User login
Unusually Early-Onset Plantar Verrucous Carcinoma
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
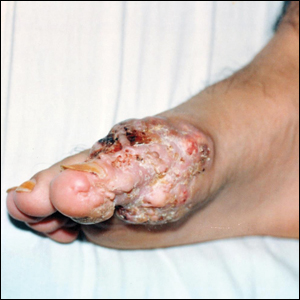
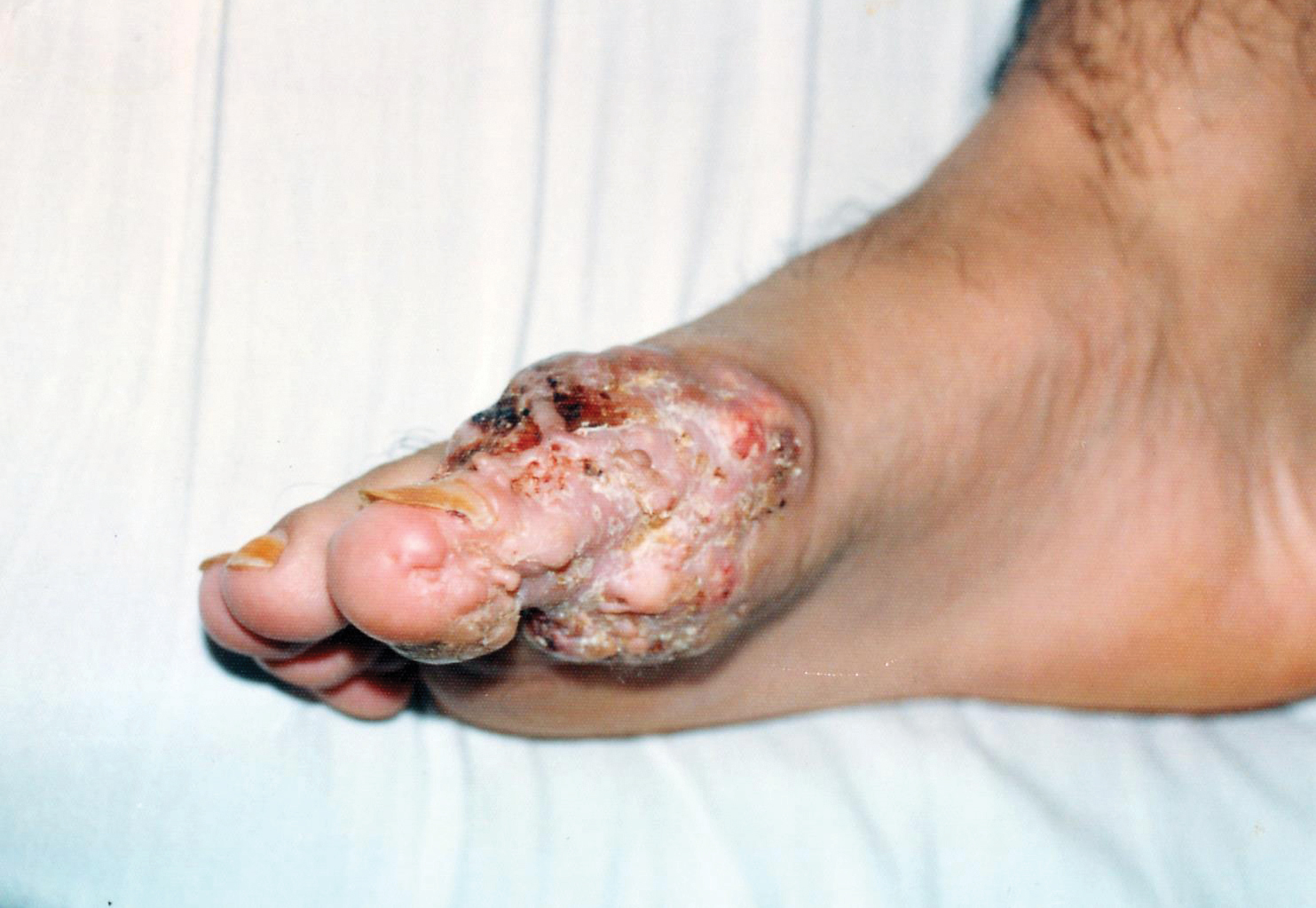
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.
The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
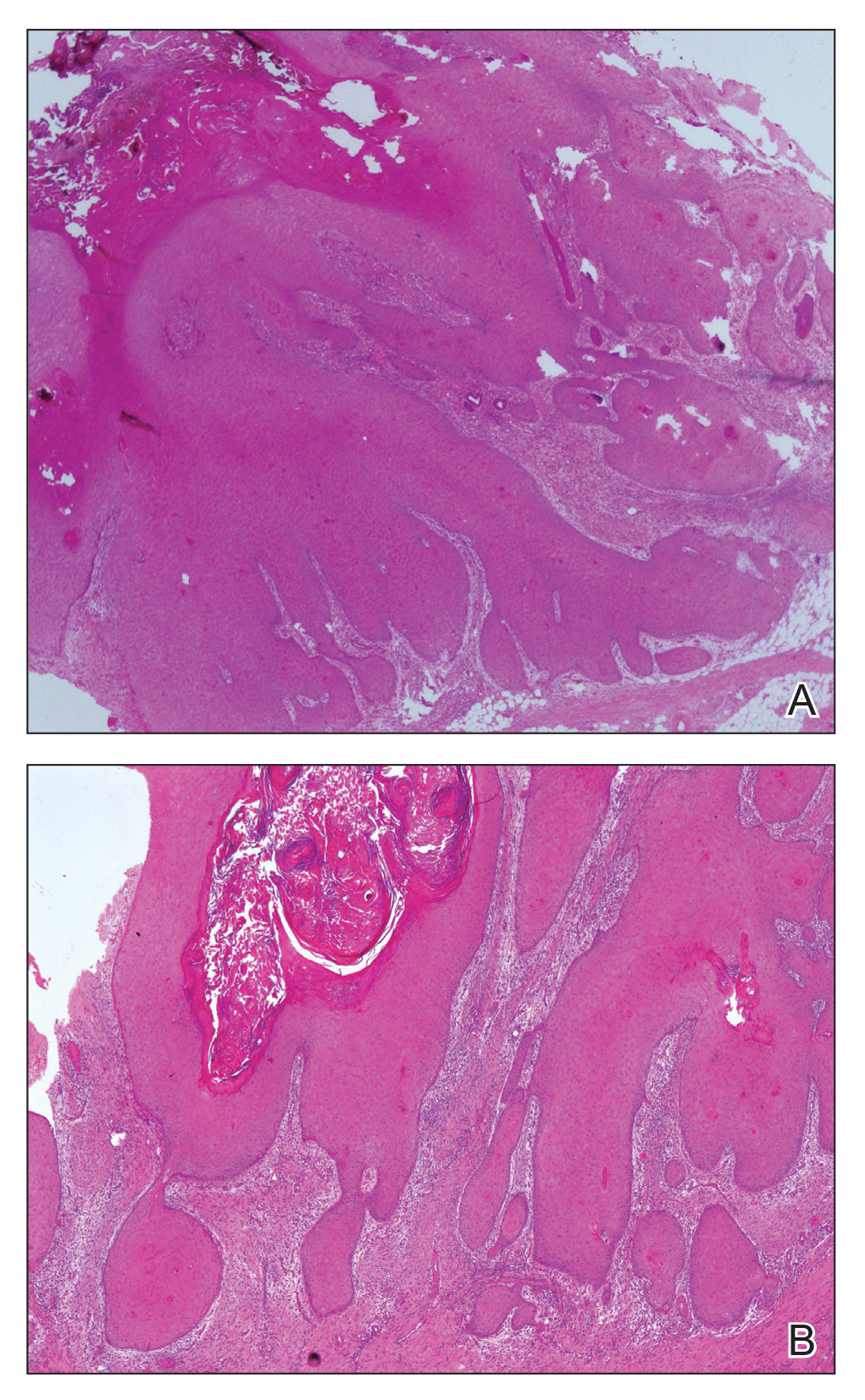
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.
The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.

The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.

The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.

The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.

The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
Practice Points
- Verrucous carcinoma (VC) frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, the anogenital area, and on the plantar surface.
- Plantar VC is rare, with a male predominance and most patients presenting in the fifth to sixth decades of life.
- Differentiating VS from benign tumors may be difficult, especially if only superficial biopsies are taken. Multiple biopsies and a close clinical correlation are required before a definite diagnosis is possible.
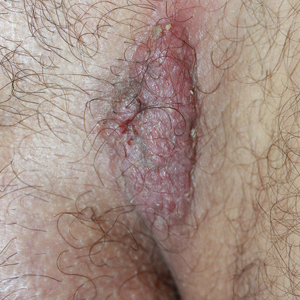
Solitary Exophytic Plaque on the Left Groin
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Vegetans
A punch biopsy was taken from the verrucous plaque, and microscopic examination demonstrated prominent epidermal hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses and a superficial dermatitis with abundant eosinophils (Figure 1A). Suprabasal acantholytic cleft formation was noted in a focal area (Figure 1B). Another punch biopsy was performed from the perilesional skin for direct immunofluorescence examination, which revealed intercellular deposits of IgG and C3 throughout the lower half of the epidermis (Figure 1C). Indirect immunofluorescence performed on monkey esophagus substrate showed circulating intercellular IgG antibodies in all the titers of up to 1/160 and an elevated level of IgG antidesmoglein 3 (anti-Dsg3) antibody (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index value, >200 RU/mL [reference range, <20 RU/mL]).
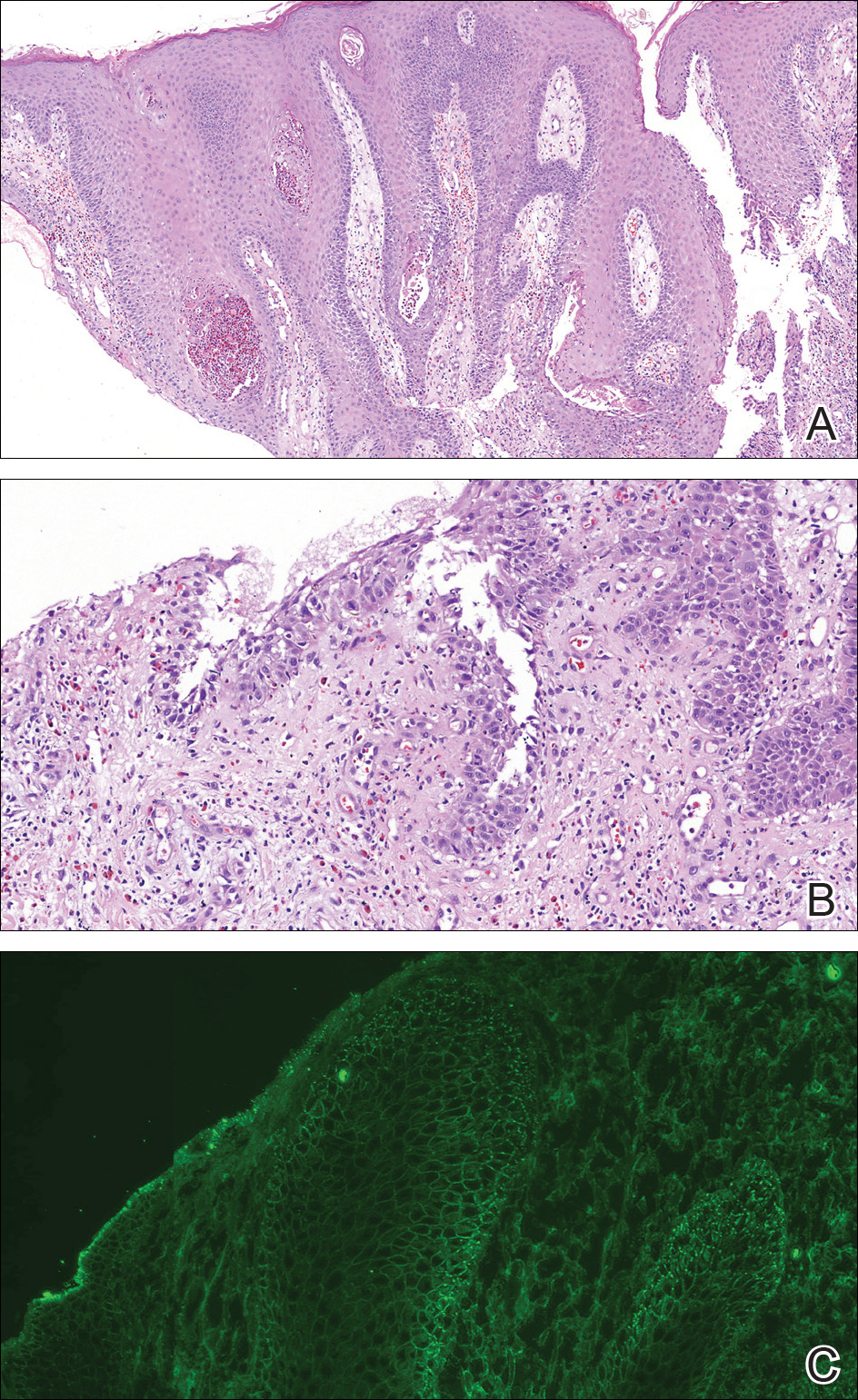
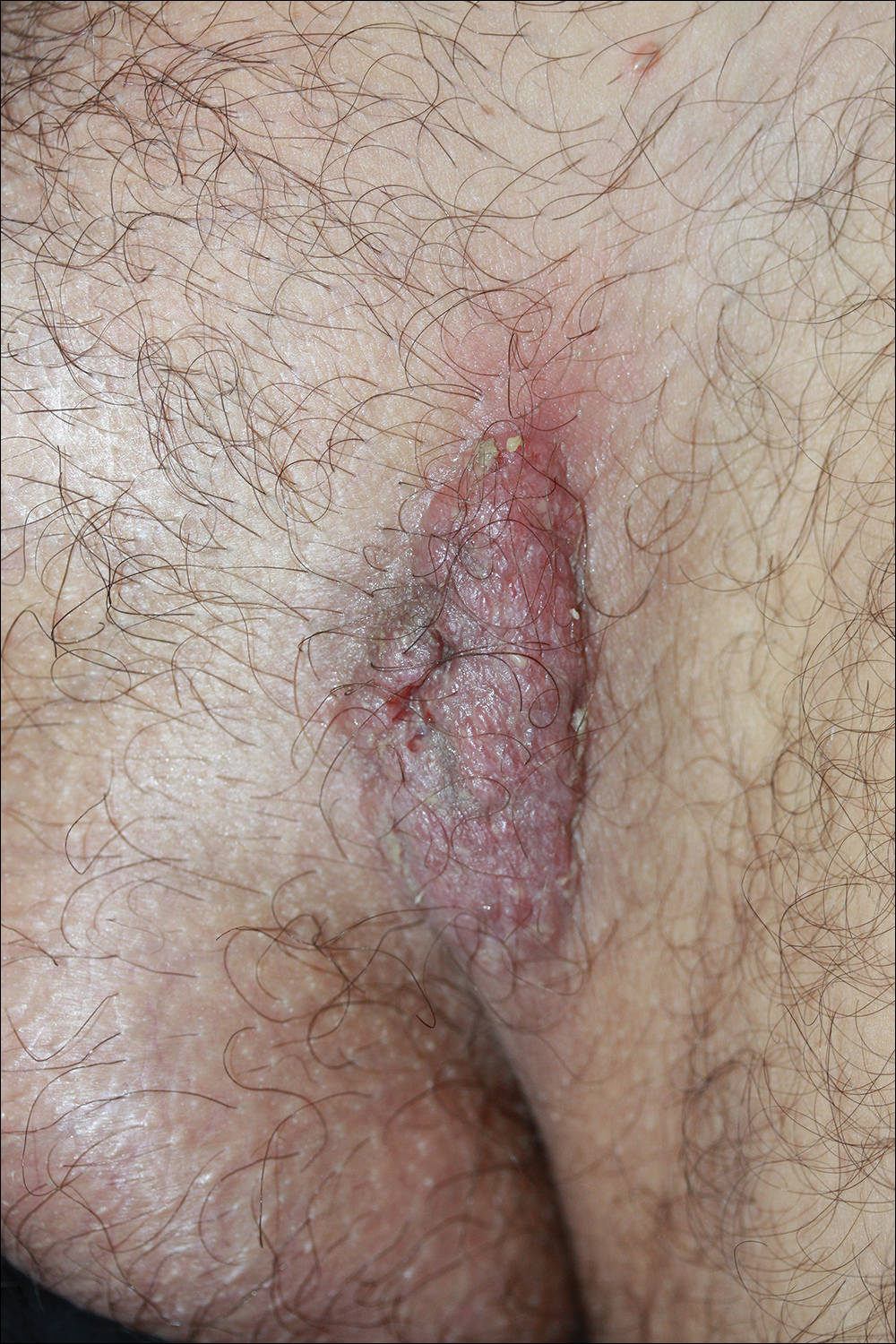
Because there was a solitary lesion, the decision was made to perform local treatment. One intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injection (20 mg/mL) resulted in remarkable flattening of the lesion (Figure 2). Subsequently, treatment was continued with clobetasol propionate ointment 3 times weekly for 1 month. During a follow-up period of 2 years, no signs of local relapse or new lesions elsewhere were noted, and the patient continued to be on long-term longitudinal evaluation.
Pemphigus vegetans (PV) is an uncommon variant of pemphigus, typically manifesting with vegetating erosions and plaques localized to the intertriginous areas of the body. Local factors such as semiocclusion, maceration, and/or bacterial or fungal colonization have been hypothesized to account for the distinctive localization and vegetation of the lesions.1,2 Traditionally, 2 clinical subtypes of PV have been described: (1) Hallopeau type presenting with pustules that later evolve into vegetating plaques, and (2) Neumann type that initially manifests as vesicles and bullae with a more disseminated distribution, transforming into hypertrophic masses with erosions.1-5 However, this distinction may not always be clear, and patients with features of both forms have been reported.2,5
At present, our case would best be regarded as a localized form of PV presenting with a solitary lesion. It may progress to more disseminated disease or remain localized during its course; the literature contains reports exemplifying both possibilities. In a large retrospective study from Tunisia encompassing almost 3 decades, the majority of the patients initially presented with unifocal involvement; however, the disease eventually became multifocal in almost all patients during the study period, emphasizing the need for long-term follow-up.2 There also are reports of PV confined to a single anatomic site, such as the scalp, sole, or vulva, that remained localized for years.2,4,6,7 Involvement of the oral mucosa is an important finding of PV and the presenting concern in approximately three-quarters of patients.2 Interestingly, the oral mucosa was not involved in our patient despite the high titer of anti-Dsg3 antibody, which suggests the need for the presence of other factors for clinical expression of the disease.
Although PV is considered a vegetating clinicomorphologic variant of pemphigus vulgaris, PV is histopathologically distinguished from pemphigus vulgaris by the presence of epidermal hyperplasia and intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses. Importantly, the epidermis displays signs of exuberant proliferation such as pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and/or papillomatosis of a varying degree.1,2,5 Of note, suprabasal acantholysis is usually overshadowed by the changes in PV and presents only focally, as in our patient. The most common autoantibody profile is IgG targeting Dsg3; however, a spectrum of other autoantibodies has been identified, such as IgG antidesmocollin 3, IgA anti-Dsg3, and IgG anti-Dsg1.8,9
The most important differential diagnosis of PV is pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. These 2 entities share many clinical and histopathological features; however, direct immunofluorescence is helpfulfor differentiation because it generally is negative in pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans.2,10 Furthermore, there is a well-established association between pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans and inflammatory bowel disorders, whereas PV has anecdotally been linked to malignancy, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and heroin abuse.1,2,10 Our patient was seronegative for human immunodeficiency virus and denied weight loss or loss of appetite. For those cases of PV involving a single anatomic site, the differential diagnosis is broader and encompasses dermatoses such as verrucae, syphilitic chancre, condylomata lata, granuloma inguinale, herpes simplex virus infection, and Kaposi sarcoma.
Treatment of PV is similar to pemphigus vulgaris and consists of a combination of systemic corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents.1,5 On the other hand, more limited presentations of PV may be suitable for intralesional treatment with triamcinolone acetonide, thus avoiding potential adverse effects of systemic therapy.1,2 In our case with localized involvement, a favorable response was obtained with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide, and we plan to utilize systemic corticosteroids if the disease becomes generalized during follow-up.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Caccavale S, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the folds (intertriginous areas). Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:471-476.
- Zaraa I, Sellami A, Bouguerra C, et al. Pemphigus vegetans: a clinical, histological, immunopathological and prognostic study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1160-1167.
- Madan V, August PJ. Exophytic plaques, blisters, and mouth ulcers. pemphigus vegetans (PV), Neumann type. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:715-720.
- Mori M, Mariotti G, Grandi V, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the scalp. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:368-370.
- Monshi B, Marker M, Feichtinger H, et al. Pemphigus vegetans--immunopathological findings in a rare variant of pemphigus vulgaris. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:179-183.
- Jain VK, Dixit VB, Mohan H. Pemphigus vegetans in an unusual site. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:352-353.
- Wong KT, Wong KK. A case of acantholytic dermatosis of the vulva with features of pemphigus vegetans. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:453-456.
- Morizane S, Yamamoto T, Hisamatsu Y, et al. Pemphigus vegetans with IgG and IgA antidesmoglein 3 antibodies. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1236-1237.
- Saruta H, Ishii N, Teye K, et al. Two cases of pemphigus vegetans with IgG anti-desmocollin 3 antibodies. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1209-1213.
- Mehravaran M, Kemény L, Husz S, et al. Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:266-269.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Vegetans
A punch biopsy was taken from the verrucous plaque, and microscopic examination demonstrated prominent epidermal hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses and a superficial dermatitis with abundant eosinophils (Figure 1A). Suprabasal acantholytic cleft formation was noted in a focal area (Figure 1B). Another punch biopsy was performed from the perilesional skin for direct immunofluorescence examination, which revealed intercellular deposits of IgG and C3 throughout the lower half of the epidermis (Figure 1C). Indirect immunofluorescence performed on monkey esophagus substrate showed circulating intercellular IgG antibodies in all the titers of up to 1/160 and an elevated level of IgG antidesmoglein 3 (anti-Dsg3) antibody (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index value, >200 RU/mL [reference range, <20 RU/mL]).

Because there was a solitary lesion, the decision was made to perform local treatment. One intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injection (20 mg/mL) resulted in remarkable flattening of the lesion (Figure 2). Subsequently, treatment was continued with clobetasol propionate ointment 3 times weekly for 1 month. During a follow-up period of 2 years, no signs of local relapse or new lesions elsewhere were noted, and the patient continued to be on long-term longitudinal evaluation.

Pemphigus vegetans (PV) is an uncommon variant of pemphigus, typically manifesting with vegetating erosions and plaques localized to the intertriginous areas of the body. Local factors such as semiocclusion, maceration, and/or bacterial or fungal colonization have been hypothesized to account for the distinctive localization and vegetation of the lesions.1,2 Traditionally, 2 clinical subtypes of PV have been described: (1) Hallopeau type presenting with pustules that later evolve into vegetating plaques, and (2) Neumann type that initially manifests as vesicles and bullae with a more disseminated distribution, transforming into hypertrophic masses with erosions.1-5 However, this distinction may not always be clear, and patients with features of both forms have been reported.2,5
At present, our case would best be regarded as a localized form of PV presenting with a solitary lesion. It may progress to more disseminated disease or remain localized during its course; the literature contains reports exemplifying both possibilities. In a large retrospective study from Tunisia encompassing almost 3 decades, the majority of the patients initially presented with unifocal involvement; however, the disease eventually became multifocal in almost all patients during the study period, emphasizing the need for long-term follow-up.2 There also are reports of PV confined to a single anatomic site, such as the scalp, sole, or vulva, that remained localized for years.2,4,6,7 Involvement of the oral mucosa is an important finding of PV and the presenting concern in approximately three-quarters of patients.2 Interestingly, the oral mucosa was not involved in our patient despite the high titer of anti-Dsg3 antibody, which suggests the need for the presence of other factors for clinical expression of the disease.
Although PV is considered a vegetating clinicomorphologic variant of pemphigus vulgaris, PV is histopathologically distinguished from pemphigus vulgaris by the presence of epidermal hyperplasia and intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses. Importantly, the epidermis displays signs of exuberant proliferation such as pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and/or papillomatosis of a varying degree.1,2,5 Of note, suprabasal acantholysis is usually overshadowed by the changes in PV and presents only focally, as in our patient. The most common autoantibody profile is IgG targeting Dsg3; however, a spectrum of other autoantibodies has been identified, such as IgG antidesmocollin 3, IgA anti-Dsg3, and IgG anti-Dsg1.8,9
The most important differential diagnosis of PV is pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. These 2 entities share many clinical and histopathological features; however, direct immunofluorescence is helpfulfor differentiation because it generally is negative in pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans.2,10 Furthermore, there is a well-established association between pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans and inflammatory bowel disorders, whereas PV has anecdotally been linked to malignancy, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and heroin abuse.1,2,10 Our patient was seronegative for human immunodeficiency virus and denied weight loss or loss of appetite. For those cases of PV involving a single anatomic site, the differential diagnosis is broader and encompasses dermatoses such as verrucae, syphilitic chancre, condylomata lata, granuloma inguinale, herpes simplex virus infection, and Kaposi sarcoma.
Treatment of PV is similar to pemphigus vulgaris and consists of a combination of systemic corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents.1,5 On the other hand, more limited presentations of PV may be suitable for intralesional treatment with triamcinolone acetonide, thus avoiding potential adverse effects of systemic therapy.1,2 In our case with localized involvement, a favorable response was obtained with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide, and we plan to utilize systemic corticosteroids if the disease becomes generalized during follow-up.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Vegetans
A punch biopsy was taken from the verrucous plaque, and microscopic examination demonstrated prominent epidermal hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses and a superficial dermatitis with abundant eosinophils (Figure 1A). Suprabasal acantholytic cleft formation was noted in a focal area (Figure 1B). Another punch biopsy was performed from the perilesional skin for direct immunofluorescence examination, which revealed intercellular deposits of IgG and C3 throughout the lower half of the epidermis (Figure 1C). Indirect immunofluorescence performed on monkey esophagus substrate showed circulating intercellular IgG antibodies in all the titers of up to 1/160 and an elevated level of IgG antidesmoglein 3 (anti-Dsg3) antibody (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index value, >200 RU/mL [reference range, <20 RU/mL]).

Because there was a solitary lesion, the decision was made to perform local treatment. One intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injection (20 mg/mL) resulted in remarkable flattening of the lesion (Figure 2). Subsequently, treatment was continued with clobetasol propionate ointment 3 times weekly for 1 month. During a follow-up period of 2 years, no signs of local relapse or new lesions elsewhere were noted, and the patient continued to be on long-term longitudinal evaluation.

Pemphigus vegetans (PV) is an uncommon variant of pemphigus, typically manifesting with vegetating erosions and plaques localized to the intertriginous areas of the body. Local factors such as semiocclusion, maceration, and/or bacterial or fungal colonization have been hypothesized to account for the distinctive localization and vegetation of the lesions.1,2 Traditionally, 2 clinical subtypes of PV have been described: (1) Hallopeau type presenting with pustules that later evolve into vegetating plaques, and (2) Neumann type that initially manifests as vesicles and bullae with a more disseminated distribution, transforming into hypertrophic masses with erosions.1-5 However, this distinction may not always be clear, and patients with features of both forms have been reported.2,5
At present, our case would best be regarded as a localized form of PV presenting with a solitary lesion. It may progress to more disseminated disease or remain localized during its course; the literature contains reports exemplifying both possibilities. In a large retrospective study from Tunisia encompassing almost 3 decades, the majority of the patients initially presented with unifocal involvement; however, the disease eventually became multifocal in almost all patients during the study period, emphasizing the need for long-term follow-up.2 There also are reports of PV confined to a single anatomic site, such as the scalp, sole, or vulva, that remained localized for years.2,4,6,7 Involvement of the oral mucosa is an important finding of PV and the presenting concern in approximately three-quarters of patients.2 Interestingly, the oral mucosa was not involved in our patient despite the high titer of anti-Dsg3 antibody, which suggests the need for the presence of other factors for clinical expression of the disease.
Although PV is considered a vegetating clinicomorphologic variant of pemphigus vulgaris, PV is histopathologically distinguished from pemphigus vulgaris by the presence of epidermal hyperplasia and intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses. Importantly, the epidermis displays signs of exuberant proliferation such as pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and/or papillomatosis of a varying degree.1,2,5 Of note, suprabasal acantholysis is usually overshadowed by the changes in PV and presents only focally, as in our patient. The most common autoantibody profile is IgG targeting Dsg3; however, a spectrum of other autoantibodies has been identified, such as IgG antidesmocollin 3, IgA anti-Dsg3, and IgG anti-Dsg1.8,9
The most important differential diagnosis of PV is pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. These 2 entities share many clinical and histopathological features; however, direct immunofluorescence is helpfulfor differentiation because it generally is negative in pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans.2,10 Furthermore, there is a well-established association between pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans and inflammatory bowel disorders, whereas PV has anecdotally been linked to malignancy, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and heroin abuse.1,2,10 Our patient was seronegative for human immunodeficiency virus and denied weight loss or loss of appetite. For those cases of PV involving a single anatomic site, the differential diagnosis is broader and encompasses dermatoses such as verrucae, syphilitic chancre, condylomata lata, granuloma inguinale, herpes simplex virus infection, and Kaposi sarcoma.
Treatment of PV is similar to pemphigus vulgaris and consists of a combination of systemic corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents.1,5 On the other hand, more limited presentations of PV may be suitable for intralesional treatment with triamcinolone acetonide, thus avoiding potential adverse effects of systemic therapy.1,2 In our case with localized involvement, a favorable response was obtained with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide, and we plan to utilize systemic corticosteroids if the disease becomes generalized during follow-up.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Caccavale S, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the folds (intertriginous areas). Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:471-476.
- Zaraa I, Sellami A, Bouguerra C, et al. Pemphigus vegetans: a clinical, histological, immunopathological and prognostic study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1160-1167.
- Madan V, August PJ. Exophytic plaques, blisters, and mouth ulcers. pemphigus vegetans (PV), Neumann type. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:715-720.
- Mori M, Mariotti G, Grandi V, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the scalp. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:368-370.
- Monshi B, Marker M, Feichtinger H, et al. Pemphigus vegetans--immunopathological findings in a rare variant of pemphigus vulgaris. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:179-183.
- Jain VK, Dixit VB, Mohan H. Pemphigus vegetans in an unusual site. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:352-353.
- Wong KT, Wong KK. A case of acantholytic dermatosis of the vulva with features of pemphigus vegetans. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:453-456.
- Morizane S, Yamamoto T, Hisamatsu Y, et al. Pemphigus vegetans with IgG and IgA antidesmoglein 3 antibodies. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1236-1237.
- Saruta H, Ishii N, Teye K, et al. Two cases of pemphigus vegetans with IgG anti-desmocollin 3 antibodies. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1209-1213.
- Mehravaran M, Kemény L, Husz S, et al. Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:266-269.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Caccavale S, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the folds (intertriginous areas). Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:471-476.
- Zaraa I, Sellami A, Bouguerra C, et al. Pemphigus vegetans: a clinical, histological, immunopathological and prognostic study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1160-1167.
- Madan V, August PJ. Exophytic plaques, blisters, and mouth ulcers. pemphigus vegetans (PV), Neumann type. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:715-720.
- Mori M, Mariotti G, Grandi V, et al. Pemphigus vegetans of the scalp. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:368-370.
- Monshi B, Marker M, Feichtinger H, et al. Pemphigus vegetans--immunopathological findings in a rare variant of pemphigus vulgaris. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:179-183.
- Jain VK, Dixit VB, Mohan H. Pemphigus vegetans in an unusual site. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:352-353.
- Wong KT, Wong KK. A case of acantholytic dermatosis of the vulva with features of pemphigus vegetans. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:453-456.
- Morizane S, Yamamoto T, Hisamatsu Y, et al. Pemphigus vegetans with IgG and IgA antidesmoglein 3 antibodies. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1236-1237.
- Saruta H, Ishii N, Teye K, et al. Two cases of pemphigus vegetans with IgG anti-desmocollin 3 antibodies. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1209-1213.
- Mehravaran M, Kemény L, Husz S, et al. Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:266-269.
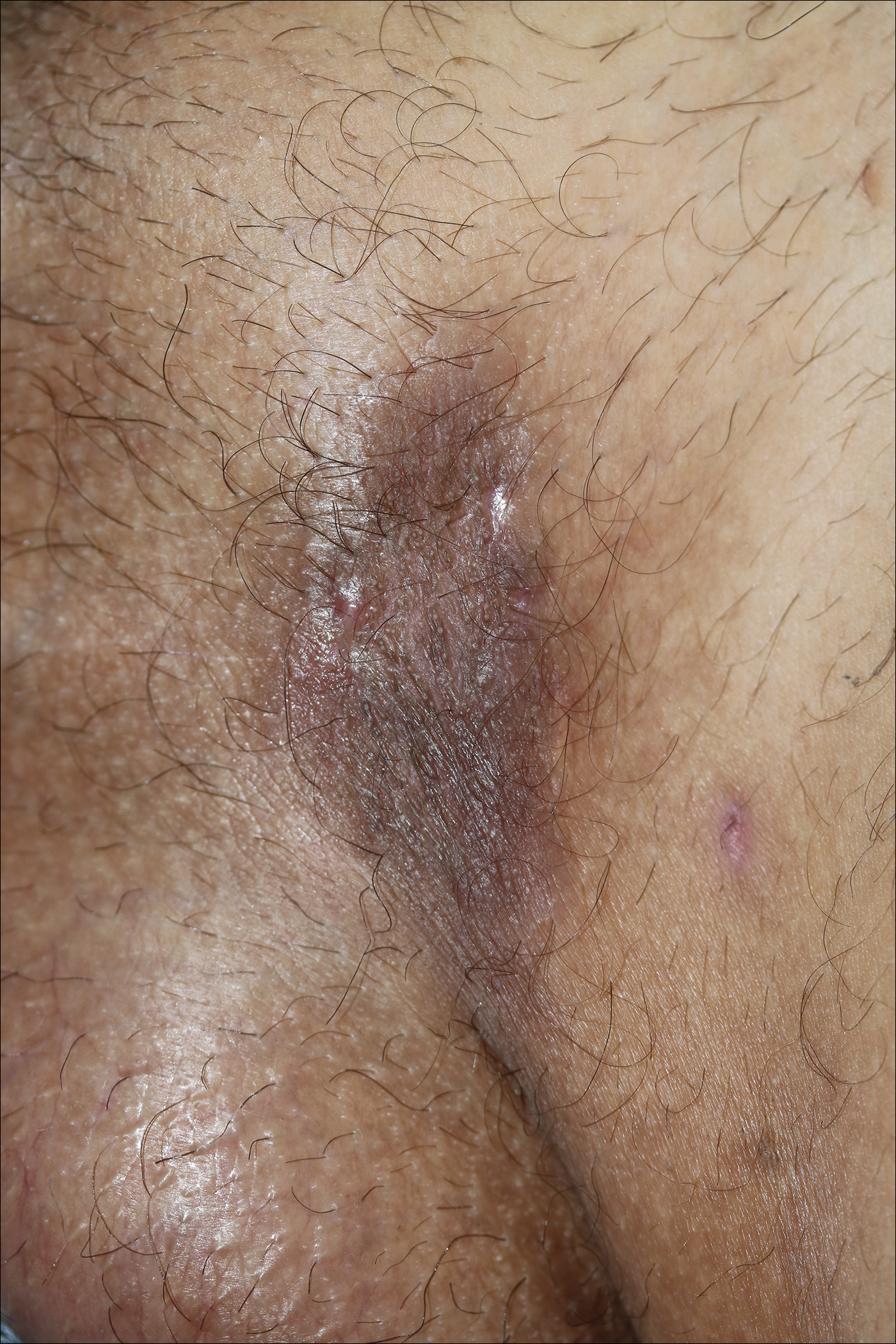
A 40-year-old otherwise healthy man presented with an exophytic plaque on the left groin of 1 month's duration. The lesion reportedly emerged as pustules that slowly expanded and coalesced. At an outside institution, cryotherapy was planned for a presumed diagnosis of condyloma acuminatum; however, the patient decided to get a second opinion. He denied recent intake of new drugs. Six months prior he had traveled to China and engaged in unprotected sexual intercourse. Physical examination revealed an approximately 4×2-cm exophytic plaque with a partially eroded and exudative surface on the left inguinal fold. Dermatologic examination, including the oral mucosa, was otherwise normal. Complete blood cell count and sexually transmitted disease panel were unremarkable.