User login
Diffuse Dermal Angiomatosis
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis (DDA) is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder that was originally thought to be a variant of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis (CREA) but is now considered to be on the spectrum of CREA. This article will focus on DDA and review the literature of prior case reports with brief descriptions of the differential diagnosis.
Case Report
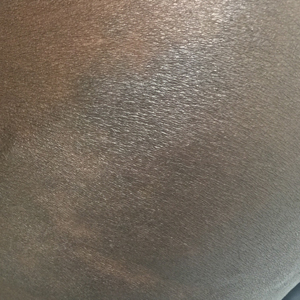
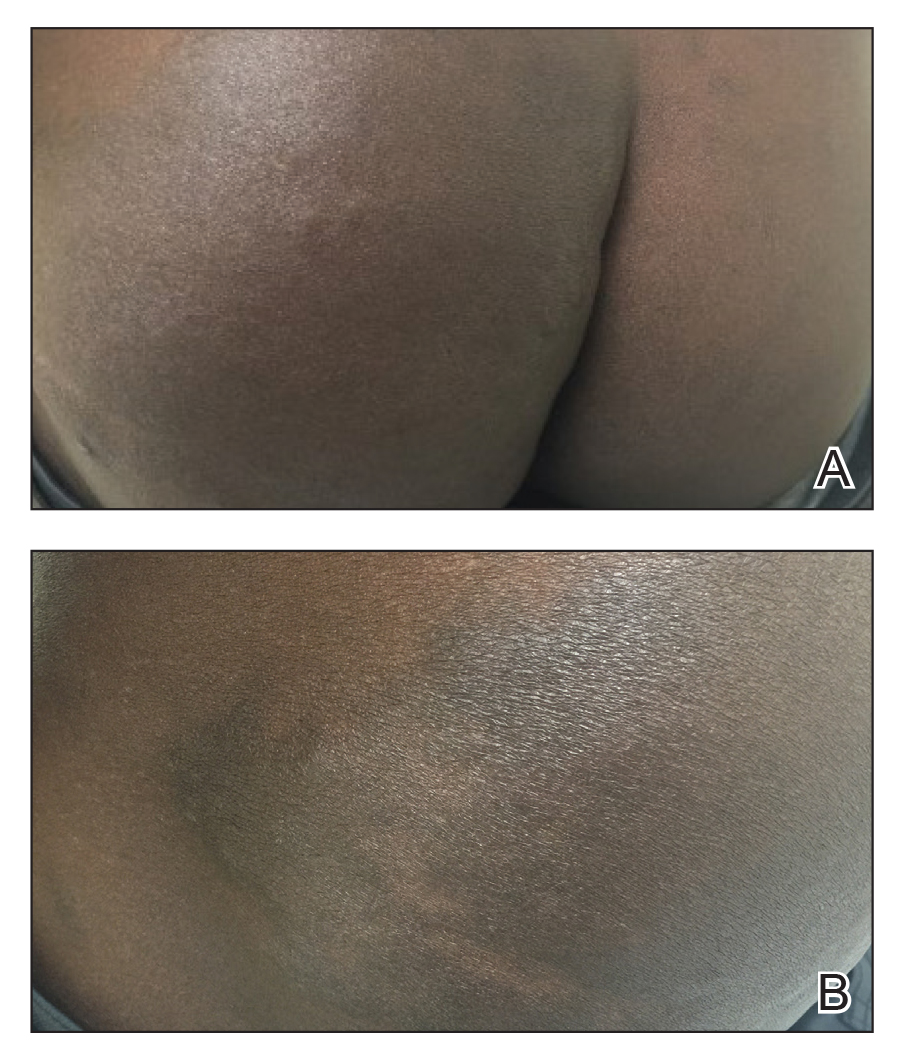
A 43-year-old Haitian man presented to the clinic with a lesion on the left buttock that had developed over the last 6 years. The patient stated the lesion had been enlarging over the last several months. Upon examination, there was a large (15-cm diameter), indurated, hyperpigmented plaque covering the left buttock (Figure 1). The patient reported no medical or contributory family history. Upon review of systems, he described a burning sensation sometimes in the area of the lesion that would develop randomly throughout the year.
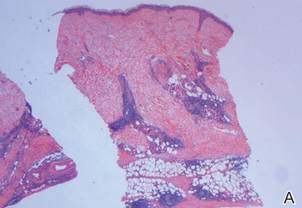
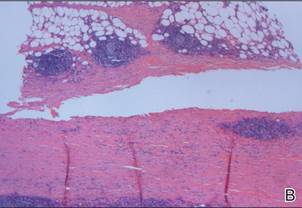
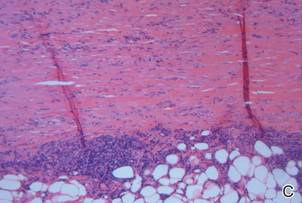
Three biopsies were performed, which revealed a collection of slightly dilated blood vessels with normal-appearing endothelial cells occupying the mid dermis and deep dermis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical stains with antibodies were directed against human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD31, CD34, the cell surface glycoprotein podoplanin, Ki-67, and smooth muscle actin antigens, with appropriate controls. The vessel walls were positive for CD31, CD34, and smooth muscle actin, and negative for HHV-8 and podoplanin; Ki-67 was not increased. These histologic findings were consistent with a diagnosis of DDA. A detailed history was taken. The cause of DDA in our patient was uncertain.
Comment
Classification and Epidemiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder first described by Krell et al1 in 1994. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is benign and is classified in the group of cutaneous reactive angiomatoses,2 which are benign vascular disorders marked by intravascular and extravascular hyperplasia of endothelial cells that may or may not include pericytes.2 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis was originally described as a variant of CREA, which is characterized by hyperplasia of endothelial dermal cells and intravascular proliferation.3 However, DDA has more recently been identified as a distinct disorder on the spectrum of CREA rather than as a variant of CREA.2 Given the recent reclassification, not all physicians make this distinction. However, as more case reports of DDA are published, physicians continue to support this change.4 Nevertheless, DDA has been an established disorder since 1994.1
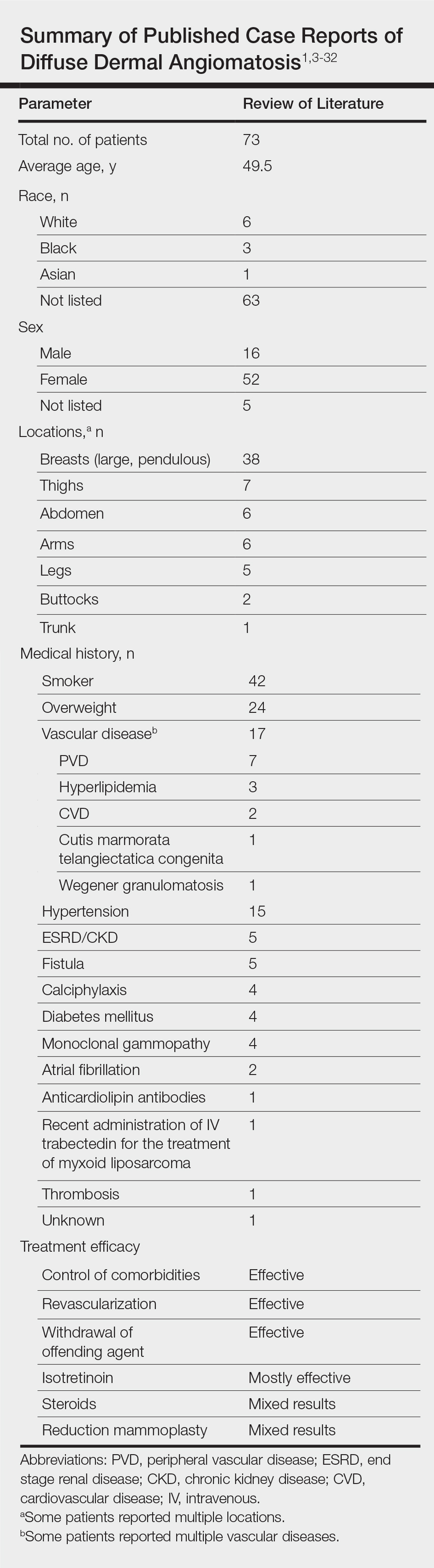
Vascular proliferation in DDA is hypothesized to stem from ischemia or inflammation.5 Peripheral vascular atherosclerosis has been associated with DDA.6 The epidemiology of DDA is not well known because of the rarity of the disease. We performed a more specific review of the literature by limiting the PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to the term diffuse dermal angiomatosis rather than a broader search including all reactive angioendotheliomatoses. Only 31 case reports have been published1,3-32; of them, only adults were affected. Most reported cases were in middle-aged females. A summary of the demographics of DDA is provided in the Table.1,3-32
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of DDA remains unclear. It has been hypothesized that ischemia or inflammation creates local hypoxia, leading to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor with subsequent endothelial proliferation and neovascularization.5 Rongioletti and Robora2 supported this hypothesis, proposing that occlusion or inflammation of the vasculature creates microthrombi and thus hypoxia. Afterward, histiocytes are recruited to reabsorb the microthrombi while hyperplasia of endothelial cells and pericytes ensues.7 Complete resolution of skin lesions following revascularization provides support for this theory.8
Etiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare complication of ischemia that may be secondary to atherosclerosis, arteriovenous fistula, or macromastia.9-11 In DDA of the breasts, ulcerations of fatty tissue occur due to trauma in these patients who have large pendulous breasts, causing angiogenesis resembling DDA histologically.2 One case of DDA was reported secondary to relative ischemia from cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita,12 whereas another case highlighted Wegener granulomatosis as the cause of ischemia.7 There also have been reported cases associated with calciphylaxis and anticardiolipin antibiodies.13 In general, any medical condition that can lead to ischemia can cause DDA. Comorbid conditions for DDA include cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and most often severe peripheral vascular disease. Many patients also have a history of smoking.14 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis rarely presents without underlying comorbidity, with only 1 case report of unknown cause (Table).
Presentation, Histopathology, and Differential Diagnosis
Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis disorders present the same clinically, with multiple erythematous to violaceous purpuric patches and plaques that can progress to necrosis and ulceration. Lesions are widely distributed but are predisposed to the upper and lower extremities.2 The differential diagnosis of DDA includes CREA, acroangiodermatitis (pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma), or vascular malignancies such as Kaposi sarcoma and low-grade angiosarcoma.7
In DDA, lesions may be painful and sometimes have a central ulceration.15 They often are associated with notable peripheral vascular atherosclerotic disease and are mainly found on the lower extremities.12,16 Histologically, DDA presents as a diffuse proliferation of endothelial cells between collagen bundles. The endothelial cells are distributed throughout the papillary and reticular dermis and develop into vascular lumina.17 Furthermore, the proliferating endothelial cells are spindle shaped and contain vacuolated cytoplasm.14
Acroangiodermatitis, or pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma, presents as slow-growing, erythematous to violaceous, brown, or dusky macules, papules, or plaques of the legs.14 Histologically, acroangiodermatitis presents with relatively less proliferation of endothelial cells found intravascularly rather than extravascularly, as in DDA, forming new thick-walled vessels in a lobular pattern in the papillary dermis.14
Vascular malignancies, such as Kaposi sarcoma and angiosarcoma, may present similarly to DDA. Kaposi sarcoma, for example, presents as erythematous to violaceous patches, plaques, or nodules found mostly on the extremities.7 Histologically, spindle cells and vascular structures also are found but in a clefting pattern representative of Kaposi sarcoma (so-called vascular slits).7 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis and vascular malignancies can further be distinguished based on atypia of the proliferations and staining for HHV-8.7,14 Lastly, DDA differs from vascular tumors in that vascular tumors are reactive to locations of occluded vessels, with vascular proliferation ceasing once the underlying cause of hypoxia is removed.2
Treatment
There is no standard treatment of DDA.7 Treatment of the underlying cause of ischemia is the primary goal, which will cause the DDA to resolve in most cases. Stenting, removal of an arteriovenous fistula, or other forms of revascularization may be warranted.1,5,6,10,17,29,30
Reported medical therapies for DDA include systemic or topical corticosteroids used for their antiangiogenic properties with varying results.7 Isotretinoin also has been used, which has been found to be effective in several cases of DDA of the breast, though 1 study reported a subsequent elevated lipid profile, requiring a decrease in dosage.14,15,27,31
Most interestingly, a study by Sanz-Motilva et al16 demonstrated that control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, led to improvement, which highlights the importance of incorporating nonpharmacotherapy rather than initiating treatment solely with medication. The Table summarizes treatments used and their efficacy.
Conclusion
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is associated with medical conditions that predispose an individual to ischemia. Although rare, DDA can present as painful and visibly disturbing lesions that can affect the daily life of afflicted patients. By reporting the few cases that do arise and reviewing prior cases and their treatments, physicians can consider DDA within the differential diagnosis and identify which treatment is most efficient for a given patient. For all DDA patients, strict control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, should be incorporated into the treatment plan. When DDA affects the breasts, isotretinoin appears to provide the best relief. Otherwise, treatment of the underlying cause, revascularization, withdrawal of the offending agent, or steroids seem to be the best treatment options.
- Krell JM, Sanchez RL, Solomon AR. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive cutaneous angioendotheliomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:363-370.
- Rongioletti F, Robora A. Cutaneous reactive angiomatoses: patterns and classification of reactive vascular proliferation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:887-896.
- Crickx E, Saussine A, Vignon-Pennamen MD, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with severe atherosclerosis: two cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:521-524.
- Reusche R, Winocour S, Degnim A, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: a series of 22 cases from a single institution. Gland Surg. 2015;4:554-560.
- Sriphojanart T, Vachiramon V. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clue to the diagnosis of atherosclerotic vascular disease. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:100-106.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Nousari HC, Ketabchi N, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with atherosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:257-259.
- Bassi A, Arunachalam M, Maio V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis in a patient with an iatrogenic arterio-venous fistula and Wegener’s granulomatosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:93-94.
- Ormerod E, Miller K, Kennedy C. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a contributory factor to ulceration in a patient with renal transplant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:48-51.
- Kim S, Elenitsas R, James WD. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with peripheral vascular atherosclerosis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:456-458.
- Requena L, Fariña MC, Renedo G, et al. Intravascular and diffuse dermal reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to iatrogenic arteriovenous fistulas. J Cutan Pathol. 1999;26:159-164.
- Villa MT, White LE, Petronic-Rosic V, et al. The treatment of diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast with reduction mammoplasty. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:693-694.
- Halbesleben JJ, Cleveland MG, Stone MS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis arising in cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1311-1313.
- Ferreli C, Atzori L, Pinna AL, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clinical mimicker of vasculitis associated with calciphylaxis and monoclonal gammopathy. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2015;150:115-121.
- Yang H, Ahmed I, Mathew V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:343-347.
- Steele KT, Sullivan BJ, Wanat KA, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis in a patient with end-stage renal disease.J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:829-832.
- Sanz-Motilva V, Martorell-Calatayud A, Rongioletti F, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinical and histopathological features. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:445-449.
- Kirkland CR, Hawayek LH, Mutasim DF. Atherosclerosis-induced diffuse dermal angiomatosis with fatal outcome. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:684-685.
- Sommer S, Merchant WJ, Wilson CL. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis due to an iatrogenic arteriovenous fistula. Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:251-252.
- Corti MA, Rongioletti F, Borradori L, et al. Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis with combined histological pattern mimicking a cellulitis. Dermatology. 2013;227:226-230.
- Tollefson MM, McEvoy MT, Torgerson RR, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinicopathologic study of 5 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1212-1217.
- Walton K, Liggett J. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB49.
- Mayor-Ibarguren A, Gómez-Fernández C, Beato-Merino MJ, et al. Diffuse reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to the administration of trabectedin and pegfilgrastim. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:581-584.
- Lora V, Cota C, Cerroni L. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the abdomen. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:350-352.
- Pichardo RO, Lu D, Sangueza OP, et al. What is your diagnosis? diffuse dermal angiomatosis secondary to anticardiolipin antibodies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:502.
- Kutzner H, Requena L, Mentzel T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Hautarzt. 2002;53:808-812.
- McLaughlin ER, Morris R, Weiss SW, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: response to isotretinoin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:462-465.
- Prinz Vavricka BM, Barry C, Victor T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:653-657.
- Müller CS, Wagner A, Pföhler C, et al. Cup-shaped painful ulcer of abdominal wall. Hautarzt. 2008;59:656-658.
- Draper BK, Boyd AS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:646-648.
- Adams BJ, Goldberg S, Massey HD, et al. A cause of unbearably painful breast, diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Gland Surg. 2012;1. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2012.07.02.
- Quatresooz P, Fumal I, Willemaers V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a previously undescribed pattern of immunoglobulin and complement deposits in two cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:150-154.
- Morimoto K, Ioka H, Asada H, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42:381-383.
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis (DDA) is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder that was originally thought to be a variant of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis (CREA) but is now considered to be on the spectrum of CREA. This article will focus on DDA and review the literature of prior case reports with brief descriptions of the differential diagnosis.
Case Report
A 43-year-old Haitian man presented to the clinic with a lesion on the left buttock that had developed over the last 6 years. The patient stated the lesion had been enlarging over the last several months. Upon examination, there was a large (15-cm diameter), indurated, hyperpigmented plaque covering the left buttock (Figure 1). The patient reported no medical or contributory family history. Upon review of systems, he described a burning sensation sometimes in the area of the lesion that would develop randomly throughout the year.

Three biopsies were performed, which revealed a collection of slightly dilated blood vessels with normal-appearing endothelial cells occupying the mid dermis and deep dermis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical stains with antibodies were directed against human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD31, CD34, the cell surface glycoprotein podoplanin, Ki-67, and smooth muscle actin antigens, with appropriate controls. The vessel walls were positive for CD31, CD34, and smooth muscle actin, and negative for HHV-8 and podoplanin; Ki-67 was not increased. These histologic findings were consistent with a diagnosis of DDA. A detailed history was taken. The cause of DDA in our patient was uncertain.

Comment
Classification and Epidemiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder first described by Krell et al1 in 1994. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is benign and is classified in the group of cutaneous reactive angiomatoses,2 which are benign vascular disorders marked by intravascular and extravascular hyperplasia of endothelial cells that may or may not include pericytes.2 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis was originally described as a variant of CREA, which is characterized by hyperplasia of endothelial dermal cells and intravascular proliferation.3 However, DDA has more recently been identified as a distinct disorder on the spectrum of CREA rather than as a variant of CREA.2 Given the recent reclassification, not all physicians make this distinction. However, as more case reports of DDA are published, physicians continue to support this change.4 Nevertheless, DDA has been an established disorder since 1994.1
Vascular proliferation in DDA is hypothesized to stem from ischemia or inflammation.5 Peripheral vascular atherosclerosis has been associated with DDA.6 The epidemiology of DDA is not well known because of the rarity of the disease. We performed a more specific review of the literature by limiting the PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to the term diffuse dermal angiomatosis rather than a broader search including all reactive angioendotheliomatoses. Only 31 case reports have been published1,3-32; of them, only adults were affected. Most reported cases were in middle-aged females. A summary of the demographics of DDA is provided in the Table.1,3-32

Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of DDA remains unclear. It has been hypothesized that ischemia or inflammation creates local hypoxia, leading to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor with subsequent endothelial proliferation and neovascularization.5 Rongioletti and Robora2 supported this hypothesis, proposing that occlusion or inflammation of the vasculature creates microthrombi and thus hypoxia. Afterward, histiocytes are recruited to reabsorb the microthrombi while hyperplasia of endothelial cells and pericytes ensues.7 Complete resolution of skin lesions following revascularization provides support for this theory.8
Etiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare complication of ischemia that may be secondary to atherosclerosis, arteriovenous fistula, or macromastia.9-11 In DDA of the breasts, ulcerations of fatty tissue occur due to trauma in these patients who have large pendulous breasts, causing angiogenesis resembling DDA histologically.2 One case of DDA was reported secondary to relative ischemia from cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita,12 whereas another case highlighted Wegener granulomatosis as the cause of ischemia.7 There also have been reported cases associated with calciphylaxis and anticardiolipin antibiodies.13 In general, any medical condition that can lead to ischemia can cause DDA. Comorbid conditions for DDA include cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and most often severe peripheral vascular disease. Many patients also have a history of smoking.14 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis rarely presents without underlying comorbidity, with only 1 case report of unknown cause (Table).
Presentation, Histopathology, and Differential Diagnosis
Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis disorders present the same clinically, with multiple erythematous to violaceous purpuric patches and plaques that can progress to necrosis and ulceration. Lesions are widely distributed but are predisposed to the upper and lower extremities.2 The differential diagnosis of DDA includes CREA, acroangiodermatitis (pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma), or vascular malignancies such as Kaposi sarcoma and low-grade angiosarcoma.7
In DDA, lesions may be painful and sometimes have a central ulceration.15 They often are associated with notable peripheral vascular atherosclerotic disease and are mainly found on the lower extremities.12,16 Histologically, DDA presents as a diffuse proliferation of endothelial cells between collagen bundles. The endothelial cells are distributed throughout the papillary and reticular dermis and develop into vascular lumina.17 Furthermore, the proliferating endothelial cells are spindle shaped and contain vacuolated cytoplasm.14
Acroangiodermatitis, or pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma, presents as slow-growing, erythematous to violaceous, brown, or dusky macules, papules, or plaques of the legs.14 Histologically, acroangiodermatitis presents with relatively less proliferation of endothelial cells found intravascularly rather than extravascularly, as in DDA, forming new thick-walled vessels in a lobular pattern in the papillary dermis.14
Vascular malignancies, such as Kaposi sarcoma and angiosarcoma, may present similarly to DDA. Kaposi sarcoma, for example, presents as erythematous to violaceous patches, plaques, or nodules found mostly on the extremities.7 Histologically, spindle cells and vascular structures also are found but in a clefting pattern representative of Kaposi sarcoma (so-called vascular slits).7 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis and vascular malignancies can further be distinguished based on atypia of the proliferations and staining for HHV-8.7,14 Lastly, DDA differs from vascular tumors in that vascular tumors are reactive to locations of occluded vessels, with vascular proliferation ceasing once the underlying cause of hypoxia is removed.2
Treatment
There is no standard treatment of DDA.7 Treatment of the underlying cause of ischemia is the primary goal, which will cause the DDA to resolve in most cases. Stenting, removal of an arteriovenous fistula, or other forms of revascularization may be warranted.1,5,6,10,17,29,30
Reported medical therapies for DDA include systemic or topical corticosteroids used for their antiangiogenic properties with varying results.7 Isotretinoin also has been used, which has been found to be effective in several cases of DDA of the breast, though 1 study reported a subsequent elevated lipid profile, requiring a decrease in dosage.14,15,27,31
Most interestingly, a study by Sanz-Motilva et al16 demonstrated that control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, led to improvement, which highlights the importance of incorporating nonpharmacotherapy rather than initiating treatment solely with medication. The Table summarizes treatments used and their efficacy.
Conclusion
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is associated with medical conditions that predispose an individual to ischemia. Although rare, DDA can present as painful and visibly disturbing lesions that can affect the daily life of afflicted patients. By reporting the few cases that do arise and reviewing prior cases and their treatments, physicians can consider DDA within the differential diagnosis and identify which treatment is most efficient for a given patient. For all DDA patients, strict control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, should be incorporated into the treatment plan. When DDA affects the breasts, isotretinoin appears to provide the best relief. Otherwise, treatment of the underlying cause, revascularization, withdrawal of the offending agent, or steroids seem to be the best treatment options.
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis (DDA) is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder that was originally thought to be a variant of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis (CREA) but is now considered to be on the spectrum of CREA. This article will focus on DDA and review the literature of prior case reports with brief descriptions of the differential diagnosis.
Case Report
A 43-year-old Haitian man presented to the clinic with a lesion on the left buttock that had developed over the last 6 years. The patient stated the lesion had been enlarging over the last several months. Upon examination, there was a large (15-cm diameter), indurated, hyperpigmented plaque covering the left buttock (Figure 1). The patient reported no medical or contributory family history. Upon review of systems, he described a burning sensation sometimes in the area of the lesion that would develop randomly throughout the year.

Three biopsies were performed, which revealed a collection of slightly dilated blood vessels with normal-appearing endothelial cells occupying the mid dermis and deep dermis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical stains with antibodies were directed against human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD31, CD34, the cell surface glycoprotein podoplanin, Ki-67, and smooth muscle actin antigens, with appropriate controls. The vessel walls were positive for CD31, CD34, and smooth muscle actin, and negative for HHV-8 and podoplanin; Ki-67 was not increased. These histologic findings were consistent with a diagnosis of DDA. A detailed history was taken. The cause of DDA in our patient was uncertain.

Comment
Classification and Epidemiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare acquired, cutaneous, reactive, vascular disorder first described by Krell et al1 in 1994. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is benign and is classified in the group of cutaneous reactive angiomatoses,2 which are benign vascular disorders marked by intravascular and extravascular hyperplasia of endothelial cells that may or may not include pericytes.2 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis was originally described as a variant of CREA, which is characterized by hyperplasia of endothelial dermal cells and intravascular proliferation.3 However, DDA has more recently been identified as a distinct disorder on the spectrum of CREA rather than as a variant of CREA.2 Given the recent reclassification, not all physicians make this distinction. However, as more case reports of DDA are published, physicians continue to support this change.4 Nevertheless, DDA has been an established disorder since 1994.1
Vascular proliferation in DDA is hypothesized to stem from ischemia or inflammation.5 Peripheral vascular atherosclerosis has been associated with DDA.6 The epidemiology of DDA is not well known because of the rarity of the disease. We performed a more specific review of the literature by limiting the PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to the term diffuse dermal angiomatosis rather than a broader search including all reactive angioendotheliomatoses. Only 31 case reports have been published1,3-32; of them, only adults were affected. Most reported cases were in middle-aged females. A summary of the demographics of DDA is provided in the Table.1,3-32

Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of DDA remains unclear. It has been hypothesized that ischemia or inflammation creates local hypoxia, leading to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor with subsequent endothelial proliferation and neovascularization.5 Rongioletti and Robora2 supported this hypothesis, proposing that occlusion or inflammation of the vasculature creates microthrombi and thus hypoxia. Afterward, histiocytes are recruited to reabsorb the microthrombi while hyperplasia of endothelial cells and pericytes ensues.7 Complete resolution of skin lesions following revascularization provides support for this theory.8
Etiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare complication of ischemia that may be secondary to atherosclerosis, arteriovenous fistula, or macromastia.9-11 In DDA of the breasts, ulcerations of fatty tissue occur due to trauma in these patients who have large pendulous breasts, causing angiogenesis resembling DDA histologically.2 One case of DDA was reported secondary to relative ischemia from cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita,12 whereas another case highlighted Wegener granulomatosis as the cause of ischemia.7 There also have been reported cases associated with calciphylaxis and anticardiolipin antibiodies.13 In general, any medical condition that can lead to ischemia can cause DDA. Comorbid conditions for DDA include cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and most often severe peripheral vascular disease. Many patients also have a history of smoking.14 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis rarely presents without underlying comorbidity, with only 1 case report of unknown cause (Table).
Presentation, Histopathology, and Differential Diagnosis
Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis disorders present the same clinically, with multiple erythematous to violaceous purpuric patches and plaques that can progress to necrosis and ulceration. Lesions are widely distributed but are predisposed to the upper and lower extremities.2 The differential diagnosis of DDA includes CREA, acroangiodermatitis (pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma), or vascular malignancies such as Kaposi sarcoma and low-grade angiosarcoma.7
In DDA, lesions may be painful and sometimes have a central ulceration.15 They often are associated with notable peripheral vascular atherosclerotic disease and are mainly found on the lower extremities.12,16 Histologically, DDA presents as a diffuse proliferation of endothelial cells between collagen bundles. The endothelial cells are distributed throughout the papillary and reticular dermis and develop into vascular lumina.17 Furthermore, the proliferating endothelial cells are spindle shaped and contain vacuolated cytoplasm.14
Acroangiodermatitis, or pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma, presents as slow-growing, erythematous to violaceous, brown, or dusky macules, papules, or plaques of the legs.14 Histologically, acroangiodermatitis presents with relatively less proliferation of endothelial cells found intravascularly rather than extravascularly, as in DDA, forming new thick-walled vessels in a lobular pattern in the papillary dermis.14
Vascular malignancies, such as Kaposi sarcoma and angiosarcoma, may present similarly to DDA. Kaposi sarcoma, for example, presents as erythematous to violaceous patches, plaques, or nodules found mostly on the extremities.7 Histologically, spindle cells and vascular structures also are found but in a clefting pattern representative of Kaposi sarcoma (so-called vascular slits).7 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis and vascular malignancies can further be distinguished based on atypia of the proliferations and staining for HHV-8.7,14 Lastly, DDA differs from vascular tumors in that vascular tumors are reactive to locations of occluded vessels, with vascular proliferation ceasing once the underlying cause of hypoxia is removed.2
Treatment
There is no standard treatment of DDA.7 Treatment of the underlying cause of ischemia is the primary goal, which will cause the DDA to resolve in most cases. Stenting, removal of an arteriovenous fistula, or other forms of revascularization may be warranted.1,5,6,10,17,29,30
Reported medical therapies for DDA include systemic or topical corticosteroids used for their antiangiogenic properties with varying results.7 Isotretinoin also has been used, which has been found to be effective in several cases of DDA of the breast, though 1 study reported a subsequent elevated lipid profile, requiring a decrease in dosage.14,15,27,31
Most interestingly, a study by Sanz-Motilva et al16 demonstrated that control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, led to improvement, which highlights the importance of incorporating nonpharmacotherapy rather than initiating treatment solely with medication. The Table summarizes treatments used and their efficacy.
Conclusion
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is associated with medical conditions that predispose an individual to ischemia. Although rare, DDA can present as painful and visibly disturbing lesions that can affect the daily life of afflicted patients. By reporting the few cases that do arise and reviewing prior cases and their treatments, physicians can consider DDA within the differential diagnosis and identify which treatment is most efficient for a given patient. For all DDA patients, strict control of comorbidities, especially smoking cessation, should be incorporated into the treatment plan. When DDA affects the breasts, isotretinoin appears to provide the best relief. Otherwise, treatment of the underlying cause, revascularization, withdrawal of the offending agent, or steroids seem to be the best treatment options.
- Krell JM, Sanchez RL, Solomon AR. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive cutaneous angioendotheliomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:363-370.
- Rongioletti F, Robora A. Cutaneous reactive angiomatoses: patterns and classification of reactive vascular proliferation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:887-896.
- Crickx E, Saussine A, Vignon-Pennamen MD, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with severe atherosclerosis: two cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:521-524.
- Reusche R, Winocour S, Degnim A, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: a series of 22 cases from a single institution. Gland Surg. 2015;4:554-560.
- Sriphojanart T, Vachiramon V. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clue to the diagnosis of atherosclerotic vascular disease. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:100-106.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Nousari HC, Ketabchi N, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with atherosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:257-259.
- Bassi A, Arunachalam M, Maio V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis in a patient with an iatrogenic arterio-venous fistula and Wegener’s granulomatosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:93-94.
- Ormerod E, Miller K, Kennedy C. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a contributory factor to ulceration in a patient with renal transplant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:48-51.
- Kim S, Elenitsas R, James WD. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with peripheral vascular atherosclerosis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:456-458.
- Requena L, Fariña MC, Renedo G, et al. Intravascular and diffuse dermal reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to iatrogenic arteriovenous fistulas. J Cutan Pathol. 1999;26:159-164.
- Villa MT, White LE, Petronic-Rosic V, et al. The treatment of diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast with reduction mammoplasty. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:693-694.
- Halbesleben JJ, Cleveland MG, Stone MS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis arising in cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1311-1313.
- Ferreli C, Atzori L, Pinna AL, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clinical mimicker of vasculitis associated with calciphylaxis and monoclonal gammopathy. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2015;150:115-121.
- Yang H, Ahmed I, Mathew V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:343-347.
- Steele KT, Sullivan BJ, Wanat KA, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis in a patient with end-stage renal disease.J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:829-832.
- Sanz-Motilva V, Martorell-Calatayud A, Rongioletti F, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinical and histopathological features. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:445-449.
- Kirkland CR, Hawayek LH, Mutasim DF. Atherosclerosis-induced diffuse dermal angiomatosis with fatal outcome. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:684-685.
- Sommer S, Merchant WJ, Wilson CL. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis due to an iatrogenic arteriovenous fistula. Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:251-252.
- Corti MA, Rongioletti F, Borradori L, et al. Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis with combined histological pattern mimicking a cellulitis. Dermatology. 2013;227:226-230.
- Tollefson MM, McEvoy MT, Torgerson RR, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinicopathologic study of 5 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1212-1217.
- Walton K, Liggett J. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB49.
- Mayor-Ibarguren A, Gómez-Fernández C, Beato-Merino MJ, et al. Diffuse reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to the administration of trabectedin and pegfilgrastim. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:581-584.
- Lora V, Cota C, Cerroni L. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the abdomen. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:350-352.
- Pichardo RO, Lu D, Sangueza OP, et al. What is your diagnosis? diffuse dermal angiomatosis secondary to anticardiolipin antibodies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:502.
- Kutzner H, Requena L, Mentzel T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Hautarzt. 2002;53:808-812.
- McLaughlin ER, Morris R, Weiss SW, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: response to isotretinoin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:462-465.
- Prinz Vavricka BM, Barry C, Victor T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:653-657.
- Müller CS, Wagner A, Pföhler C, et al. Cup-shaped painful ulcer of abdominal wall. Hautarzt. 2008;59:656-658.
- Draper BK, Boyd AS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:646-648.
- Adams BJ, Goldberg S, Massey HD, et al. A cause of unbearably painful breast, diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Gland Surg. 2012;1. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2012.07.02.
- Quatresooz P, Fumal I, Willemaers V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a previously undescribed pattern of immunoglobulin and complement deposits in two cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:150-154.
- Morimoto K, Ioka H, Asada H, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42:381-383.
- Krell JM, Sanchez RL, Solomon AR. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive cutaneous angioendotheliomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:363-370.
- Rongioletti F, Robora A. Cutaneous reactive angiomatoses: patterns and classification of reactive vascular proliferation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:887-896.
- Crickx E, Saussine A, Vignon-Pennamen MD, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with severe atherosclerosis: two cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:521-524.
- Reusche R, Winocour S, Degnim A, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: a series of 22 cases from a single institution. Gland Surg. 2015;4:554-560.
- Sriphojanart T, Vachiramon V. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clue to the diagnosis of atherosclerotic vascular disease. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:100-106.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Nousari HC, Ketabchi N, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with atherosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:257-259.
- Bassi A, Arunachalam M, Maio V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis in a patient with an iatrogenic arterio-venous fistula and Wegener’s granulomatosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2013;93:93-94.
- Ormerod E, Miller K, Kennedy C. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a contributory factor to ulceration in a patient with renal transplant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:48-51.
- Kim S, Elenitsas R, James WD. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis associated with peripheral vascular atherosclerosis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:456-458.
- Requena L, Fariña MC, Renedo G, et al. Intravascular and diffuse dermal reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to iatrogenic arteriovenous fistulas. J Cutan Pathol. 1999;26:159-164.
- Villa MT, White LE, Petronic-Rosic V, et al. The treatment of diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast with reduction mammoplasty. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:693-694.
- Halbesleben JJ, Cleveland MG, Stone MS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis arising in cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1311-1313.
- Ferreli C, Atzori L, Pinna AL, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a clinical mimicker of vasculitis associated with calciphylaxis and monoclonal gammopathy. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2015;150:115-121.
- Yang H, Ahmed I, Mathew V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:343-347.
- Steele KT, Sullivan BJ, Wanat KA, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis in a patient with end-stage renal disease.J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:829-832.
- Sanz-Motilva V, Martorell-Calatayud A, Rongioletti F, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinical and histopathological features. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:445-449.
- Kirkland CR, Hawayek LH, Mutasim DF. Atherosclerosis-induced diffuse dermal angiomatosis with fatal outcome. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:684-685.
- Sommer S, Merchant WJ, Wilson CL. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis due to an iatrogenic arteriovenous fistula. Acta Derm Venereol. 2004;84:251-252.
- Corti MA, Rongioletti F, Borradori L, et al. Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis with combined histological pattern mimicking a cellulitis. Dermatology. 2013;227:226-230.
- Tollefson MM, McEvoy MT, Torgerson RR, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: clinicopathologic study of 5 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1212-1217.
- Walton K, Liggett J. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB49.
- Mayor-Ibarguren A, Gómez-Fernández C, Beato-Merino MJ, et al. Diffuse reactive angioendotheliomatosis secondary to the administration of trabectedin and pegfilgrastim. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:581-584.
- Lora V, Cota C, Cerroni L. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the abdomen. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:350-352.
- Pichardo RO, Lu D, Sangueza OP, et al. What is your diagnosis? diffuse dermal angiomatosis secondary to anticardiolipin antibodies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:502.
- Kutzner H, Requena L, Mentzel T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Hautarzt. 2002;53:808-812.
- McLaughlin ER, Morris R, Weiss SW, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis of the breast: response to isotretinoin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:462-465.
- Prinz Vavricka BM, Barry C, Victor T, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis associated with calciphylaxis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:653-657.
- Müller CS, Wagner A, Pföhler C, et al. Cup-shaped painful ulcer of abdominal wall. Hautarzt. 2008;59:656-658.
- Draper BK, Boyd AS. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:646-648.
- Adams BJ, Goldberg S, Massey HD, et al. A cause of unbearably painful breast, diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Gland Surg. 2012;1. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2012.07.02.
- Quatresooz P, Fumal I, Willemaers V, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis: a previously undescribed pattern of immunoglobulin and complement deposits in two cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:150-154.
- Morimoto K, Ioka H, Asada H, et al. Diffuse dermal angiomatosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42:381-383.
Practice Points
- Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is commonly reported in patients with hypoxic comorbidities such as smoking or vascular disease as well as in women with large pendulous breasts.
- Effective treatments include control of comorbidities, revascularization, withdrawal of the offending agent, steroids, and isotretinoin.
Solitary Morphea Profunda Following Trauma Sustained in an Automobile Accident
Case Report
A 50-year-old white woman presented to our clinic for evaluation of what she described as a “very hard red line” on the right upper arm. The lesion had developed suddenly overnight. Several months prior to presentation the patient sustained trauma to the same area in a car accident and she thought the lesion might be related to the resulting nerve damage. Initially she presented to her primary care physician who used ultrasonography of the area to rule out muscle or bone involvement. The patient presented to our dermatology clinic 2 months later with an 18×4-cm, brownish, rectangular, sclerotic, bound-down, hypertrophic plaque that started on the right mid forearm and extended to the right shoulder (Figure 1). Her medical history was notable for high blood pressure, which was controlled with valsartan.
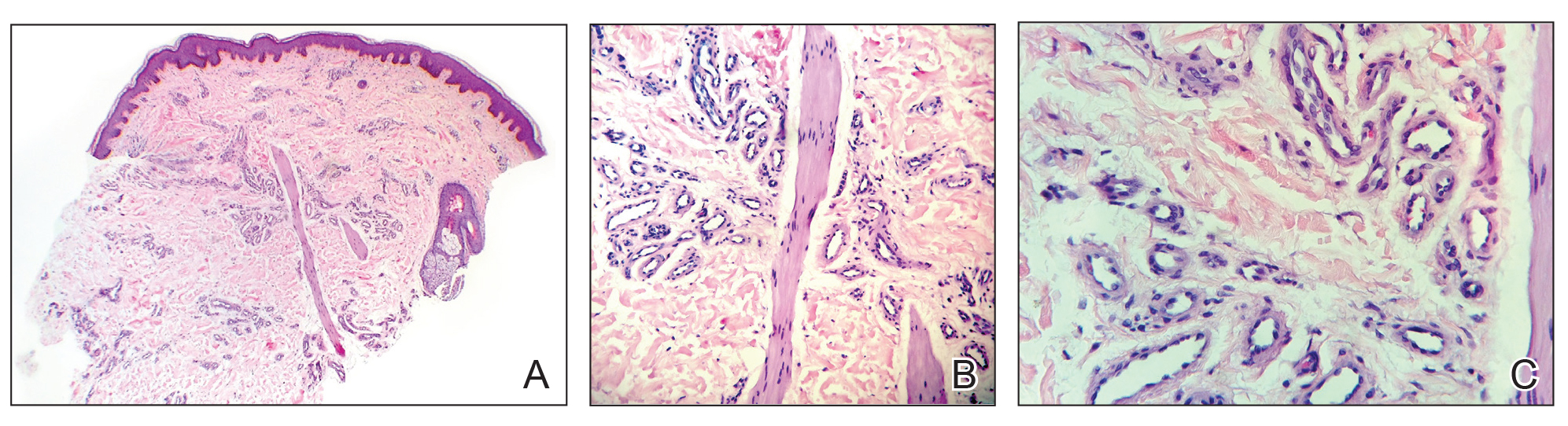
A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed a well-developed, well-nourished woman. Examination of the right arm revealed no motion restriction (muscle strength, 5/5) and no pain; however, she described a burning sensation at the site of the lesion. She reported no allergies. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and laboratory tests were ordered including an antinuclear antibody (ANA) test with reflex, double-stranded DNA test, DNA antitopoisomerase antibodies test, and Lyme titers (IgM and IgG). Initially, the patient was treated with calcipotriene 0.005%–betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% ointment twice daily; she also was treated empirically for Lyme disease with doxycycline 50 mg twice daily. All laboratory tests were within reference range, and a punch biopsy revealed markedly thickened fibrous septa within the subcutaneous fat. At the edge of the septa there were nodular aggregates of lymphocytes. Due to clinical presentation, laboratory data, and histopathology, solitary morphea profunda (SMP) was diagnosed.
Following histopathologic examination (Figure 2), the patient was instructed to continue treatment with calcipotriene–betamethasone dipropionate as well as doxycycline. A trial of prednisone and/or hydroxychloroquine also was considered pending her response to the initial treatment. At approximately 1-month follow-up, remarkable improvement of the lesion was noted.
Comment
|
There is limited literature available about the diagnosis and treatment of SMP. Our case prompted us to further examine the data to emphasize the necessity of greater research surrounding SMP.
Classification of SMP
Morphea is a localized form of scleroderma, an inflammatory disease that primarily affects the dermis but can extend down to the bone and also can limit motion. There are several types of morphea that are classified according to the extent, depth, and distribution of the lesions, including plaque, generalized, bullous, linear (including morphea en coup de sabre), guttate, nodular, and deep morphea.1,2 Other subtypes have been described including subcutaneous morphea, eosinophilic fasciitis (EF), pansclerotic morphea, and morphea profunda.3 Linear and deep morphea are characterized by involvement of the deep dermis, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and/or superficial muscle.2,4
In 1981, Su and Person5 first described morphea profunda (MP). In their study, 22 of 23 patients presented with generalized MP. One patient developed a single lesion,5 which ultimately was classified as SMP by Whittaker et al6 in 1989.
Epidemiology
Morphea profunda occurs more frequently in females than in males, with sclerosis manifesting over a period of several months.7 In 2004, Azad et al4 suggested that only 9 cases of SMP had been reported in the literature. Although there is insignificant data to determine the epidemiology of SMP, the authors concluded that it most commonly affects middle-aged individuals with equal sex distribution.4 The single plaque in patients with SMP most commonly presents on the shoulder, back, or neck or in the paraspinal area.
Etiology
Because of the limited amount of literature on MP, a definitive etiology is unknown, but investigators have cited many possible causes. Genetic, autoimmune, hormonal, traumatic,8 vaccination,2,8 radiation,9 viral, neurogenic, and vascular factors all have been implicated,10 as well as infectious agents such as Borrelia burgdorferi in the United States,11,12Borrelia afzelii in Europe,2 and Borrelia garinii in Japan.2 Because our patient experienced a traumatic episode several months prior to presentation, it is important to investigate trauma as a likely etiology. Furthermore, traumatic events have been reported in 23% of children with linear morphea.13
Diagnostic Studies
Morphea profunda is diagnosed clinically and skin biopsy can be used for confirmation. Biopsy requires deep excision down to the muscle, which can aid in determining if the fascia is incorporated. Elevated levels of IgG and IgM have been detected in deep and linear morphea and are known to correlate with disease activity and the development of joint contractures in linear morphea.2 Serum procollagen type I has been considered by some as a useful indicator of disease severity.14 Elevated serum levels of antifibrillin-1 antibodies also have been demonstrated in patients with localized scleroderma (LS).15 Radiography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used for monitoring and analyzing lesion depth. Furthermore, magnetic resonance imaging can be used to differentiate MP from EF.2
The presence of ANAs in LS is controversial. According to Nguyen et al,2 ANAs are present in approximately 46% to 80% of patients with morphea, with a higher prevalence in patients with generalized, linear, and deep subtypes. However, Savoia et al16 found that patients with morphea typically do not present with ANAs; rather ANAs usually are found in patients with EF.
Pathogenesis
After the inflammatory phase in LS, fibrillar collagen types I and III accumulate, causing dermal fibrosis. The extracellular matrix increases due to the activation of connective tissue growth factor, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), TGF-β receptors, IL-4, and several other cytokines.17 The TGF-β receptors combine with the connective tissue growth factor released by fibroblasts to create an autocrine production loop that causes fibroblast and matrix production.17 As the inflammation progresses to sclerosis, the CD34 count decreases.18
Physical Findings
In patients with MP, lesions manifest as thickened taut skin with deep, solitary, and sclerotic indurated plaques. Clinically, plaques are mildly inflamed, hyperpigmented, symmetric, and somewhat ill defined, and the skin feels thickened and bound to the underlying fascia and muscle. Plaques usually are smooth and shiny, but areas of both dermal and subcutaneous atrophy may be present, particularly in chronic lesions.19 Morphea profunda also can be described as having a cobblestone or pseudocellulite appearance. The groove sign is used to describe a depression along the course of a vein and/or between muscle groups. Both clinical presentations may manifest later in the course of disease.2
Histopathology
Su and Person5 described 3 main characteristics of MP that stand out histopathologically. First, there is thickening and hyalinization of collagen bundles in the deep dermis, subcutis, and fascia that are prominent between the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat. There also are fewer sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Second, MP presents with an increased inflammatory cell infiltrate composed mainly of lymphocytes located around small blood vessels and the interstitium. In some patients, the lymphocytes consist predominantly of collections of plasma cells. Third, MP contains deposits of mucin in deep portions of the dermis with occasional eosinophils and mast cells. The presence of eosinophils allows EF to be a part of this spectrum and to be included as a differential diagnosis.5 Eosinophilic fasciitis has a similar presentation to MP because the fibrosis affects the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and underlying structures.20 Although EF presents with the histopathologic characteristic of fascial fibrosis, a clear distinction between EF and morphea has not been established in the literature. Some authors classify EF as a variant of morphea, whereas others consider it as its own entity. We believe EF is its own entity. Eosinophilic fasciitis can be distinguished from morphea because 60% to 80% of patients with EF have peripheral eosinophilia and 20% to 70% of patients with EF have hypergammaglobulinemia. Additionally, morphea does not present as symmetrically or abruptly as EF.21
Treatment
To date, there is conflicting literature regarding the treatment regimen for MP. There is controversy regarding whether MP responds to corticosteroids.19 Different treatment regimens have been discussed for LS, but there is a lack of reports specifically describing therapies for MP and SMP. Because MP and SMP fall under the umbrella of LS, many investigators have reported using the following treatment regimens for patients with MP and SMP: bosentan,22 D-penicillamine,23 phototherapy,24-26 retinoids,26 oral steroids,27 methotrexate,27-29 vitamin D3 (oral calcitriol),30,31 cyclosporine,32 mycophenolate mofetil,33 and extracorporeal photochemotherapy.34
Falanga and Medsger23 reported 64% (7/11) treatment success with D-penicillamine in patients who exhibited severe LS. Psoralen plus UVA,24 methoxsalen, and UVA1 therapy are widely used in the treatment of LS.25 Kreuter et al25 advocated for phototherapy as the first approach in the management of LS after reporting improvement in all participants in their study (N=64), 2 participants with deep morphea while the rest exhibited other forms of morphea. Ozdemir et al26 proposed that retinoic acid combined with psoralen plus UVA is a good treatment choice for plaque-type LS; however, UVA only has the ability to target the epidermis and dermis, which may not be useful for deep forms of morphea.
Several studies have shown positive results in patients treated with methylprednisolone combined with low-dose methotrexate sodium.27-29 Kreuter et al30 and Elst et al31 proposed that calcitriol is effective in treating LS, whereas Hulshof et al35 indicated that it is not. It should be noted that none of these studies specifically mentioned MP. Martini et al33 demonstrated success with mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of 10 LS patients who were resistant to methotrexate sodium and corticosteroids. Although none of the participants in the study had MP, 2 patients had disabling pansclerotic morphea, 3 had generalized morphea, and 5 had linear scleroderma (morphea en coup de sabre) affecting the limbs (n=2) and face (n=3).33 Because there is no established therapy or consensus for the treatment of MP, we have found success in starting with corticosteroids and then trying alternative therapies.
Prognosis
Morphea has transitioned into systemic scleroderma in a small number of reported cases.10,16,20,36 Therefore, patient follow-up is imperative to consistently identify systemic evolution. Although visceral complications are rare in the setting of LS, associated clinical findings have been reported, including arthralgia, arthritis, contractures, and carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as pulmonary, esophageal, and cardiac abnormalities.7,34
Conclusion
The morphologic features observed in our patient appear to correspond most closely to the type of lesion described by Su and Person5 and Whittaker et al.6 Although our case was clinically difficult to distinguish from linear morphea, the histology suggested SMP over other causes. If our patient’s SMP progressed to the joints, physical therapy would be needed to maintain range of motion and function of the extremities,2 and mandatory long-term follow-up would be required due to the risk for relapse after discontinuation of therapy. Our case highlights the inherent difficulties in the treatment of MP. Due to limited reports of SMP and MP in the literature as well as the conflicting views regarding effective and appropriate treatment options, additional investigation of these conditions and therapeutic options are necessary to further understand this debilitating condition.
1. Peterson LS, Nelson AM, Su WP. Classification of morphea (localized scleroderma). Mayo Clin Proc. 1995;70:1068-1076.
2. Nguyen JV, Werth VP, Fett N. Morphea treatment & management. Medscape Web site. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1065782-treatment. Updated July 21, 2014. Accessed December 16, 2104.
3. Melani L, Cardinali C, Giomi B, et al. Case study: periodic follow-up is necessary in morphea profunda to identify systemic evolution. Skinmed. 2005;4:188-190.
4. Azad J, Dawn G, Shaffrali FC, et al. Does solitary morphoea profunda progress? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:25-27.
5. Su WP, Person JR. Morphea profunda. a new concept and a histopathologic study of 23 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1981;3:251-260.
6. Whittaker SJ, Smith NP, Jones RR. Solitary morphoea profunda. Br J Dermatol. 1989;120:431-440.
7. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
8. Torrelo A, Suárez J, Colmenero I, et al. Deep morphea after vaccination in two young children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:484-487.
9. Kreft B, Wohlrab J, Radant K, et al. Unrecognized radiation-induced localized scleroderma: a cause of postoperative wound-healing disorder [published online ahead of print June 22, 2009]. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e383-e384.
10. Braun-Falco O, Plewig G, Wolff HH, et al, eds. Dermatology. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2002.
11. Prinz JC, Kutasi Z, Weisenseel P, et al. “Borrelia-associated early-onset morphea”: a particular type of scleroderma in childhood and adolescence with high titer antinuclear antibodies? results of a cohort analysis and presentation of three cases [published online ahead of print November 20, 2008]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:248-255.
12. Wojas-Pelc A, Wielowieyska-Szybińska D, Kiełtyka A. Presence of the antinuclear antibodies and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi among patients with morphea en plaque, deep linear scleroderma and atrophoderma Pasini-Pierini [in Polish]. Przegl Lek. 2002;59:898-902.
13. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr, Reichlin M, et al. Linear scleroderma. clinical spectrum, prognosis, and laboratory abnormalities. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104:849-857.
14. Kikuchi K, Sato S, Kadono T, et al. Serum concentration of procollagen type I carboxyterminal propeptide in localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1269-1272.
15. Arnett FC, Tan FK, Uziel Y, et al. Autoantibodies to the extracellular matrix microfibrillar protein, fibrilin 1, in patients with localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:2656-2659.
16. Savoia P, Zaccagna A, Bernengo MG. Guess what? inflammatory disseminated morphea profunda. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:654-656.
17. Igarashi A, Nashiro K, Kikuchi K, et al. Connective tissue growth factor gene expression in tissue sections from localized scleroderma, keloid, and other fibrotic skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:729-733.
18. Gilmour TK, Wilkinson B, Breit SN, et al. Analysis of dendritic cell populations using a revised histological staging of morphoea. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1183-1192.
19. Sayama K, Chen M, Shiraishi S, et al. Morphea profunda. Int J Dermatol. 1991;30:873-875.
20. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
21. Bischoff L, Derk CT. Eosinophilic fasciitis: demographics disease pattern and response to treatment: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:29-35.
22. Roldan R, Morote G, Castro Mdel C, et al. Efficacy of bosentan in treatment of unresponsive cutaneous ulceration in disabling pansclerotic morphea in children. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2538-2540.
23. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr. D-penicillamine in the treatment of localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:609-612.
24. Breuckmann F, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P, et al. UVA/UVA1 phototherapy and PUVA photochemotherapy in connective tissue diseases and related disorders: a research based review. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:11.
25. Kreuter A, Hyun J, Stücker M, et al. A randomized controlled study of low-dose UVA1, medium-dose UVA1, and narrowband UVB phototherapy in the treatment of localized scleroderma [published online ahead of print January 30, 2006]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:440-447.
26. Ozdemir M, Engin B, Toy H, et al. Treatment of plaque-type localized scleroderma with retinoic acid and ultraviolet A plus the photosensitizer psoralen: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:519-521.
27. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, et al. Pulsed high-dose corticosteroids combined with low-dose methotrexate in severe localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:847-852.
28. Kroft EB, Creemers MC, van den Hoogen FH, et al. Effectiveness, side-effects and period of remission after treatment with methotrexate in localized scleroderma and related sclerotic skin diseases: an inception cohort study [published online ahead of print February 4, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:1075-1082.
29. Weibel L, Sampaio MC, Visentin MT, et al. Evaluation of methotrexate and corticosteroids for the treatment of localized scleroderma (morphoea) in children. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1013-1020.
30. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Avermaete A, et al. Combined treatment with calcipotriol ointment and low-dose ultraviolet A1 phototherapy in childhood morphea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2001;18:241-245.
31. Elst EF, Van Suijlekom-Smit LW, Oranje AP. Treatment of linear scleroderma with oral 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 (calcitriol) in seven children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:53-58.
32. Crespo MP, Mas IB, Díaz JM, et al. Rapid response to cyclosporine and maintenance with methotrexate in linear scleroderma in a young girl. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:118-120.
33. Martini G, Ramanan AV, Falcini F, et al. Successful treatment of severe or methotrexate-resistant juvenile localized scleroderma with mycophenolate mofetil [published online ahead of print August 27, 2009]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48:1410-1413.
34. Neustadter JH, Samarin F, Carlson KR, et al. Extracorporeal photochemotherapy for generalized deep morphea. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:127-130.
35. Hulshof MM, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Bergman W, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral calcitriol for the treatment of localized and systemic scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1017-1023.
36. Toledano C, Rabhi S, Kettaneh A, et al. Localized scleroderma: a series of 52 patients [published online ahead of print September 17, 2008]. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:331-336.
Case Report
A 50-year-old white woman presented to our clinic for evaluation of what she described as a “very hard red line” on the right upper arm. The lesion had developed suddenly overnight. Several months prior to presentation the patient sustained trauma to the same area in a car accident and she thought the lesion might be related to the resulting nerve damage. Initially she presented to her primary care physician who used ultrasonography of the area to rule out muscle or bone involvement. The patient presented to our dermatology clinic 2 months later with an 18×4-cm, brownish, rectangular, sclerotic, bound-down, hypertrophic plaque that started on the right mid forearm and extended to the right shoulder (Figure 1). Her medical history was notable for high blood pressure, which was controlled with valsartan.
A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed a well-developed, well-nourished woman. Examination of the right arm revealed no motion restriction (muscle strength, 5/5) and no pain; however, she described a burning sensation at the site of the lesion. She reported no allergies. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and laboratory tests were ordered including an antinuclear antibody (ANA) test with reflex, double-stranded DNA test, DNA antitopoisomerase antibodies test, and Lyme titers (IgM and IgG). Initially, the patient was treated with calcipotriene 0.005%–betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% ointment twice daily; she also was treated empirically for Lyme disease with doxycycline 50 mg twice daily. All laboratory tests were within reference range, and a punch biopsy revealed markedly thickened fibrous septa within the subcutaneous fat. At the edge of the septa there were nodular aggregates of lymphocytes. Due to clinical presentation, laboratory data, and histopathology, solitary morphea profunda (SMP) was diagnosed.
Following histopathologic examination (Figure 2), the patient was instructed to continue treatment with calcipotriene–betamethasone dipropionate as well as doxycycline. A trial of prednisone and/or hydroxychloroquine also was considered pending her response to the initial treatment. At approximately 1-month follow-up, remarkable improvement of the lesion was noted.
Comment
|
There is limited literature available about the diagnosis and treatment of SMP. Our case prompted us to further examine the data to emphasize the necessity of greater research surrounding SMP.
Classification of SMP
Morphea is a localized form of scleroderma, an inflammatory disease that primarily affects the dermis but can extend down to the bone and also can limit motion. There are several types of morphea that are classified according to the extent, depth, and distribution of the lesions, including plaque, generalized, bullous, linear (including morphea en coup de sabre), guttate, nodular, and deep morphea.1,2 Other subtypes have been described including subcutaneous morphea, eosinophilic fasciitis (EF), pansclerotic morphea, and morphea profunda.3 Linear and deep morphea are characterized by involvement of the deep dermis, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and/or superficial muscle.2,4
In 1981, Su and Person5 first described morphea profunda (MP). In their study, 22 of 23 patients presented with generalized MP. One patient developed a single lesion,5 which ultimately was classified as SMP by Whittaker et al6 in 1989.
Epidemiology
Morphea profunda occurs more frequently in females than in males, with sclerosis manifesting over a period of several months.7 In 2004, Azad et al4 suggested that only 9 cases of SMP had been reported in the literature. Although there is insignificant data to determine the epidemiology of SMP, the authors concluded that it most commonly affects middle-aged individuals with equal sex distribution.4 The single plaque in patients with SMP most commonly presents on the shoulder, back, or neck or in the paraspinal area.
Etiology
Because of the limited amount of literature on MP, a definitive etiology is unknown, but investigators have cited many possible causes. Genetic, autoimmune, hormonal, traumatic,8 vaccination,2,8 radiation,9 viral, neurogenic, and vascular factors all have been implicated,10 as well as infectious agents such as Borrelia burgdorferi in the United States,11,12Borrelia afzelii in Europe,2 and Borrelia garinii in Japan.2 Because our patient experienced a traumatic episode several months prior to presentation, it is important to investigate trauma as a likely etiology. Furthermore, traumatic events have been reported in 23% of children with linear morphea.13
Diagnostic Studies
Morphea profunda is diagnosed clinically and skin biopsy can be used for confirmation. Biopsy requires deep excision down to the muscle, which can aid in determining if the fascia is incorporated. Elevated levels of IgG and IgM have been detected in deep and linear morphea and are known to correlate with disease activity and the development of joint contractures in linear morphea.2 Serum procollagen type I has been considered by some as a useful indicator of disease severity.14 Elevated serum levels of antifibrillin-1 antibodies also have been demonstrated in patients with localized scleroderma (LS).15 Radiography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used for monitoring and analyzing lesion depth. Furthermore, magnetic resonance imaging can be used to differentiate MP from EF.2
The presence of ANAs in LS is controversial. According to Nguyen et al,2 ANAs are present in approximately 46% to 80% of patients with morphea, with a higher prevalence in patients with generalized, linear, and deep subtypes. However, Savoia et al16 found that patients with morphea typically do not present with ANAs; rather ANAs usually are found in patients with EF.
Pathogenesis
After the inflammatory phase in LS, fibrillar collagen types I and III accumulate, causing dermal fibrosis. The extracellular matrix increases due to the activation of connective tissue growth factor, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), TGF-β receptors, IL-4, and several other cytokines.17 The TGF-β receptors combine with the connective tissue growth factor released by fibroblasts to create an autocrine production loop that causes fibroblast and matrix production.17 As the inflammation progresses to sclerosis, the CD34 count decreases.18
Physical Findings
In patients with MP, lesions manifest as thickened taut skin with deep, solitary, and sclerotic indurated plaques. Clinically, plaques are mildly inflamed, hyperpigmented, symmetric, and somewhat ill defined, and the skin feels thickened and bound to the underlying fascia and muscle. Plaques usually are smooth and shiny, but areas of both dermal and subcutaneous atrophy may be present, particularly in chronic lesions.19 Morphea profunda also can be described as having a cobblestone or pseudocellulite appearance. The groove sign is used to describe a depression along the course of a vein and/or between muscle groups. Both clinical presentations may manifest later in the course of disease.2
Histopathology
Su and Person5 described 3 main characteristics of MP that stand out histopathologically. First, there is thickening and hyalinization of collagen bundles in the deep dermis, subcutis, and fascia that are prominent between the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat. There also are fewer sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Second, MP presents with an increased inflammatory cell infiltrate composed mainly of lymphocytes located around small blood vessels and the interstitium. In some patients, the lymphocytes consist predominantly of collections of plasma cells. Third, MP contains deposits of mucin in deep portions of the dermis with occasional eosinophils and mast cells. The presence of eosinophils allows EF to be a part of this spectrum and to be included as a differential diagnosis.5 Eosinophilic fasciitis has a similar presentation to MP because the fibrosis affects the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and underlying structures.20 Although EF presents with the histopathologic characteristic of fascial fibrosis, a clear distinction between EF and morphea has not been established in the literature. Some authors classify EF as a variant of morphea, whereas others consider it as its own entity. We believe EF is its own entity. Eosinophilic fasciitis can be distinguished from morphea because 60% to 80% of patients with EF have peripheral eosinophilia and 20% to 70% of patients with EF have hypergammaglobulinemia. Additionally, morphea does not present as symmetrically or abruptly as EF.21
Treatment
To date, there is conflicting literature regarding the treatment regimen for MP. There is controversy regarding whether MP responds to corticosteroids.19 Different treatment regimens have been discussed for LS, but there is a lack of reports specifically describing therapies for MP and SMP. Because MP and SMP fall under the umbrella of LS, many investigators have reported using the following treatment regimens for patients with MP and SMP: bosentan,22 D-penicillamine,23 phototherapy,24-26 retinoids,26 oral steroids,27 methotrexate,27-29 vitamin D3 (oral calcitriol),30,31 cyclosporine,32 mycophenolate mofetil,33 and extracorporeal photochemotherapy.34
Falanga and Medsger23 reported 64% (7/11) treatment success with D-penicillamine in patients who exhibited severe LS. Psoralen plus UVA,24 methoxsalen, and UVA1 therapy are widely used in the treatment of LS.25 Kreuter et al25 advocated for phototherapy as the first approach in the management of LS after reporting improvement in all participants in their study (N=64), 2 participants with deep morphea while the rest exhibited other forms of morphea. Ozdemir et al26 proposed that retinoic acid combined with psoralen plus UVA is a good treatment choice for plaque-type LS; however, UVA only has the ability to target the epidermis and dermis, which may not be useful for deep forms of morphea.
Several studies have shown positive results in patients treated with methylprednisolone combined with low-dose methotrexate sodium.27-29 Kreuter et al30 and Elst et al31 proposed that calcitriol is effective in treating LS, whereas Hulshof et al35 indicated that it is not. It should be noted that none of these studies specifically mentioned MP. Martini et al33 demonstrated success with mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of 10 LS patients who were resistant to methotrexate sodium and corticosteroids. Although none of the participants in the study had MP, 2 patients had disabling pansclerotic morphea, 3 had generalized morphea, and 5 had linear scleroderma (morphea en coup de sabre) affecting the limbs (n=2) and face (n=3).33 Because there is no established therapy or consensus for the treatment of MP, we have found success in starting with corticosteroids and then trying alternative therapies.
Prognosis
Morphea has transitioned into systemic scleroderma in a small number of reported cases.10,16,20,36 Therefore, patient follow-up is imperative to consistently identify systemic evolution. Although visceral complications are rare in the setting of LS, associated clinical findings have been reported, including arthralgia, arthritis, contractures, and carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as pulmonary, esophageal, and cardiac abnormalities.7,34
Conclusion
The morphologic features observed in our patient appear to correspond most closely to the type of lesion described by Su and Person5 and Whittaker et al.6 Although our case was clinically difficult to distinguish from linear morphea, the histology suggested SMP over other causes. If our patient’s SMP progressed to the joints, physical therapy would be needed to maintain range of motion and function of the extremities,2 and mandatory long-term follow-up would be required due to the risk for relapse after discontinuation of therapy. Our case highlights the inherent difficulties in the treatment of MP. Due to limited reports of SMP and MP in the literature as well as the conflicting views regarding effective and appropriate treatment options, additional investigation of these conditions and therapeutic options are necessary to further understand this debilitating condition.
Case Report
A 50-year-old white woman presented to our clinic for evaluation of what she described as a “very hard red line” on the right upper arm. The lesion had developed suddenly overnight. Several months prior to presentation the patient sustained trauma to the same area in a car accident and she thought the lesion might be related to the resulting nerve damage. Initially she presented to her primary care physician who used ultrasonography of the area to rule out muscle or bone involvement. The patient presented to our dermatology clinic 2 months later with an 18×4-cm, brownish, rectangular, sclerotic, bound-down, hypertrophic plaque that started on the right mid forearm and extended to the right shoulder (Figure 1). Her medical history was notable for high blood pressure, which was controlled with valsartan.
A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed a well-developed, well-nourished woman. Examination of the right arm revealed no motion restriction (muscle strength, 5/5) and no pain; however, she described a burning sensation at the site of the lesion. She reported no allergies. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and laboratory tests were ordered including an antinuclear antibody (ANA) test with reflex, double-stranded DNA test, DNA antitopoisomerase antibodies test, and Lyme titers (IgM and IgG). Initially, the patient was treated with calcipotriene 0.005%–betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% ointment twice daily; she also was treated empirically for Lyme disease with doxycycline 50 mg twice daily. All laboratory tests were within reference range, and a punch biopsy revealed markedly thickened fibrous septa within the subcutaneous fat. At the edge of the septa there were nodular aggregates of lymphocytes. Due to clinical presentation, laboratory data, and histopathology, solitary morphea profunda (SMP) was diagnosed.
Following histopathologic examination (Figure 2), the patient was instructed to continue treatment with calcipotriene–betamethasone dipropionate as well as doxycycline. A trial of prednisone and/or hydroxychloroquine also was considered pending her response to the initial treatment. At approximately 1-month follow-up, remarkable improvement of the lesion was noted.
Comment
|
There is limited literature available about the diagnosis and treatment of SMP. Our case prompted us to further examine the data to emphasize the necessity of greater research surrounding SMP.
Classification of SMP
Morphea is a localized form of scleroderma, an inflammatory disease that primarily affects the dermis but can extend down to the bone and also can limit motion. There are several types of morphea that are classified according to the extent, depth, and distribution of the lesions, including plaque, generalized, bullous, linear (including morphea en coup de sabre), guttate, nodular, and deep morphea.1,2 Other subtypes have been described including subcutaneous morphea, eosinophilic fasciitis (EF), pansclerotic morphea, and morphea profunda.3 Linear and deep morphea are characterized by involvement of the deep dermis, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and/or superficial muscle.2,4
In 1981, Su and Person5 first described morphea profunda (MP). In their study, 22 of 23 patients presented with generalized MP. One patient developed a single lesion,5 which ultimately was classified as SMP by Whittaker et al6 in 1989.
Epidemiology
Morphea profunda occurs more frequently in females than in males, with sclerosis manifesting over a period of several months.7 In 2004, Azad et al4 suggested that only 9 cases of SMP had been reported in the literature. Although there is insignificant data to determine the epidemiology of SMP, the authors concluded that it most commonly affects middle-aged individuals with equal sex distribution.4 The single plaque in patients with SMP most commonly presents on the shoulder, back, or neck or in the paraspinal area.
Etiology
Because of the limited amount of literature on MP, a definitive etiology is unknown, but investigators have cited many possible causes. Genetic, autoimmune, hormonal, traumatic,8 vaccination,2,8 radiation,9 viral, neurogenic, and vascular factors all have been implicated,10 as well as infectious agents such as Borrelia burgdorferi in the United States,11,12Borrelia afzelii in Europe,2 and Borrelia garinii in Japan.2 Because our patient experienced a traumatic episode several months prior to presentation, it is important to investigate trauma as a likely etiology. Furthermore, traumatic events have been reported in 23% of children with linear morphea.13
Diagnostic Studies
Morphea profunda is diagnosed clinically and skin biopsy can be used for confirmation. Biopsy requires deep excision down to the muscle, which can aid in determining if the fascia is incorporated. Elevated levels of IgG and IgM have been detected in deep and linear morphea and are known to correlate with disease activity and the development of joint contractures in linear morphea.2 Serum procollagen type I has been considered by some as a useful indicator of disease severity.14 Elevated serum levels of antifibrillin-1 antibodies also have been demonstrated in patients with localized scleroderma (LS).15 Radiography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used for monitoring and analyzing lesion depth. Furthermore, magnetic resonance imaging can be used to differentiate MP from EF.2
The presence of ANAs in LS is controversial. According to Nguyen et al,2 ANAs are present in approximately 46% to 80% of patients with morphea, with a higher prevalence in patients with generalized, linear, and deep subtypes. However, Savoia et al16 found that patients with morphea typically do not present with ANAs; rather ANAs usually are found in patients with EF.
Pathogenesis
After the inflammatory phase in LS, fibrillar collagen types I and III accumulate, causing dermal fibrosis. The extracellular matrix increases due to the activation of connective tissue growth factor, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), TGF-β receptors, IL-4, and several other cytokines.17 The TGF-β receptors combine with the connective tissue growth factor released by fibroblasts to create an autocrine production loop that causes fibroblast and matrix production.17 As the inflammation progresses to sclerosis, the CD34 count decreases.18
Physical Findings
In patients with MP, lesions manifest as thickened taut skin with deep, solitary, and sclerotic indurated plaques. Clinically, plaques are mildly inflamed, hyperpigmented, symmetric, and somewhat ill defined, and the skin feels thickened and bound to the underlying fascia and muscle. Plaques usually are smooth and shiny, but areas of both dermal and subcutaneous atrophy may be present, particularly in chronic lesions.19 Morphea profunda also can be described as having a cobblestone or pseudocellulite appearance. The groove sign is used to describe a depression along the course of a vein and/or between muscle groups. Both clinical presentations may manifest later in the course of disease.2
Histopathology
Su and Person5 described 3 main characteristics of MP that stand out histopathologically. First, there is thickening and hyalinization of collagen bundles in the deep dermis, subcutis, and fascia that are prominent between the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat. There also are fewer sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Second, MP presents with an increased inflammatory cell infiltrate composed mainly of lymphocytes located around small blood vessels and the interstitium. In some patients, the lymphocytes consist predominantly of collections of plasma cells. Third, MP contains deposits of mucin in deep portions of the dermis with occasional eosinophils and mast cells. The presence of eosinophils allows EF to be a part of this spectrum and to be included as a differential diagnosis.5 Eosinophilic fasciitis has a similar presentation to MP because the fibrosis affects the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and underlying structures.20 Although EF presents with the histopathologic characteristic of fascial fibrosis, a clear distinction between EF and morphea has not been established in the literature. Some authors classify EF as a variant of morphea, whereas others consider it as its own entity. We believe EF is its own entity. Eosinophilic fasciitis can be distinguished from morphea because 60% to 80% of patients with EF have peripheral eosinophilia and 20% to 70% of patients with EF have hypergammaglobulinemia. Additionally, morphea does not present as symmetrically or abruptly as EF.21
Treatment
To date, there is conflicting literature regarding the treatment regimen for MP. There is controversy regarding whether MP responds to corticosteroids.19 Different treatment regimens have been discussed for LS, but there is a lack of reports specifically describing therapies for MP and SMP. Because MP and SMP fall under the umbrella of LS, many investigators have reported using the following treatment regimens for patients with MP and SMP: bosentan,22 D-penicillamine,23 phototherapy,24-26 retinoids,26 oral steroids,27 methotrexate,27-29 vitamin D3 (oral calcitriol),30,31 cyclosporine,32 mycophenolate mofetil,33 and extracorporeal photochemotherapy.34
Falanga and Medsger23 reported 64% (7/11) treatment success with D-penicillamine in patients who exhibited severe LS. Psoralen plus UVA,24 methoxsalen, and UVA1 therapy are widely used in the treatment of LS.25 Kreuter et al25 advocated for phototherapy as the first approach in the management of LS after reporting improvement in all participants in their study (N=64), 2 participants with deep morphea while the rest exhibited other forms of morphea. Ozdemir et al26 proposed that retinoic acid combined with psoralen plus UVA is a good treatment choice for plaque-type LS; however, UVA only has the ability to target the epidermis and dermis, which may not be useful for deep forms of morphea.
Several studies have shown positive results in patients treated with methylprednisolone combined with low-dose methotrexate sodium.27-29 Kreuter et al30 and Elst et al31 proposed that calcitriol is effective in treating LS, whereas Hulshof et al35 indicated that it is not. It should be noted that none of these studies specifically mentioned MP. Martini et al33 demonstrated success with mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of 10 LS patients who were resistant to methotrexate sodium and corticosteroids. Although none of the participants in the study had MP, 2 patients had disabling pansclerotic morphea, 3 had generalized morphea, and 5 had linear scleroderma (morphea en coup de sabre) affecting the limbs (n=2) and face (n=3).33 Because there is no established therapy or consensus for the treatment of MP, we have found success in starting with corticosteroids and then trying alternative therapies.
Prognosis
Morphea has transitioned into systemic scleroderma in a small number of reported cases.10,16,20,36 Therefore, patient follow-up is imperative to consistently identify systemic evolution. Although visceral complications are rare in the setting of LS, associated clinical findings have been reported, including arthralgia, arthritis, contractures, and carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as pulmonary, esophageal, and cardiac abnormalities.7,34
Conclusion
The morphologic features observed in our patient appear to correspond most closely to the type of lesion described by Su and Person5 and Whittaker et al.6 Although our case was clinically difficult to distinguish from linear morphea, the histology suggested SMP over other causes. If our patient’s SMP progressed to the joints, physical therapy would be needed to maintain range of motion and function of the extremities,2 and mandatory long-term follow-up would be required due to the risk for relapse after discontinuation of therapy. Our case highlights the inherent difficulties in the treatment of MP. Due to limited reports of SMP and MP in the literature as well as the conflicting views regarding effective and appropriate treatment options, additional investigation of these conditions and therapeutic options are necessary to further understand this debilitating condition.
1. Peterson LS, Nelson AM, Su WP. Classification of morphea (localized scleroderma). Mayo Clin Proc. 1995;70:1068-1076.
2. Nguyen JV, Werth VP, Fett N. Morphea treatment & management. Medscape Web site. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1065782-treatment. Updated July 21, 2014. Accessed December 16, 2104.
3. Melani L, Cardinali C, Giomi B, et al. Case study: periodic follow-up is necessary in morphea profunda to identify systemic evolution. Skinmed. 2005;4:188-190.
4. Azad J, Dawn G, Shaffrali FC, et al. Does solitary morphoea profunda progress? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:25-27.
5. Su WP, Person JR. Morphea profunda. a new concept and a histopathologic study of 23 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1981;3:251-260.
6. Whittaker SJ, Smith NP, Jones RR. Solitary morphoea profunda. Br J Dermatol. 1989;120:431-440.
7. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
8. Torrelo A, Suárez J, Colmenero I, et al. Deep morphea after vaccination in two young children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:484-487.
9. Kreft B, Wohlrab J, Radant K, et al. Unrecognized radiation-induced localized scleroderma: a cause of postoperative wound-healing disorder [published online ahead of print June 22, 2009]. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e383-e384.
10. Braun-Falco O, Plewig G, Wolff HH, et al, eds. Dermatology. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2002.
11. Prinz JC, Kutasi Z, Weisenseel P, et al. “Borrelia-associated early-onset morphea”: a particular type of scleroderma in childhood and adolescence with high titer antinuclear antibodies? results of a cohort analysis and presentation of three cases [published online ahead of print November 20, 2008]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:248-255.
12. Wojas-Pelc A, Wielowieyska-Szybińska D, Kiełtyka A. Presence of the antinuclear antibodies and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi among patients with morphea en plaque, deep linear scleroderma and atrophoderma Pasini-Pierini [in Polish]. Przegl Lek. 2002;59:898-902.
13. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr, Reichlin M, et al. Linear scleroderma. clinical spectrum, prognosis, and laboratory abnormalities. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104:849-857.
14. Kikuchi K, Sato S, Kadono T, et al. Serum concentration of procollagen type I carboxyterminal propeptide in localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1269-1272.
15. Arnett FC, Tan FK, Uziel Y, et al. Autoantibodies to the extracellular matrix microfibrillar protein, fibrilin 1, in patients with localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:2656-2659.
16. Savoia P, Zaccagna A, Bernengo MG. Guess what? inflammatory disseminated morphea profunda. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:654-656.
17. Igarashi A, Nashiro K, Kikuchi K, et al. Connective tissue growth factor gene expression in tissue sections from localized scleroderma, keloid, and other fibrotic skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:729-733.
18. Gilmour TK, Wilkinson B, Breit SN, et al. Analysis of dendritic cell populations using a revised histological staging of morphoea. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1183-1192.
19. Sayama K, Chen M, Shiraishi S, et al. Morphea profunda. Int J Dermatol. 1991;30:873-875.
20. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
21. Bischoff L, Derk CT. Eosinophilic fasciitis: demographics disease pattern and response to treatment: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:29-35.
22. Roldan R, Morote G, Castro Mdel C, et al. Efficacy of bosentan in treatment of unresponsive cutaneous ulceration in disabling pansclerotic morphea in children. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2538-2540.
23. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr. D-penicillamine in the treatment of localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:609-612.
24. Breuckmann F, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P, et al. UVA/UVA1 phototherapy and PUVA photochemotherapy in connective tissue diseases and related disorders: a research based review. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:11.
25. Kreuter A, Hyun J, Stücker M, et al. A randomized controlled study of low-dose UVA1, medium-dose UVA1, and narrowband UVB phototherapy in the treatment of localized scleroderma [published online ahead of print January 30, 2006]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:440-447.
26. Ozdemir M, Engin B, Toy H, et al. Treatment of plaque-type localized scleroderma with retinoic acid and ultraviolet A plus the photosensitizer psoralen: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:519-521.
27. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, et al. Pulsed high-dose corticosteroids combined with low-dose methotrexate in severe localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:847-852.
28. Kroft EB, Creemers MC, van den Hoogen FH, et al. Effectiveness, side-effects and period of remission after treatment with methotrexate in localized scleroderma and related sclerotic skin diseases: an inception cohort study [published online ahead of print February 4, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:1075-1082.
29. Weibel L, Sampaio MC, Visentin MT, et al. Evaluation of methotrexate and corticosteroids for the treatment of localized scleroderma (morphoea) in children. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1013-1020.
30. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Avermaete A, et al. Combined treatment with calcipotriol ointment and low-dose ultraviolet A1 phototherapy in childhood morphea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2001;18:241-245.
31. Elst EF, Van Suijlekom-Smit LW, Oranje AP. Treatment of linear scleroderma with oral 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 (calcitriol) in seven children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:53-58.
32. Crespo MP, Mas IB, Díaz JM, et al. Rapid response to cyclosporine and maintenance with methotrexate in linear scleroderma in a young girl. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:118-120.
33. Martini G, Ramanan AV, Falcini F, et al. Successful treatment of severe or methotrexate-resistant juvenile localized scleroderma with mycophenolate mofetil [published online ahead of print August 27, 2009]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48:1410-1413.
34. Neustadter JH, Samarin F, Carlson KR, et al. Extracorporeal photochemotherapy for generalized deep morphea. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:127-130.
35. Hulshof MM, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Bergman W, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral calcitriol for the treatment of localized and systemic scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1017-1023.
36. Toledano C, Rabhi S, Kettaneh A, et al. Localized scleroderma: a series of 52 patients [published online ahead of print September 17, 2008]. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:331-336.
1. Peterson LS, Nelson AM, Su WP. Classification of morphea (localized scleroderma). Mayo Clin Proc. 1995;70:1068-1076.
2. Nguyen JV, Werth VP, Fett N. Morphea treatment & management. Medscape Web site. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1065782-treatment. Updated July 21, 2014. Accessed December 16, 2104.
3. Melani L, Cardinali C, Giomi B, et al. Case study: periodic follow-up is necessary in morphea profunda to identify systemic evolution. Skinmed. 2005;4:188-190.
4. Azad J, Dawn G, Shaffrali FC, et al. Does solitary morphoea profunda progress? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:25-27.
5. Su WP, Person JR. Morphea profunda. a new concept and a histopathologic study of 23 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1981;3:251-260.
6. Whittaker SJ, Smith NP, Jones RR. Solitary morphoea profunda. Br J Dermatol. 1989;120:431-440.
7. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
8. Torrelo A, Suárez J, Colmenero I, et al. Deep morphea after vaccination in two young children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:484-487.
9. Kreft B, Wohlrab J, Radant K, et al. Unrecognized radiation-induced localized scleroderma: a cause of postoperative wound-healing disorder [published online ahead of print June 22, 2009]. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e383-e384.
10. Braun-Falco O, Plewig G, Wolff HH, et al, eds. Dermatology. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2002.
11. Prinz JC, Kutasi Z, Weisenseel P, et al. “Borrelia-associated early-onset morphea”: a particular type of scleroderma in childhood and adolescence with high titer antinuclear antibodies? results of a cohort analysis and presentation of three cases [published online ahead of print November 20, 2008]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:248-255.
12. Wojas-Pelc A, Wielowieyska-Szybińska D, Kiełtyka A. Presence of the antinuclear antibodies and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi among patients with morphea en plaque, deep linear scleroderma and atrophoderma Pasini-Pierini [in Polish]. Przegl Lek. 2002;59:898-902.
13. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr, Reichlin M, et al. Linear scleroderma. clinical spectrum, prognosis, and laboratory abnormalities. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104:849-857.
14. Kikuchi K, Sato S, Kadono T, et al. Serum concentration of procollagen type I carboxyterminal propeptide in localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1269-1272.
15. Arnett FC, Tan FK, Uziel Y, et al. Autoantibodies to the extracellular matrix microfibrillar protein, fibrilin 1, in patients with localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:2656-2659.
16. Savoia P, Zaccagna A, Bernengo MG. Guess what? inflammatory disseminated morphea profunda. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:654-656.
17. Igarashi A, Nashiro K, Kikuchi K, et al. Connective tissue growth factor gene expression in tissue sections from localized scleroderma, keloid, and other fibrotic skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:729-733.
18. Gilmour TK, Wilkinson B, Breit SN, et al. Analysis of dendritic cell populations using a revised histological staging of morphoea. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1183-1192.
19. Sayama K, Chen M, Shiraishi S, et al. Morphea profunda. Int J Dermatol. 1991;30:873-875.
20. Bielsa I, Ariza A. Deep morphea. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:90-95.
21. Bischoff L, Derk CT. Eosinophilic fasciitis: demographics disease pattern and response to treatment: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:29-35.
22. Roldan R, Morote G, Castro Mdel C, et al. Efficacy of bosentan in treatment of unresponsive cutaneous ulceration in disabling pansclerotic morphea in children. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2538-2540.
23. Falanga V, Medsger TA Jr. D-penicillamine in the treatment of localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:609-612.
24. Breuckmann F, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P, et al. UVA/UVA1 phototherapy and PUVA photochemotherapy in connective tissue diseases and related disorders: a research based review. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:11.
25. Kreuter A, Hyun J, Stücker M, et al. A randomized controlled study of low-dose UVA1, medium-dose UVA1, and narrowband UVB phototherapy in the treatment of localized scleroderma [published online ahead of print January 30, 2006]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:440-447.
26. Ozdemir M, Engin B, Toy H, et al. Treatment of plaque-type localized scleroderma with retinoic acid and ultraviolet A plus the photosensitizer psoralen: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:519-521.
27. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, et al. Pulsed high-dose corticosteroids combined with low-dose methotrexate in severe localized scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:847-852.
28. Kroft EB, Creemers MC, van den Hoogen FH, et al. Effectiveness, side-effects and period of remission after treatment with methotrexate in localized scleroderma and related sclerotic skin diseases: an inception cohort study [published online ahead of print February 4, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:1075-1082.
29. Weibel L, Sampaio MC, Visentin MT, et al. Evaluation of methotrexate and corticosteroids for the treatment of localized scleroderma (morphoea) in children. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1013-1020.
30. Kreuter A, Gambichler T, Avermaete A, et al. Combined treatment with calcipotriol ointment and low-dose ultraviolet A1 phototherapy in childhood morphea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2001;18:241-245.
31. Elst EF, Van Suijlekom-Smit LW, Oranje AP. Treatment of linear scleroderma with oral 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 (calcitriol) in seven children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:53-58.
32. Crespo MP, Mas IB, Díaz JM, et al. Rapid response to cyclosporine and maintenance with methotrexate in linear scleroderma in a young girl. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:118-120.
33. Martini G, Ramanan AV, Falcini F, et al. Successful treatment of severe or methotrexate-resistant juvenile localized scleroderma with mycophenolate mofetil [published online ahead of print August 27, 2009]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48:1410-1413.
34. Neustadter JH, Samarin F, Carlson KR, et al. Extracorporeal photochemotherapy for generalized deep morphea. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:127-130.
35. Hulshof MM, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Bergman W, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral calcitriol for the treatment of localized and systemic scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1017-1023.
36. Toledano C, Rabhi S, Kettaneh A, et al. Localized scleroderma: a series of 52 patients [published online ahead of print September 17, 2008]. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:331-336.
Practice Points
- Localized trauma to the skin may be an inciting event to trigger morphea.
- Morphea is a clinical diagnosis but should be confirmed through biopsy to differentiate it from other similar entities.