User login
Lupus Erythematosus Tumidus Clinical Characteristics and Treatment: A Retrospective Review of 25 Patients
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rare photosensitive dermatosis1 that previously was considered a subtype of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus; however, the clinical course and favorable prognosis of LET led to its reclassification into another category, called intermittent cutaneous lupus erythematosus.2 Although known about for more than 100 years, the association of LET with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), its autoantibody profile, and its prognosis are not well characterized. The purpose of this study was to describe the demographics, clinical characteristics, autoantibody profile, comorbidities, and treatment of LET based on a retrospective review of patients with LET.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted in patients with histologically diagnosed LET who presented to the Department of Dermatology at the Wake Forest School of Medicine (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) over 6 years (July 2012 to July 2018). Inclusion criteria included males or females aged 18 to 75 years with clinical and histopathology-proven LET, which was defined as a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate with abundant mucin deposition in the reticular dermis and absent or focal dermoepidermal junction alterations. Exclusion criteria included males or females younger than 18 years or older than 75 years or patients without clinical and histopathologically proven LET. Medical records were evaluated for demographics, clinical characteristics, diagnoses, autoantibodies, treatment, and recurrence. Photosensitivity was confirmed by clinical history. This study was approved by the Wake Forest School of Medicine institutional review board.
Results
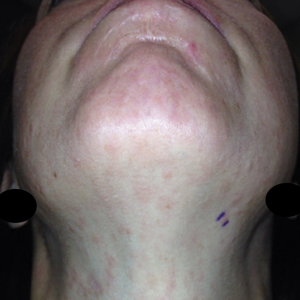
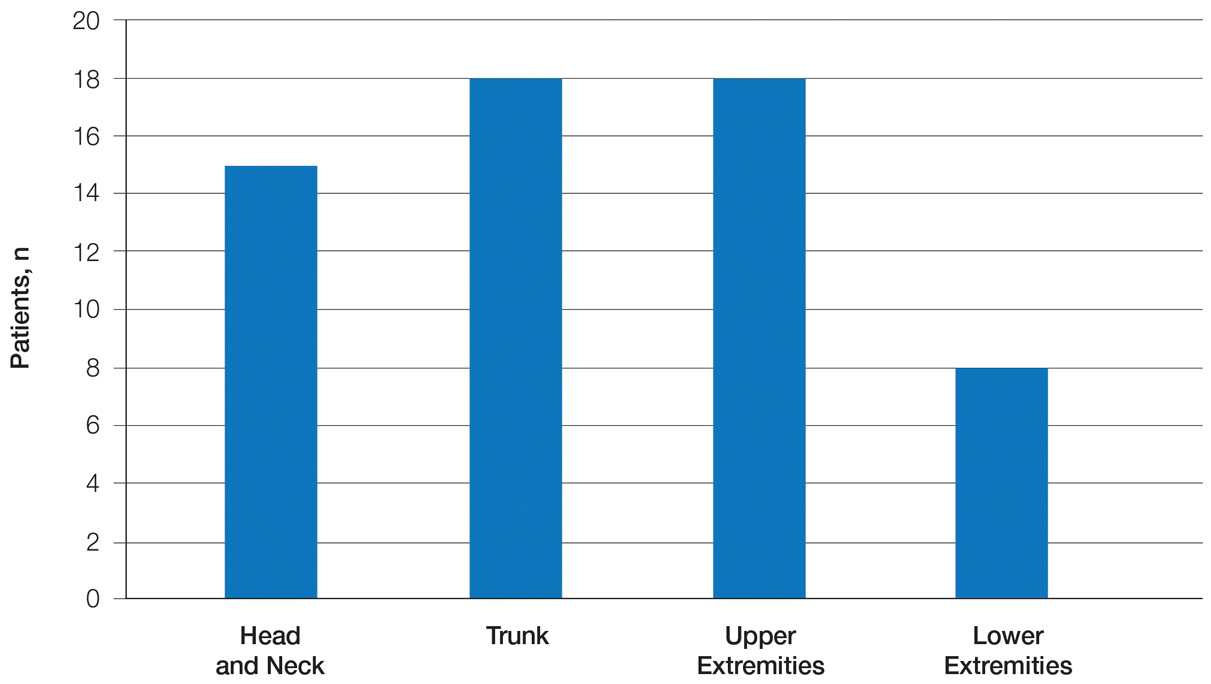
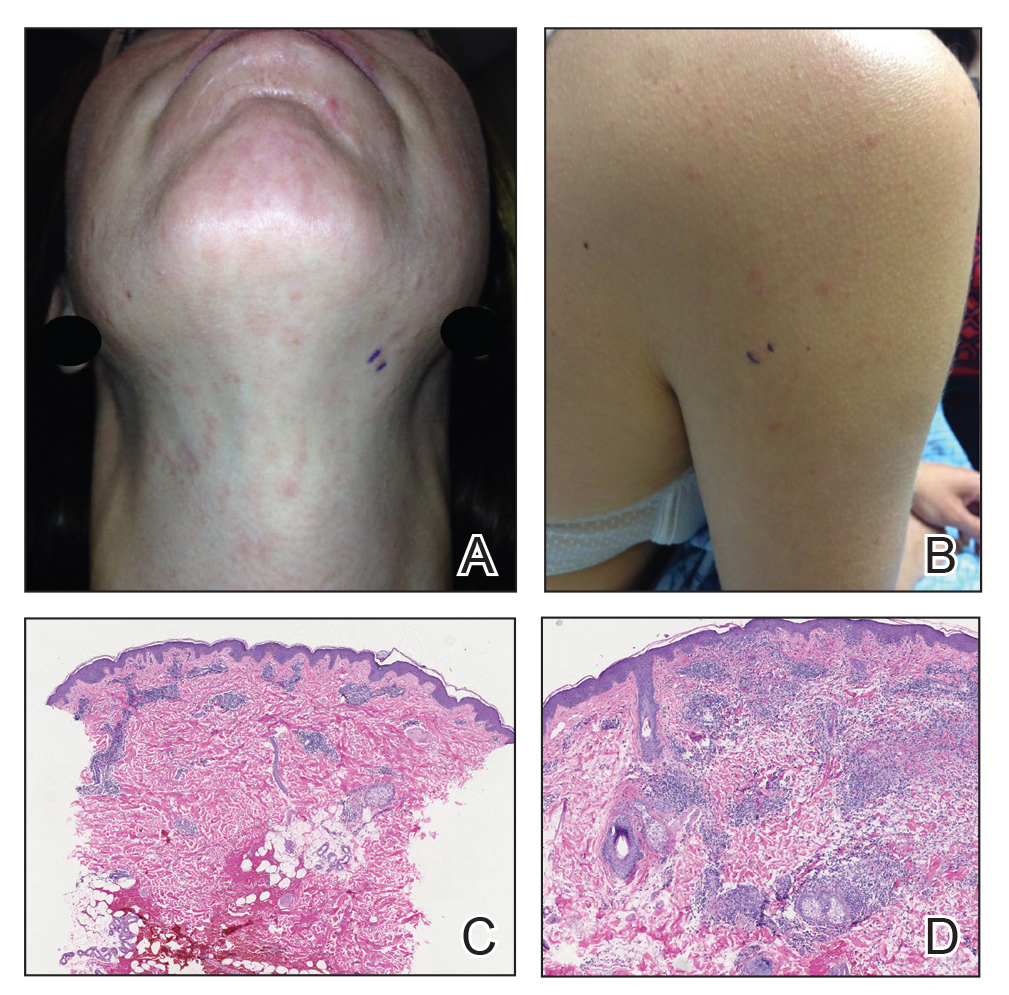
Twenty-five patients were included in the study (eTable). The mean age (SD) at diagnosis was 46 (10.9) years, with a male to female ratio of 1:4. Twenty-two (88%) patients were White non-Hispanic, whereas 3 (12%) were Black. Lupus erythematosus tumidus most commonly affected the trunk (18/25 [72%]) and upper extremities (18/25 [72%]), followed by the head and neck (15/25 [60%]) and lower extremities (8/25 [32%])(Figure 1). The most common morphologies were plaques (18/25 [72%]), papules (17/25 [68%]), and nodules (6/25 [24%])(Figures 2 and 3). Most patients experienced painful (14/25 [56%]) or pruritic (13/25 [52%]) lesions as well as photosensitivity (13/25 [52%]). Of all measured autoantibodies, 5 of 22 (23%) patients had positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers greater than 1:80, 1 of 14 (7%) patients had positive anti-Ro (anti-SSA), 1 of 14 (7%) had positive anti-La (anti-SSB), 2 of 10 (20%) had positive anti–double-stranded DNA, and 0 of 6 (0%) patients had positive anti-Smith antibodies. Four (16%) patients with SLE had skin and joint involvement, whereas 1 had lupus nephritis. One (4%) patient had discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Seventeen (68%) patients reported recurrences or flares. The mean duration of symptoms (SD) was 28 (44) months.
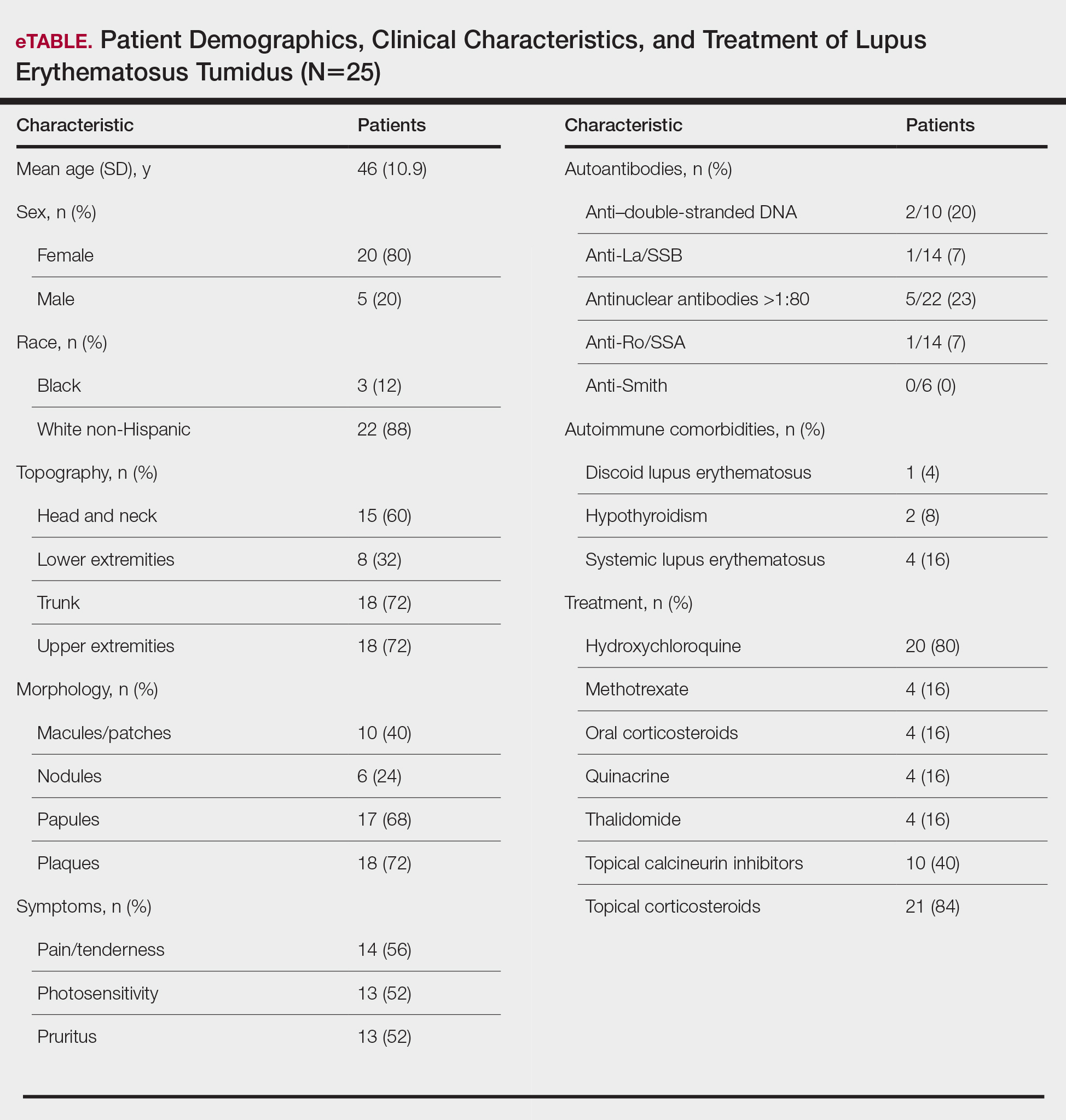
Topical corticosteroids (21/25 [84%]) and hydroxychloroquine (20/25 [80%]) were the most commonly prescribed treatments. Hydroxychloroquine monotherapy achieved clearance or almost clearance in 12 (60%) patients. Four patients were prescribed thalidomide after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 2 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide and hydroxychloroquine, 1 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide monotherapy, and 1 improved but did not clear. Four patients were concurrently started on quinacrine (mepacrine) after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 1 patient had no clearance, 1 discontinued because of allergy, 1 improved, and 1 cleared. Four patients had short courses of prednisone lasting 1 to 4 weeks. Three of 4 patients treated with methotrexate discontinued because of adverse effects, and 1 patient improved. Other prescribed treatments included topical calcineurin inhibitors (10/25 [40%]), dapsone (1/25 [4%]), and clofazimine (1/25 [4%]).
Comment
Prevalence of LET—Although other European LET case series reported a male predominance or equal male to female ratio, our case series reported female predominance (1:4).1,3-5 Our male to female ratio resembles similar ratios in DLE and subacute lupus erythematosus, whereas relative to our study, SLE male to female ratios favored females over males.6,7

Clinical Distribution of LET—In one study enrolling 24 patients with LET, 79% (19/24) of patients had facial involvement, 50% (12/24) had V-neck involvement, 50% (12/24) had back involvement, and 46% (11/24) had arm involvement,2 whereas our study reported 72% involvement of the trunk, 72% involvement of the upper extremities, 60% involvement of the head and neck region, and 32% involvement of the lower extremities. Although our study reported more lower extremity involvement, the aforementioned study used precise topographic locations, whereas we used more generalized topographic locations. Therefore, it was difficult to compare disease distribution between both studies.2
Presence of Autoantibodies and Comorbidities—Of the 22 patients tested for ANA, 23% reported titers greater than 1:80, similar to the 20% positive ANA prevalence in an LET case series of 25 patients.5 Of 4 patients diagnosed with SLE, 3 had articular and skin involvement, and 1 had renal involvement. These findings resemble a similar LET case series.2 Nonetheless, given the numerous skin criteria in the American College of Rheumatology SLE classification criteria, patients with predominant skin disease and positive autoantibodies are diagnosed as having SLE without notable extracutaneous involvement.2 Therefore, SLE diagnosis in the setting of LET could be reassessed periodically in this population. One patient in our study was diagnosed with DLE several years later. It is uncommon for LET to be reported concomitantly with DLE.8
Treatment of LET—Evidence supporting efficacious treatment options for LET is limited to case series. Sun protection is recommended in all patients with LET. Earlier case series reported a high response rate with sun protection and topical corticosteroids, with 19% to 55% of patients requiring subsequent systemic antimalarials.3,4 However, one case series presented a need for systemic antimalarials,5 similar to our study. Hydroxychloroquine 200 to 400 mg daily is considered the first-line systemic treatment for LET. Its response rate varies among studies and may be influenced by dosage.1,3 Second-line treatments include methotrexate 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly, thalidomide 50 to 100 mg daily, and quinacrine. However, quinacrine is not currently commercially available. Thalidomide and quinacrine represented useful alternatives when hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed. As with other immunomodulators, adverse effects should be monitored periodically.
Conclusion
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is characterized by erythematous papules and plaques that may be tender or pruritic. It follows an intermittent course and rarely is associated with SLE. Hydroxychloroquine is considered the first-line systemic treatment; however, recalcitrant disease could be managed with other immunomodulators, including methotrexate, thalidomide, or quinacrine.
- Kuhn A, Bein D, Bonsmann G. The 100th anniversary of lupus erythematosus tumidus. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:441-448.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Rodriguez-Caruncho C, Bielsa I, Fernandez-Figueras MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a clinical and histological study of 25 cases. Lupus. 2015;24:751-755.
- Patsinakidis N, Gambichler T, Lahner N, et al. Cutaneous characteristics and association with antinuclear antibodies in 402 patients with different subtypes of lupus erythematosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:2097-2104.
- Petersen MP, Moller S, Bygum A, et al. Epidemiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the associated risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Lupus. 2018;27:1424-1430.
- Dekle CL, Mannes KD, Davis LS, et al. Lupus tumidus. J Am AcadDermatol. 1999;41:250-253.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rare photosensitive dermatosis1 that previously was considered a subtype of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus; however, the clinical course and favorable prognosis of LET led to its reclassification into another category, called intermittent cutaneous lupus erythematosus.2 Although known about for more than 100 years, the association of LET with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), its autoantibody profile, and its prognosis are not well characterized. The purpose of this study was to describe the demographics, clinical characteristics, autoantibody profile, comorbidities, and treatment of LET based on a retrospective review of patients with LET.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted in patients with histologically diagnosed LET who presented to the Department of Dermatology at the Wake Forest School of Medicine (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) over 6 years (July 2012 to July 2018). Inclusion criteria included males or females aged 18 to 75 years with clinical and histopathology-proven LET, which was defined as a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate with abundant mucin deposition in the reticular dermis and absent or focal dermoepidermal junction alterations. Exclusion criteria included males or females younger than 18 years or older than 75 years or patients without clinical and histopathologically proven LET. Medical records were evaluated for demographics, clinical characteristics, diagnoses, autoantibodies, treatment, and recurrence. Photosensitivity was confirmed by clinical history. This study was approved by the Wake Forest School of Medicine institutional review board.

Results
Twenty-five patients were included in the study (eTable). The mean age (SD) at diagnosis was 46 (10.9) years, with a male to female ratio of 1:4. Twenty-two (88%) patients were White non-Hispanic, whereas 3 (12%) were Black. Lupus erythematosus tumidus most commonly affected the trunk (18/25 [72%]) and upper extremities (18/25 [72%]), followed by the head and neck (15/25 [60%]) and lower extremities (8/25 [32%])(Figure 1). The most common morphologies were plaques (18/25 [72%]), papules (17/25 [68%]), and nodules (6/25 [24%])(Figures 2 and 3). Most patients experienced painful (14/25 [56%]) or pruritic (13/25 [52%]) lesions as well as photosensitivity (13/25 [52%]). Of all measured autoantibodies, 5 of 22 (23%) patients had positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers greater than 1:80, 1 of 14 (7%) patients had positive anti-Ro (anti-SSA), 1 of 14 (7%) had positive anti-La (anti-SSB), 2 of 10 (20%) had positive anti–double-stranded DNA, and 0 of 6 (0%) patients had positive anti-Smith antibodies. Four (16%) patients with SLE had skin and joint involvement, whereas 1 had lupus nephritis. One (4%) patient had discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Seventeen (68%) patients reported recurrences or flares. The mean duration of symptoms (SD) was 28 (44) months.

Topical corticosteroids (21/25 [84%]) and hydroxychloroquine (20/25 [80%]) were the most commonly prescribed treatments. Hydroxychloroquine monotherapy achieved clearance or almost clearance in 12 (60%) patients. Four patients were prescribed thalidomide after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 2 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide and hydroxychloroquine, 1 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide monotherapy, and 1 improved but did not clear. Four patients were concurrently started on quinacrine (mepacrine) after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 1 patient had no clearance, 1 discontinued because of allergy, 1 improved, and 1 cleared. Four patients had short courses of prednisone lasting 1 to 4 weeks. Three of 4 patients treated with methotrexate discontinued because of adverse effects, and 1 patient improved. Other prescribed treatments included topical calcineurin inhibitors (10/25 [40%]), dapsone (1/25 [4%]), and clofazimine (1/25 [4%]).

Comment
Prevalence of LET—Although other European LET case series reported a male predominance or equal male to female ratio, our case series reported female predominance (1:4).1,3-5 Our male to female ratio resembles similar ratios in DLE and subacute lupus erythematosus, whereas relative to our study, SLE male to female ratios favored females over males.6,7

Clinical Distribution of LET—In one study enrolling 24 patients with LET, 79% (19/24) of patients had facial involvement, 50% (12/24) had V-neck involvement, 50% (12/24) had back involvement, and 46% (11/24) had arm involvement,2 whereas our study reported 72% involvement of the trunk, 72% involvement of the upper extremities, 60% involvement of the head and neck region, and 32% involvement of the lower extremities. Although our study reported more lower extremity involvement, the aforementioned study used precise topographic locations, whereas we used more generalized topographic locations. Therefore, it was difficult to compare disease distribution between both studies.2
Presence of Autoantibodies and Comorbidities—Of the 22 patients tested for ANA, 23% reported titers greater than 1:80, similar to the 20% positive ANA prevalence in an LET case series of 25 patients.5 Of 4 patients diagnosed with SLE, 3 had articular and skin involvement, and 1 had renal involvement. These findings resemble a similar LET case series.2 Nonetheless, given the numerous skin criteria in the American College of Rheumatology SLE classification criteria, patients with predominant skin disease and positive autoantibodies are diagnosed as having SLE without notable extracutaneous involvement.2 Therefore, SLE diagnosis in the setting of LET could be reassessed periodically in this population. One patient in our study was diagnosed with DLE several years later. It is uncommon for LET to be reported concomitantly with DLE.8
Treatment of LET—Evidence supporting efficacious treatment options for LET is limited to case series. Sun protection is recommended in all patients with LET. Earlier case series reported a high response rate with sun protection and topical corticosteroids, with 19% to 55% of patients requiring subsequent systemic antimalarials.3,4 However, one case series presented a need for systemic antimalarials,5 similar to our study. Hydroxychloroquine 200 to 400 mg daily is considered the first-line systemic treatment for LET. Its response rate varies among studies and may be influenced by dosage.1,3 Second-line treatments include methotrexate 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly, thalidomide 50 to 100 mg daily, and quinacrine. However, quinacrine is not currently commercially available. Thalidomide and quinacrine represented useful alternatives when hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed. As with other immunomodulators, adverse effects should be monitored periodically.
Conclusion
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is characterized by erythematous papules and plaques that may be tender or pruritic. It follows an intermittent course and rarely is associated with SLE. Hydroxychloroquine is considered the first-line systemic treatment; however, recalcitrant disease could be managed with other immunomodulators, including methotrexate, thalidomide, or quinacrine.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rare photosensitive dermatosis1 that previously was considered a subtype of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus; however, the clinical course and favorable prognosis of LET led to its reclassification into another category, called intermittent cutaneous lupus erythematosus.2 Although known about for more than 100 years, the association of LET with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), its autoantibody profile, and its prognosis are not well characterized. The purpose of this study was to describe the demographics, clinical characteristics, autoantibody profile, comorbidities, and treatment of LET based on a retrospective review of patients with LET.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted in patients with histologically diagnosed LET who presented to the Department of Dermatology at the Wake Forest School of Medicine (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) over 6 years (July 2012 to July 2018). Inclusion criteria included males or females aged 18 to 75 years with clinical and histopathology-proven LET, which was defined as a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate with abundant mucin deposition in the reticular dermis and absent or focal dermoepidermal junction alterations. Exclusion criteria included males or females younger than 18 years or older than 75 years or patients without clinical and histopathologically proven LET. Medical records were evaluated for demographics, clinical characteristics, diagnoses, autoantibodies, treatment, and recurrence. Photosensitivity was confirmed by clinical history. This study was approved by the Wake Forest School of Medicine institutional review board.

Results
Twenty-five patients were included in the study (eTable). The mean age (SD) at diagnosis was 46 (10.9) years, with a male to female ratio of 1:4. Twenty-two (88%) patients were White non-Hispanic, whereas 3 (12%) were Black. Lupus erythematosus tumidus most commonly affected the trunk (18/25 [72%]) and upper extremities (18/25 [72%]), followed by the head and neck (15/25 [60%]) and lower extremities (8/25 [32%])(Figure 1). The most common morphologies were plaques (18/25 [72%]), papules (17/25 [68%]), and nodules (6/25 [24%])(Figures 2 and 3). Most patients experienced painful (14/25 [56%]) or pruritic (13/25 [52%]) lesions as well as photosensitivity (13/25 [52%]). Of all measured autoantibodies, 5 of 22 (23%) patients had positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers greater than 1:80, 1 of 14 (7%) patients had positive anti-Ro (anti-SSA), 1 of 14 (7%) had positive anti-La (anti-SSB), 2 of 10 (20%) had positive anti–double-stranded DNA, and 0 of 6 (0%) patients had positive anti-Smith antibodies. Four (16%) patients with SLE had skin and joint involvement, whereas 1 had lupus nephritis. One (4%) patient had discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Seventeen (68%) patients reported recurrences or flares. The mean duration of symptoms (SD) was 28 (44) months.

Topical corticosteroids (21/25 [84%]) and hydroxychloroquine (20/25 [80%]) were the most commonly prescribed treatments. Hydroxychloroquine monotherapy achieved clearance or almost clearance in 12 (60%) patients. Four patients were prescribed thalidomide after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 2 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide and hydroxychloroquine, 1 achieved complete clearance with thalidomide monotherapy, and 1 improved but did not clear. Four patients were concurrently started on quinacrine (mepacrine) after hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed; 1 patient had no clearance, 1 discontinued because of allergy, 1 improved, and 1 cleared. Four patients had short courses of prednisone lasting 1 to 4 weeks. Three of 4 patients treated with methotrexate discontinued because of adverse effects, and 1 patient improved. Other prescribed treatments included topical calcineurin inhibitors (10/25 [40%]), dapsone (1/25 [4%]), and clofazimine (1/25 [4%]).

Comment
Prevalence of LET—Although other European LET case series reported a male predominance or equal male to female ratio, our case series reported female predominance (1:4).1,3-5 Our male to female ratio resembles similar ratios in DLE and subacute lupus erythematosus, whereas relative to our study, SLE male to female ratios favored females over males.6,7

Clinical Distribution of LET—In one study enrolling 24 patients with LET, 79% (19/24) of patients had facial involvement, 50% (12/24) had V-neck involvement, 50% (12/24) had back involvement, and 46% (11/24) had arm involvement,2 whereas our study reported 72% involvement of the trunk, 72% involvement of the upper extremities, 60% involvement of the head and neck region, and 32% involvement of the lower extremities. Although our study reported more lower extremity involvement, the aforementioned study used precise topographic locations, whereas we used more generalized topographic locations. Therefore, it was difficult to compare disease distribution between both studies.2
Presence of Autoantibodies and Comorbidities—Of the 22 patients tested for ANA, 23% reported titers greater than 1:80, similar to the 20% positive ANA prevalence in an LET case series of 25 patients.5 Of 4 patients diagnosed with SLE, 3 had articular and skin involvement, and 1 had renal involvement. These findings resemble a similar LET case series.2 Nonetheless, given the numerous skin criteria in the American College of Rheumatology SLE classification criteria, patients with predominant skin disease and positive autoantibodies are diagnosed as having SLE without notable extracutaneous involvement.2 Therefore, SLE diagnosis in the setting of LET could be reassessed periodically in this population. One patient in our study was diagnosed with DLE several years later. It is uncommon for LET to be reported concomitantly with DLE.8
Treatment of LET—Evidence supporting efficacious treatment options for LET is limited to case series. Sun protection is recommended in all patients with LET. Earlier case series reported a high response rate with sun protection and topical corticosteroids, with 19% to 55% of patients requiring subsequent systemic antimalarials.3,4 However, one case series presented a need for systemic antimalarials,5 similar to our study. Hydroxychloroquine 200 to 400 mg daily is considered the first-line systemic treatment for LET. Its response rate varies among studies and may be influenced by dosage.1,3 Second-line treatments include methotrexate 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly, thalidomide 50 to 100 mg daily, and quinacrine. However, quinacrine is not currently commercially available. Thalidomide and quinacrine represented useful alternatives when hydroxychloroquine monotherapy failed. As with other immunomodulators, adverse effects should be monitored periodically.
Conclusion
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is characterized by erythematous papules and plaques that may be tender or pruritic. It follows an intermittent course and rarely is associated with SLE. Hydroxychloroquine is considered the first-line systemic treatment; however, recalcitrant disease could be managed with other immunomodulators, including methotrexate, thalidomide, or quinacrine.
- Kuhn A, Bein D, Bonsmann G. The 100th anniversary of lupus erythematosus tumidus. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:441-448.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Rodriguez-Caruncho C, Bielsa I, Fernandez-Figueras MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a clinical and histological study of 25 cases. Lupus. 2015;24:751-755.
- Patsinakidis N, Gambichler T, Lahner N, et al. Cutaneous characteristics and association with antinuclear antibodies in 402 patients with different subtypes of lupus erythematosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:2097-2104.
- Petersen MP, Moller S, Bygum A, et al. Epidemiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the associated risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Lupus. 2018;27:1424-1430.
- Dekle CL, Mannes KD, Davis LS, et al. Lupus tumidus. J Am AcadDermatol. 1999;41:250-253.
- Kuhn A, Bein D, Bonsmann G. The 100th anniversary of lupus erythematosus tumidus. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:441-448.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Rodriguez-Caruncho C, Bielsa I, Fernandez-Figueras MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a clinical and histological study of 25 cases. Lupus. 2015;24:751-755.
- Patsinakidis N, Gambichler T, Lahner N, et al. Cutaneous characteristics and association with antinuclear antibodies in 402 patients with different subtypes of lupus erythematosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:2097-2104.
- Petersen MP, Moller S, Bygum A, et al. Epidemiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the associated risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Lupus. 2018;27:1424-1430.
- Dekle CL, Mannes KD, Davis LS, et al. Lupus tumidus. J Am AcadDermatol. 1999;41:250-253.
Practice Points
- Approximately 20% of patients with lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) will have positive antinuclear antibody titers.
- Along with cutaneous manifestations, approximately 50% of patients with LET also will have pruritus, tenderness, and photosensitivity.
- If LET is resistant to hydroxychloroquine, consider using quinacrine, methotrexate, or thalidomide.
Is There an Association Between Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Fibromyalgia?
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
Practice Point
- Although fibromyalgia does not occur more frequently in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) patients, it is important to recognize that HS patients can have comorbidities that should be addressed when possible to improve overall quality of life.