User login
The troubling trend of repackaging feminine hygiene products for the next generation
Feminine hygiene products have been commercially available for decades. They are commonly marketed to reduce odor or clean vaginal discharge and menses. Multiple formulas are available as topical washes, wipes, creams, sprays, powders, deodorants, and douches.1 Products on the market range from those used externally on the vulva, such as wipes and sprays, to liquid solutions used intravaginally, such as washes and douches.
Who uses feminine hygiene products?
According to a 2006 study, the majority of women who use douches started using them between age 15 and 19 years, but some women initiate this practice habit as early as age 10 to 14.1 Predictably, women who douche are more likely to perceive douche products as safe.1
Demographic data on douche utilization are mixed: Some studies show that there are no significant racial differences in douching practices,2 while others have found that Black and African American women are more likely to practice douching than White and Hispanic women.1,3 Studies have shown a significant difference in attitudes toward douching and knowledge of normal vaginal symptoms among US racial demographics, although this must be examined through the historical context of racism and the lens of medical anthropology.4
Women cite that common reasons they use feminine hygiene products are to feel clean, to control odor, and to use after menses and intercourse.1,2
Modern marketing approaches
From wipes to soaps to douches, feminine hygiene products often are advertised to promote “funk-free periods”5 and “freshness,” fostering an environment in which women and men develop unrealistic standards for what is considered normal genital odor and resulting in poor body image.6
Recently, Vagisil (Combe Incorporated) marketing efforts faced backlash from the ObGyn community for targeting younger populations with a specific product line for adolescents called OMV! In addition, attention has been drawn to VCF vaginal odor eliminating film (Apothecus Pharmaceutical Corp), small stamp-sized dissolving films that are placed in the vaginal canal in contact with the epithelium. This product has entered the market of feminine hygiene products accompanied by slogans of eliminating “feminine odor” and providing “confidence for women to be intimate.”
Continue to: Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome...
Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome
Frequent use of feminine hygiene products has been associated with recurrent vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, and general irritation/itch,7,8 which can cause more discharge and odor. Ironically, this may result in women using the product more frequently since they often seek out these products to eliminate odor and discharge.1,2
The pH of the vagina changes during a woman’s lifetime, but in the reproductive years, the normal pH range is typically 3.8 to 4.4.9 This range allows for a normal vaginal flora to form with bacteria such as Lactobacillus species and Gardnerella vaginalis, while feminine hygiene products have a wide range of pH.9,10
Regardless of the formulation, most feminine hygiene products contain ingredients and compositions that potentially are detrimental to the health of the vulva and vagina. Many products contain acidic ingredients, such as citric acid, lactic acid, and dehydroacetic acid, that can alter the vaginal pH and weaken the vaginal barrier by wiping out normal vaginal flora10 despite being advertised for use on “sensitive areas” (TABLE). Lactic acid also has been found to increase diverse anaerobic bacteria in the vaginal microbiome.11 Some feminine hygiene products have been shown to suppress Lactobacillus growth at 2 hours after use and to kill all lactobacilli at 24 hours.10 Shifts in microbiota numbers often occur when the vaginal pH has been altered, as is frequently the case with feminine hygiene products. In the absence of microbiome bacteria, the presence of vaginal hygiene products has been shown to increase interleukin-8 (IL-8), suggesting a proinflammatory reaction.10
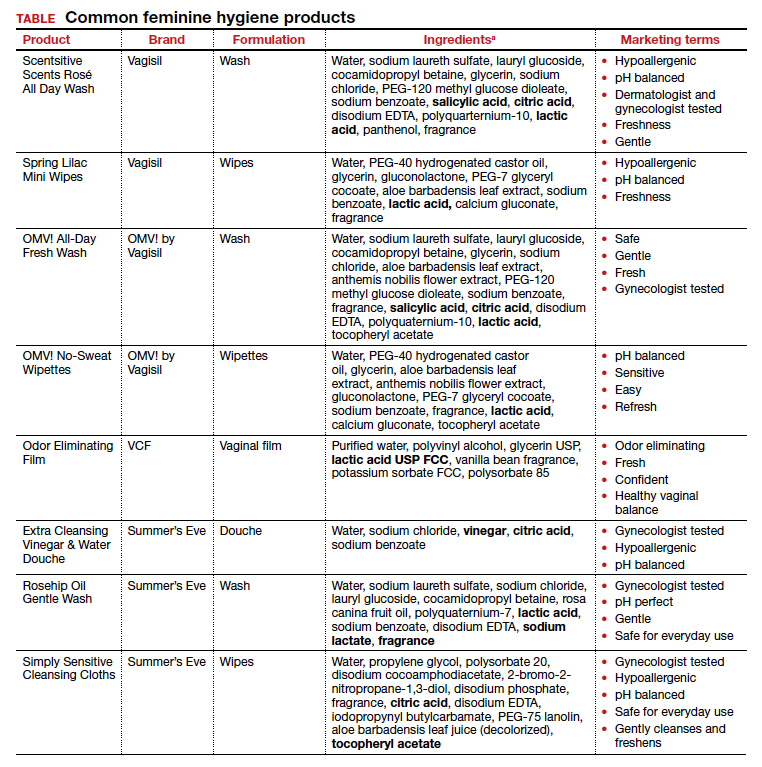
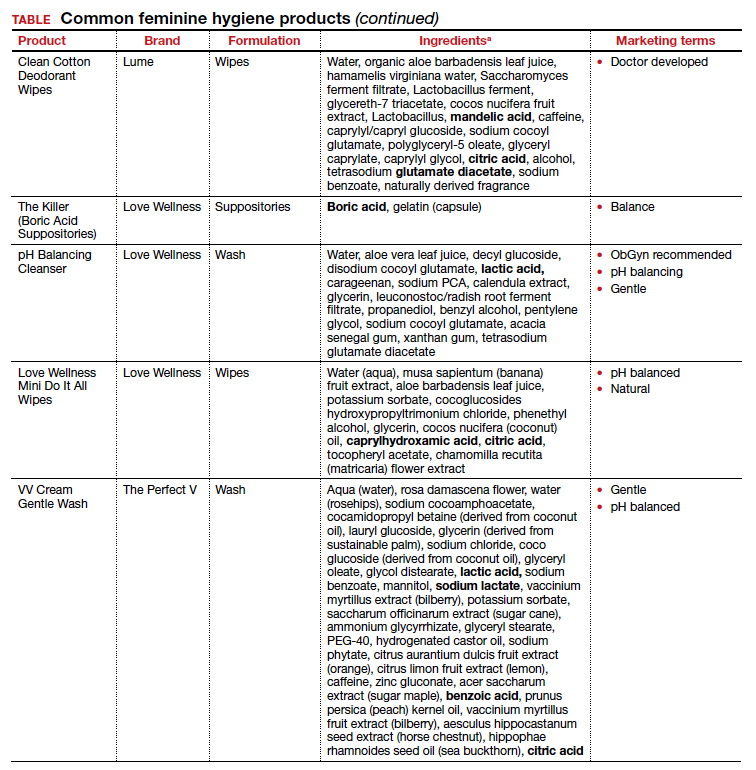
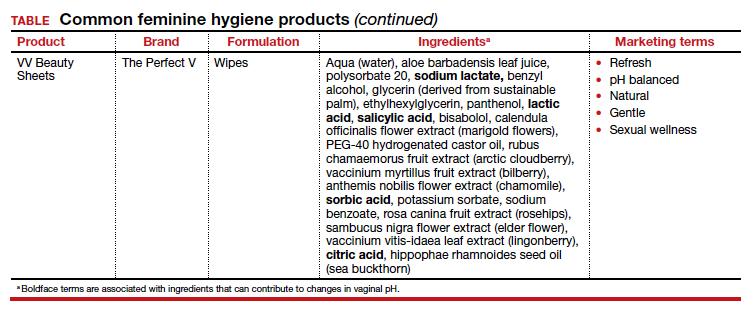
A study in the United Kingdom found that women who used bubble bath, antiseptics, or douche products had a higher incidence of bacterial vaginosis compared with women who did not use such products.7 Women in Canada who used feminine hygiene products were more likely to report adverse conditions, including yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.8 Furthermore, a significant association exists between vaginal douching and endometrial infection by bacterial vaginosis–associated organisms.12
Additionally, a study that analyzed volatile organic compound levels in the blood with the use of feminine hygiene products revealed a significant positive dose-exposure relationship between the frequency of vaginal douching in the last 6 months and concentrations of 1,4-dichloromethane, one of the volatile organic compounds.3 This points to the issue of not only disruption of pH and vaginal flora but also to the introduction of harmful substances that can further disrupt the vaginal barrier.
Understand the products to help educate patients
Use of feminine hygiene products is common among women. While women depend on the market to filter out products that are considered unsafe or may have harmful side effects,1 unfortunately that is not necessarily the case. With increasingly more feminine products on the market and the target demographic becoming younger, women of all ages are susceptible to misinformation that could affect their vaginal health long term.
It is vital that clinicians understand the topical effects of these products in order to properly educate and counsel patients. Ultimately, research on feminine hygiene products is limited and, as more products come to market, we must continue to reassess the effects of topical products on the vaginal epithelium and vulvar tissues. ●
- Grimley DM, Annang L, Foushee HR, et al. Vaginal douches and other feminine hygiene products: women’s practices and perceptions of product safety. Matern Child Health J. 2006;10:303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10995-005-0054-y.
- Foch BJ, McDaniel ND, Chacko MR. Racial differences in vaginal douching knowledge, attitude, and practices among sexually active adolescents. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2001;14:29-33. doi: 10.1016/S1083-3188(00)00080-2.
- Lin N, Ding N, Meza-Wilson E, et al. Volatile organic compounds in feminine hygiene products sold in the US market: a survey of products and health risks. Environ Int. 2020;144:105740. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105740.
- Wayne State University Digital Commons. Guy-Lee AK. Rituals reproducing race: African American women’s feminine hygiene practices, shared experiences, and power. 2017. http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_dissertations/1806. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- YouTube. OMV! by Vagisil—Intimate care products designed by teens. July 10, 2020. www.youtube.com/ watch?v=VkVsCagrAw0. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- Jenkins A, O’Doherty KC. The clean vagina, the healthy vagina, and the dirty vagina: exploring women’s portrayals of the vagina in relation to vaginal cleansing product use. Fem Psychol. 2021;31:192-211. doi: 10.1177/0959353520944144.
- Rajamanoharan S, Low N, Jones SB, et al. Bacterial vaginosis, ethnicity, and the use of genital cleansing agents: a case control study. Sex Transm Dis. 1999;26:404-409.
- Crann SE, Cunningham S, Albert A, et al. Vaginal health and hygiene practices and product use in Canada: a national cross-sectional survey. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18:52. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0543-y.
- Chen Y, Bruning E, Rubino J, et al. Role of female intimate hygiene in vulvovaginal health: global hygiene practices and product usage. Womens Health (London). 2017;13:58-67. doi: 10.1177/1745505717731011.
- Fashemi B, Delaney ML, Onderdonk AB, et al. Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal mucosal biome. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2013;24. doi: 10.3402/mehd. v24i0.19703.
- Van der Veer C, Bruisten SM, Van Houdt R, et al. Effects of an over-the-counter lactic-acid containing intra-vaginal douching product on the vaginal microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:168. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1545-0.
- Gondwe T, Ness R, Totten PA, et al. Novel bacterial vaginosis-associated organisms mediate the relationship between vaginal douching and pelvic inflammatory disease. Sex Transm Infect. 2020;96:439-444. doi: 10.1136/ sextrans-2019-054191.
Feminine hygiene products have been commercially available for decades. They are commonly marketed to reduce odor or clean vaginal discharge and menses. Multiple formulas are available as topical washes, wipes, creams, sprays, powders, deodorants, and douches.1 Products on the market range from those used externally on the vulva, such as wipes and sprays, to liquid solutions used intravaginally, such as washes and douches.
Who uses feminine hygiene products?
According to a 2006 study, the majority of women who use douches started using them between age 15 and 19 years, but some women initiate this practice habit as early as age 10 to 14.1 Predictably, women who douche are more likely to perceive douche products as safe.1
Demographic data on douche utilization are mixed: Some studies show that there are no significant racial differences in douching practices,2 while others have found that Black and African American women are more likely to practice douching than White and Hispanic women.1,3 Studies have shown a significant difference in attitudes toward douching and knowledge of normal vaginal symptoms among US racial demographics, although this must be examined through the historical context of racism and the lens of medical anthropology.4
Women cite that common reasons they use feminine hygiene products are to feel clean, to control odor, and to use after menses and intercourse.1,2
Modern marketing approaches
From wipes to soaps to douches, feminine hygiene products often are advertised to promote “funk-free periods”5 and “freshness,” fostering an environment in which women and men develop unrealistic standards for what is considered normal genital odor and resulting in poor body image.6
Recently, Vagisil (Combe Incorporated) marketing efforts faced backlash from the ObGyn community for targeting younger populations with a specific product line for adolescents called OMV! In addition, attention has been drawn to VCF vaginal odor eliminating film (Apothecus Pharmaceutical Corp), small stamp-sized dissolving films that are placed in the vaginal canal in contact with the epithelium. This product has entered the market of feminine hygiene products accompanied by slogans of eliminating “feminine odor” and providing “confidence for women to be intimate.”
Continue to: Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome...
Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome
Frequent use of feminine hygiene products has been associated with recurrent vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, and general irritation/itch,7,8 which can cause more discharge and odor. Ironically, this may result in women using the product more frequently since they often seek out these products to eliminate odor and discharge.1,2
The pH of the vagina changes during a woman’s lifetime, but in the reproductive years, the normal pH range is typically 3.8 to 4.4.9 This range allows for a normal vaginal flora to form with bacteria such as Lactobacillus species and Gardnerella vaginalis, while feminine hygiene products have a wide range of pH.9,10
Regardless of the formulation, most feminine hygiene products contain ingredients and compositions that potentially are detrimental to the health of the vulva and vagina. Many products contain acidic ingredients, such as citric acid, lactic acid, and dehydroacetic acid, that can alter the vaginal pH and weaken the vaginal barrier by wiping out normal vaginal flora10 despite being advertised for use on “sensitive areas” (TABLE). Lactic acid also has been found to increase diverse anaerobic bacteria in the vaginal microbiome.11 Some feminine hygiene products have been shown to suppress Lactobacillus growth at 2 hours after use and to kill all lactobacilli at 24 hours.10 Shifts in microbiota numbers often occur when the vaginal pH has been altered, as is frequently the case with feminine hygiene products. In the absence of microbiome bacteria, the presence of vaginal hygiene products has been shown to increase interleukin-8 (IL-8), suggesting a proinflammatory reaction.10



A study in the United Kingdom found that women who used bubble bath, antiseptics, or douche products had a higher incidence of bacterial vaginosis compared with women who did not use such products.7 Women in Canada who used feminine hygiene products were more likely to report adverse conditions, including yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.8 Furthermore, a significant association exists between vaginal douching and endometrial infection by bacterial vaginosis–associated organisms.12
Additionally, a study that analyzed volatile organic compound levels in the blood with the use of feminine hygiene products revealed a significant positive dose-exposure relationship between the frequency of vaginal douching in the last 6 months and concentrations of 1,4-dichloromethane, one of the volatile organic compounds.3 This points to the issue of not only disruption of pH and vaginal flora but also to the introduction of harmful substances that can further disrupt the vaginal barrier.
Understand the products to help educate patients
Use of feminine hygiene products is common among women. While women depend on the market to filter out products that are considered unsafe or may have harmful side effects,1 unfortunately that is not necessarily the case. With increasingly more feminine products on the market and the target demographic becoming younger, women of all ages are susceptible to misinformation that could affect their vaginal health long term.
It is vital that clinicians understand the topical effects of these products in order to properly educate and counsel patients. Ultimately, research on feminine hygiene products is limited and, as more products come to market, we must continue to reassess the effects of topical products on the vaginal epithelium and vulvar tissues. ●
Feminine hygiene products have been commercially available for decades. They are commonly marketed to reduce odor or clean vaginal discharge and menses. Multiple formulas are available as topical washes, wipes, creams, sprays, powders, deodorants, and douches.1 Products on the market range from those used externally on the vulva, such as wipes and sprays, to liquid solutions used intravaginally, such as washes and douches.
Who uses feminine hygiene products?
According to a 2006 study, the majority of women who use douches started using them between age 15 and 19 years, but some women initiate this practice habit as early as age 10 to 14.1 Predictably, women who douche are more likely to perceive douche products as safe.1
Demographic data on douche utilization are mixed: Some studies show that there are no significant racial differences in douching practices,2 while others have found that Black and African American women are more likely to practice douching than White and Hispanic women.1,3 Studies have shown a significant difference in attitudes toward douching and knowledge of normal vaginal symptoms among US racial demographics, although this must be examined through the historical context of racism and the lens of medical anthropology.4
Women cite that common reasons they use feminine hygiene products are to feel clean, to control odor, and to use after menses and intercourse.1,2
Modern marketing approaches
From wipes to soaps to douches, feminine hygiene products often are advertised to promote “funk-free periods”5 and “freshness,” fostering an environment in which women and men develop unrealistic standards for what is considered normal genital odor and resulting in poor body image.6
Recently, Vagisil (Combe Incorporated) marketing efforts faced backlash from the ObGyn community for targeting younger populations with a specific product line for adolescents called OMV! In addition, attention has been drawn to VCF vaginal odor eliminating film (Apothecus Pharmaceutical Corp), small stamp-sized dissolving films that are placed in the vaginal canal in contact with the epithelium. This product has entered the market of feminine hygiene products accompanied by slogans of eliminating “feminine odor” and providing “confidence for women to be intimate.”
Continue to: Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome...
Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal microbiome
Frequent use of feminine hygiene products has been associated with recurrent vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, and general irritation/itch,7,8 which can cause more discharge and odor. Ironically, this may result in women using the product more frequently since they often seek out these products to eliminate odor and discharge.1,2
The pH of the vagina changes during a woman’s lifetime, but in the reproductive years, the normal pH range is typically 3.8 to 4.4.9 This range allows for a normal vaginal flora to form with bacteria such as Lactobacillus species and Gardnerella vaginalis, while feminine hygiene products have a wide range of pH.9,10
Regardless of the formulation, most feminine hygiene products contain ingredients and compositions that potentially are detrimental to the health of the vulva and vagina. Many products contain acidic ingredients, such as citric acid, lactic acid, and dehydroacetic acid, that can alter the vaginal pH and weaken the vaginal barrier by wiping out normal vaginal flora10 despite being advertised for use on “sensitive areas” (TABLE). Lactic acid also has been found to increase diverse anaerobic bacteria in the vaginal microbiome.11 Some feminine hygiene products have been shown to suppress Lactobacillus growth at 2 hours after use and to kill all lactobacilli at 24 hours.10 Shifts in microbiota numbers often occur when the vaginal pH has been altered, as is frequently the case with feminine hygiene products. In the absence of microbiome bacteria, the presence of vaginal hygiene products has been shown to increase interleukin-8 (IL-8), suggesting a proinflammatory reaction.10



A study in the United Kingdom found that women who used bubble bath, antiseptics, or douche products had a higher incidence of bacterial vaginosis compared with women who did not use such products.7 Women in Canada who used feminine hygiene products were more likely to report adverse conditions, including yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.8 Furthermore, a significant association exists between vaginal douching and endometrial infection by bacterial vaginosis–associated organisms.12
Additionally, a study that analyzed volatile organic compound levels in the blood with the use of feminine hygiene products revealed a significant positive dose-exposure relationship between the frequency of vaginal douching in the last 6 months and concentrations of 1,4-dichloromethane, one of the volatile organic compounds.3 This points to the issue of not only disruption of pH and vaginal flora but also to the introduction of harmful substances that can further disrupt the vaginal barrier.
Understand the products to help educate patients
Use of feminine hygiene products is common among women. While women depend on the market to filter out products that are considered unsafe or may have harmful side effects,1 unfortunately that is not necessarily the case. With increasingly more feminine products on the market and the target demographic becoming younger, women of all ages are susceptible to misinformation that could affect their vaginal health long term.
It is vital that clinicians understand the topical effects of these products in order to properly educate and counsel patients. Ultimately, research on feminine hygiene products is limited and, as more products come to market, we must continue to reassess the effects of topical products on the vaginal epithelium and vulvar tissues. ●
- Grimley DM, Annang L, Foushee HR, et al. Vaginal douches and other feminine hygiene products: women’s practices and perceptions of product safety. Matern Child Health J. 2006;10:303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10995-005-0054-y.
- Foch BJ, McDaniel ND, Chacko MR. Racial differences in vaginal douching knowledge, attitude, and practices among sexually active adolescents. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2001;14:29-33. doi: 10.1016/S1083-3188(00)00080-2.
- Lin N, Ding N, Meza-Wilson E, et al. Volatile organic compounds in feminine hygiene products sold in the US market: a survey of products and health risks. Environ Int. 2020;144:105740. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105740.
- Wayne State University Digital Commons. Guy-Lee AK. Rituals reproducing race: African American women’s feminine hygiene practices, shared experiences, and power. 2017. http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_dissertations/1806. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- YouTube. OMV! by Vagisil—Intimate care products designed by teens. July 10, 2020. www.youtube.com/ watch?v=VkVsCagrAw0. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- Jenkins A, O’Doherty KC. The clean vagina, the healthy vagina, and the dirty vagina: exploring women’s portrayals of the vagina in relation to vaginal cleansing product use. Fem Psychol. 2021;31:192-211. doi: 10.1177/0959353520944144.
- Rajamanoharan S, Low N, Jones SB, et al. Bacterial vaginosis, ethnicity, and the use of genital cleansing agents: a case control study. Sex Transm Dis. 1999;26:404-409.
- Crann SE, Cunningham S, Albert A, et al. Vaginal health and hygiene practices and product use in Canada: a national cross-sectional survey. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18:52. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0543-y.
- Chen Y, Bruning E, Rubino J, et al. Role of female intimate hygiene in vulvovaginal health: global hygiene practices and product usage. Womens Health (London). 2017;13:58-67. doi: 10.1177/1745505717731011.
- Fashemi B, Delaney ML, Onderdonk AB, et al. Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal mucosal biome. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2013;24. doi: 10.3402/mehd. v24i0.19703.
- Van der Veer C, Bruisten SM, Van Houdt R, et al. Effects of an over-the-counter lactic-acid containing intra-vaginal douching product on the vaginal microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:168. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1545-0.
- Gondwe T, Ness R, Totten PA, et al. Novel bacterial vaginosis-associated organisms mediate the relationship between vaginal douching and pelvic inflammatory disease. Sex Transm Infect. 2020;96:439-444. doi: 10.1136/ sextrans-2019-054191.
- Grimley DM, Annang L, Foushee HR, et al. Vaginal douches and other feminine hygiene products: women’s practices and perceptions of product safety. Matern Child Health J. 2006;10:303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10995-005-0054-y.
- Foch BJ, McDaniel ND, Chacko MR. Racial differences in vaginal douching knowledge, attitude, and practices among sexually active adolescents. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2001;14:29-33. doi: 10.1016/S1083-3188(00)00080-2.
- Lin N, Ding N, Meza-Wilson E, et al. Volatile organic compounds in feminine hygiene products sold in the US market: a survey of products and health risks. Environ Int. 2020;144:105740. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105740.
- Wayne State University Digital Commons. Guy-Lee AK. Rituals reproducing race: African American women’s feminine hygiene practices, shared experiences, and power. 2017. http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_dissertations/1806. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- YouTube. OMV! by Vagisil—Intimate care products designed by teens. July 10, 2020. www.youtube.com/ watch?v=VkVsCagrAw0. Accessed December 13, 2021.
- Jenkins A, O’Doherty KC. The clean vagina, the healthy vagina, and the dirty vagina: exploring women’s portrayals of the vagina in relation to vaginal cleansing product use. Fem Psychol. 2021;31:192-211. doi: 10.1177/0959353520944144.
- Rajamanoharan S, Low N, Jones SB, et al. Bacterial vaginosis, ethnicity, and the use of genital cleansing agents: a case control study. Sex Transm Dis. 1999;26:404-409.
- Crann SE, Cunningham S, Albert A, et al. Vaginal health and hygiene practices and product use in Canada: a national cross-sectional survey. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18:52. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0543-y.
- Chen Y, Bruning E, Rubino J, et al. Role of female intimate hygiene in vulvovaginal health: global hygiene practices and product usage. Womens Health (London). 2017;13:58-67. doi: 10.1177/1745505717731011.
- Fashemi B, Delaney ML, Onderdonk AB, et al. Effects of feminine hygiene products on the vaginal mucosal biome. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2013;24. doi: 10.3402/mehd. v24i0.19703.
- Van der Veer C, Bruisten SM, Van Houdt R, et al. Effects of an over-the-counter lactic-acid containing intra-vaginal douching product on the vaginal microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:168. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1545-0.
- Gondwe T, Ness R, Totten PA, et al. Novel bacterial vaginosis-associated organisms mediate the relationship between vaginal douching and pelvic inflammatory disease. Sex Transm Infect. 2020;96:439-444. doi: 10.1136/ sextrans-2019-054191.


