomes in paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2022;102:adv00726. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v102.854
Commentary: Three New AD Treatments and a Study of Food Allergy, May 2023
Torrelo and colleagues described the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in pediatric patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At the high dose of 4 mg daily, the IGA success rate was about 40%, similar to what we expect for adults treated with dupilumab and less than what we might expect with upadacitinib.
Studies have already been done on efficacy and safety of baricitinib in adults with atopic dermatitis. But baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with severe alopecia areata and is not currently indicated as a treatment for anyone with atopic dermatitis, at least not in the United States. At this time, I think the most useful aspect of Torrelo and colleagues' findings is being able to tell our adult patients with alopecia areata that baricitinib was safe enough that they could test it in children as young as 2 years old with eczema.
Perälä and colleagues' report comparing topical tacrolimus and topical corticosteroids (1% hydrocortisone acetate or, if needed, 0.1% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment) in young children with atopic dermatitis is fascinating. They saw patients back at 1 week and followed them for 3 years. In just 1 week, both groups had massive and similar improvement in their atopic dermatitis, and that improvement continued throughout the study. Here are some take-home points:
- Atopic dermatitis responds rapidly to low-to-medium–strength topical steroids.
- Bringing patients back at 1 week may have been a critical aspect of this study, as adherence to topicals can be abysmal; bringing patients back at 1 week probably enables them to use their treatment much better than they would otherwise.
- If we need a nonsteroidal topical, we have an excellent one available at low cost in the form of topical tacrolimus.
Perälä and colleagues also did this study to see whether good treatment of atopic dermatitis in these young children would have long-term benefits on atopic airway issues. Because the researchers didn't have a placebo group (and considered it unethical to have one), we cannot tell whether the topical treatment provided any benefit in that regard.
Yamamoto-Hanada and colleaguesexamined whether "enhanced" topical steroid treatment would prevent food allergy in children with eczema compared with standard topical steroid treatment. Perhaps a better word than "enhanced" would be "aggressive." The enhanced treatment entailed having infants receive alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for the whole body except face and scalp. While the researchers saw a reduction in egg allergy (from roughly 40% to 30%), they also saw reduced body weight and height. A key take-home message is that with extensive use of topical steroids, we can see systemic effects.
Torrelo and colleagues described the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in pediatric patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At the high dose of 4 mg daily, the IGA success rate was about 40%, similar to what we expect for adults treated with dupilumab and less than what we might expect with upadacitinib.
Studies have already been done on efficacy and safety of baricitinib in adults with atopic dermatitis. But baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with severe alopecia areata and is not currently indicated as a treatment for anyone with atopic dermatitis, at least not in the United States. At this time, I think the most useful aspect of Torrelo and colleagues' findings is being able to tell our adult patients with alopecia areata that baricitinib was safe enough that they could test it in children as young as 2 years old with eczema.
Perälä and colleagues' report comparing topical tacrolimus and topical corticosteroids (1% hydrocortisone acetate or, if needed, 0.1% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment) in young children with atopic dermatitis is fascinating. They saw patients back at 1 week and followed them for 3 years. In just 1 week, both groups had massive and similar improvement in their atopic dermatitis, and that improvement continued throughout the study. Here are some take-home points:
- Atopic dermatitis responds rapidly to low-to-medium–strength topical steroids.
- Bringing patients back at 1 week may have been a critical aspect of this study, as adherence to topicals can be abysmal; bringing patients back at 1 week probably enables them to use their treatment much better than they would otherwise.
- If we need a nonsteroidal topical, we have an excellent one available at low cost in the form of topical tacrolimus.
Perälä and colleagues also did this study to see whether good treatment of atopic dermatitis in these young children would have long-term benefits on atopic airway issues. Because the researchers didn't have a placebo group (and considered it unethical to have one), we cannot tell whether the topical treatment provided any benefit in that regard.
Yamamoto-Hanada and colleaguesexamined whether "enhanced" topical steroid treatment would prevent food allergy in children with eczema compared with standard topical steroid treatment. Perhaps a better word than "enhanced" would be "aggressive." The enhanced treatment entailed having infants receive alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for the whole body except face and scalp. While the researchers saw a reduction in egg allergy (from roughly 40% to 30%), they also saw reduced body weight and height. A key take-home message is that with extensive use of topical steroids, we can see systemic effects.
Torrelo and colleagues described the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in pediatric patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At the high dose of 4 mg daily, the IGA success rate was about 40%, similar to what we expect for adults treated with dupilumab and less than what we might expect with upadacitinib.
Studies have already been done on efficacy and safety of baricitinib in adults with atopic dermatitis. But baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with severe alopecia areata and is not currently indicated as a treatment for anyone with atopic dermatitis, at least not in the United States. At this time, I think the most useful aspect of Torrelo and colleagues' findings is being able to tell our adult patients with alopecia areata that baricitinib was safe enough that they could test it in children as young as 2 years old with eczema.
Perälä and colleagues' report comparing topical tacrolimus and topical corticosteroids (1% hydrocortisone acetate or, if needed, 0.1% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment) in young children with atopic dermatitis is fascinating. They saw patients back at 1 week and followed them for 3 years. In just 1 week, both groups had massive and similar improvement in their atopic dermatitis, and that improvement continued throughout the study. Here are some take-home points:
- Atopic dermatitis responds rapidly to low-to-medium–strength topical steroids.
- Bringing patients back at 1 week may have been a critical aspect of this study, as adherence to topicals can be abysmal; bringing patients back at 1 week probably enables them to use their treatment much better than they would otherwise.
- If we need a nonsteroidal topical, we have an excellent one available at low cost in the form of topical tacrolimus.
Perälä and colleagues also did this study to see whether good treatment of atopic dermatitis in these young children would have long-term benefits on atopic airway issues. Because the researchers didn't have a placebo group (and considered it unethical to have one), we cannot tell whether the topical treatment provided any benefit in that regard.
Yamamoto-Hanada and colleaguesexamined whether "enhanced" topical steroid treatment would prevent food allergy in children with eczema compared with standard topical steroid treatment. Perhaps a better word than "enhanced" would be "aggressive." The enhanced treatment entailed having infants receive alclometasone dipropionate for the whole face and betamethasone valerate for the whole body except face and scalp. While the researchers saw a reduction in egg allergy (from roughly 40% to 30%), they also saw reduced body weight and height. A key take-home message is that with extensive use of topical steroids, we can see systemic effects.
Commentary: IL-31 inhibitor, e-cigarettes, and upadacitinib in AD, April 2023
Good news! There's not a lot to say about this. Dupilumab is so easy. No blood work, no immunosuppression. Dupilumab is highly effective and very safe. It's safe enough for children as young as 6 months! It's so effective that if it is not working, I question my diagnosis (Could it be contact dermatitis or mycosis fungoides instead?) and whether the patient is taking the medication properly.
Boesjes and colleagues describe in Acta Dermato-Venereologica the Dutch experience with upadacitinib in patients who have not been successfully treated with dupilumab or baricitinib. Presumably, such patients, because treatment with dupilumab or baricitinib or both was unsuccessful, have very resistant atopic dermatitis (either due to strong genetic propensity or perhaps because they don't take their medications). Despite having such refractory disease, most patients did well on the treatment with rapid disease improvement. Upadacitinib didn't work for everyone, though. About 30% of the patients discontinued upadacitinib treatment due to ineffectiveness, adverse events, or both (8.5%, 14.9%, and 6.4%, respectively).
How much of that ineffectiveness was due to poor adherence to taking the treatment was not assessed. Upadacitinib is extraordinarily effective for atopic dermatitis. I didn't think I would ever see a drug more effective than dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, but a low dose of upadacitinib (15 mg/day) seems about twice as effective as dupilumab for complete clearing of atopic dermatitis. The higher dose of 30 mg may be 3.5 times as effective as dupiliumab at getting atopic dermatitis completely clear.1
I dislike the word significant. Significant is ambiguous. It could mean that an observed association would not be likely to occur by chance, or it could mean that an observed association is clinically meaningful. Smith and colleagues in "Association between electronic cigarette use and atopic dermatitis among United States adults" reported finding a "significant" association between e-cigarette use and atopic dermatitis. A total of 23% of 2119 e-cigarette users had atopic dermatitis vs 17.1% of 26,444 nonusers. Clearly, the observed association was statistically significant (the 6% difference was not likely to occur due to chance alone). Is the finding clinically meaningful? I don't think it would affect our practice in any way.
The authors made the point that the study doesn't tell us whether e-cigarette use causes atopic dermatitis or if atopic dermatitis causes people to smoke. I wonder if just being younger (or some other factor) might make people more likely to use e-cigarettes and more likely to have atopic dermatitis (assuming atopic dermatitis gradually subsides over time, a dogma that may not be true).
Kabashima and colleagues report on the efficacy of the interleukin (IL)–31 antagonist nemolizumab. IL-31 mediates itch and having a new drug to block IL-31 may be a great treatment for our itchy patients. In this study, patients who had greater itch reduction had greater improvement in eczema and in quality of life. I'm quite sure that reducing itch improves patients' quality of life. But when it comes to the itch and the inflammation, I'm not sure which comes first. Does controlling the itch make the inflammation better? Maybe. Does controlling inflammation make itch better? Certainly.
For atopic patients with inflammation, controlling that inflammation seems to me to be the best approach, and we don't need more new treatments to accomplish that. For those patients who have a lot of itch and little inflammation, an IL-31 antagonist may be a revolutionary addition to our treatment options.
Additional References
1. Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3023. Erratum in: JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5451
Good news! There's not a lot to say about this. Dupilumab is so easy. No blood work, no immunosuppression. Dupilumab is highly effective and very safe. It's safe enough for children as young as 6 months! It's so effective that if it is not working, I question my diagnosis (Could it be contact dermatitis or mycosis fungoides instead?) and whether the patient is taking the medication properly.
Boesjes and colleagues describe in Acta Dermato-Venereologica the Dutch experience with upadacitinib in patients who have not been successfully treated with dupilumab or baricitinib. Presumably, such patients, because treatment with dupilumab or baricitinib or both was unsuccessful, have very resistant atopic dermatitis (either due to strong genetic propensity or perhaps because they don't take their medications). Despite having such refractory disease, most patients did well on the treatment with rapid disease improvement. Upadacitinib didn't work for everyone, though. About 30% of the patients discontinued upadacitinib treatment due to ineffectiveness, adverse events, or both (8.5%, 14.9%, and 6.4%, respectively).
How much of that ineffectiveness was due to poor adherence to taking the treatment was not assessed. Upadacitinib is extraordinarily effective for atopic dermatitis. I didn't think I would ever see a drug more effective than dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, but a low dose of upadacitinib (15 mg/day) seems about twice as effective as dupilumab for complete clearing of atopic dermatitis. The higher dose of 30 mg may be 3.5 times as effective as dupiliumab at getting atopic dermatitis completely clear.1
I dislike the word significant. Significant is ambiguous. It could mean that an observed association would not be likely to occur by chance, or it could mean that an observed association is clinically meaningful. Smith and colleagues in "Association between electronic cigarette use and atopic dermatitis among United States adults" reported finding a "significant" association between e-cigarette use and atopic dermatitis. A total of 23% of 2119 e-cigarette users had atopic dermatitis vs 17.1% of 26,444 nonusers. Clearly, the observed association was statistically significant (the 6% difference was not likely to occur due to chance alone). Is the finding clinically meaningful? I don't think it would affect our practice in any way.
The authors made the point that the study doesn't tell us whether e-cigarette use causes atopic dermatitis or if atopic dermatitis causes people to smoke. I wonder if just being younger (or some other factor) might make people more likely to use e-cigarettes and more likely to have atopic dermatitis (assuming atopic dermatitis gradually subsides over time, a dogma that may not be true).
Kabashima and colleagues report on the efficacy of the interleukin (IL)–31 antagonist nemolizumab. IL-31 mediates itch and having a new drug to block IL-31 may be a great treatment for our itchy patients. In this study, patients who had greater itch reduction had greater improvement in eczema and in quality of life. I'm quite sure that reducing itch improves patients' quality of life. But when it comes to the itch and the inflammation, I'm not sure which comes first. Does controlling the itch make the inflammation better? Maybe. Does controlling inflammation make itch better? Certainly.
For atopic patients with inflammation, controlling that inflammation seems to me to be the best approach, and we don't need more new treatments to accomplish that. For those patients who have a lot of itch and little inflammation, an IL-31 antagonist may be a revolutionary addition to our treatment options.
Additional References
1. Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3023. Erratum in: JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5451
Good news! There's not a lot to say about this. Dupilumab is so easy. No blood work, no immunosuppression. Dupilumab is highly effective and very safe. It's safe enough for children as young as 6 months! It's so effective that if it is not working, I question my diagnosis (Could it be contact dermatitis or mycosis fungoides instead?) and whether the patient is taking the medication properly.
Boesjes and colleagues describe in Acta Dermato-Venereologica the Dutch experience with upadacitinib in patients who have not been successfully treated with dupilumab or baricitinib. Presumably, such patients, because treatment with dupilumab or baricitinib or both was unsuccessful, have very resistant atopic dermatitis (either due to strong genetic propensity or perhaps because they don't take their medications). Despite having such refractory disease, most patients did well on the treatment with rapid disease improvement. Upadacitinib didn't work for everyone, though. About 30% of the patients discontinued upadacitinib treatment due to ineffectiveness, adverse events, or both (8.5%, 14.9%, and 6.4%, respectively).
How much of that ineffectiveness was due to poor adherence to taking the treatment was not assessed. Upadacitinib is extraordinarily effective for atopic dermatitis. I didn't think I would ever see a drug more effective than dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, but a low dose of upadacitinib (15 mg/day) seems about twice as effective as dupilumab for complete clearing of atopic dermatitis. The higher dose of 30 mg may be 3.5 times as effective as dupiliumab at getting atopic dermatitis completely clear.1
I dislike the word significant. Significant is ambiguous. It could mean that an observed association would not be likely to occur by chance, or it could mean that an observed association is clinically meaningful. Smith and colleagues in "Association between electronic cigarette use and atopic dermatitis among United States adults" reported finding a "significant" association between e-cigarette use and atopic dermatitis. A total of 23% of 2119 e-cigarette users had atopic dermatitis vs 17.1% of 26,444 nonusers. Clearly, the observed association was statistically significant (the 6% difference was not likely to occur due to chance alone). Is the finding clinically meaningful? I don't think it would affect our practice in any way.
The authors made the point that the study doesn't tell us whether e-cigarette use causes atopic dermatitis or if atopic dermatitis causes people to smoke. I wonder if just being younger (or some other factor) might make people more likely to use e-cigarettes and more likely to have atopic dermatitis (assuming atopic dermatitis gradually subsides over time, a dogma that may not be true).
Kabashima and colleagues report on the efficacy of the interleukin (IL)–31 antagonist nemolizumab. IL-31 mediates itch and having a new drug to block IL-31 may be a great treatment for our itchy patients. In this study, patients who had greater itch reduction had greater improvement in eczema and in quality of life. I'm quite sure that reducing itch improves patients' quality of life. But when it comes to the itch and the inflammation, I'm not sure which comes first. Does controlling the itch make the inflammation better? Maybe. Does controlling inflammation make itch better? Certainly.
For atopic patients with inflammation, controlling that inflammation seems to me to be the best approach, and we don't need more new treatments to accomplish that. For those patients who have a lot of itch and little inflammation, an IL-31 antagonist may be a revolutionary addition to our treatment options.
Additional References
1. Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3023. Erratum in: JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5451
Commentary: Sorting out useful atopic dermatitis research from filler, March 2023
Another study caught my attention this month for having presented a lot of information with no clinically important conclusions. In "Mode of Delivery and Offspring Atopic Dermatitis in a Swedish Nationwide Study," Mubanga and colleagues studied 1.4 million children! With that many participants, they were almost certain to find associations that were statistically significant and clinically irrelevant. They reported that children born by instrumental vaginal delivery, emergency caesarean section, and elective caesarean section were at a higher risk for AD compared with those born by uncomplicated vaginal delivery. They failed to report the absolute magnitude of the associations, which were undoubtedly so small as to be clinically meaningless. Even if the observed association were not due to some hidden bias, the association is not anything that would change treatment in any way.
On the other hand, the small, open label registry analysis, "Experiences From Daily Practice of Upadacitinib Treatment on Atopic Dermatitis With a Focus on Hand Eczema: Results From the BioDay Registry," published by Kamphuis and colleagues, is of much greater value, reporting the effectiveness and safety of upadacitinib on hand eczema. Not surprisingly, there were large improvements in the investigators' assessments of the dermatitis and in patients' quality of life. This small study is informative about efficacy; it is too small, though, to evaluate how frequently rare severe adverse events occur.
The use of probiotics to safely improve skin disease is such an appealing concept, yet it sounds a lot like hocus-pocus to me. Feíto-Rodríguez and colleagues report in the journal Clinical and Experimental Dermatology that a probiotic mixture of Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus casei improved atopic dermatitis more than did placebo. The findings are not compelling. Differences were small. Rates of being clear or almost clear weren't reported. We can get atopic dermatitis to clear up in a few days with topical triamcinolone (if we can get patients to use it); so far, the effects of probiotics on the presumed gut-immune system-skin axis seem very much underwhelming.
Another study caught my attention this month for having presented a lot of information with no clinically important conclusions. In "Mode of Delivery and Offspring Atopic Dermatitis in a Swedish Nationwide Study," Mubanga and colleagues studied 1.4 million children! With that many participants, they were almost certain to find associations that were statistically significant and clinically irrelevant. They reported that children born by instrumental vaginal delivery, emergency caesarean section, and elective caesarean section were at a higher risk for AD compared with those born by uncomplicated vaginal delivery. They failed to report the absolute magnitude of the associations, which were undoubtedly so small as to be clinically meaningless. Even if the observed association were not due to some hidden bias, the association is not anything that would change treatment in any way.
On the other hand, the small, open label registry analysis, "Experiences From Daily Practice of Upadacitinib Treatment on Atopic Dermatitis With a Focus on Hand Eczema: Results From the BioDay Registry," published by Kamphuis and colleagues, is of much greater value, reporting the effectiveness and safety of upadacitinib on hand eczema. Not surprisingly, there were large improvements in the investigators' assessments of the dermatitis and in patients' quality of life. This small study is informative about efficacy; it is too small, though, to evaluate how frequently rare severe adverse events occur.
The use of probiotics to safely improve skin disease is such an appealing concept, yet it sounds a lot like hocus-pocus to me. Feíto-Rodríguez and colleagues report in the journal Clinical and Experimental Dermatology that a probiotic mixture of Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus casei improved atopic dermatitis more than did placebo. The findings are not compelling. Differences were small. Rates of being clear or almost clear weren't reported. We can get atopic dermatitis to clear up in a few days with topical triamcinolone (if we can get patients to use it); so far, the effects of probiotics on the presumed gut-immune system-skin axis seem very much underwhelming.
Another study caught my attention this month for having presented a lot of information with no clinically important conclusions. In "Mode of Delivery and Offspring Atopic Dermatitis in a Swedish Nationwide Study," Mubanga and colleagues studied 1.4 million children! With that many participants, they were almost certain to find associations that were statistically significant and clinically irrelevant. They reported that children born by instrumental vaginal delivery, emergency caesarean section, and elective caesarean section were at a higher risk for AD compared with those born by uncomplicated vaginal delivery. They failed to report the absolute magnitude of the associations, which were undoubtedly so small as to be clinically meaningless. Even if the observed association were not due to some hidden bias, the association is not anything that would change treatment in any way.
On the other hand, the small, open label registry analysis, "Experiences From Daily Practice of Upadacitinib Treatment on Atopic Dermatitis With a Focus on Hand Eczema: Results From the BioDay Registry," published by Kamphuis and colleagues, is of much greater value, reporting the effectiveness and safety of upadacitinib on hand eczema. Not surprisingly, there were large improvements in the investigators' assessments of the dermatitis and in patients' quality of life. This small study is informative about efficacy; it is too small, though, to evaluate how frequently rare severe adverse events occur.
The use of probiotics to safely improve skin disease is such an appealing concept, yet it sounds a lot like hocus-pocus to me. Feíto-Rodríguez and colleagues report in the journal Clinical and Experimental Dermatology that a probiotic mixture of Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus casei improved atopic dermatitis more than did placebo. The findings are not compelling. Differences were small. Rates of being clear or almost clear weren't reported. We can get atopic dermatitis to clear up in a few days with topical triamcinolone (if we can get patients to use it); so far, the effects of probiotics on the presumed gut-immune system-skin axis seem very much underwhelming.