User login
A Sanaa Butt, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This was, however, the sole identifiable risk factor for treatment-limiting depressive symptoms in acne patients on isotretinoin in the study of 3,151 consecutive acne patients taking isotretinoin. There was no significant difference between those who did or did not develop depression on the oral retinoid in terms of age, gender, or daily dose of the drug at the time it was discontinued.
“Depressive symptoms occurred at any time from the date of initiation of isotretinoin up to 6 months into therapy, with no identifiable peak time period,” said Dr. Butt, a dermatologist with the U.K. National Health Service Tayside district at Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, Scotland. “Lower doses appear not to be protective,” she added.
The Tayside district has a catchment of roughly 450,000 people. The local population tends to stay put because Tayside is an economically disadvantaged and remote part of Scotland. There are very few private practice dermatologists in the area, so Dr. Butt and coinvestigators are confident their observational study of NHS patients captured the great majority of isotretinoin users in northern Scotland.
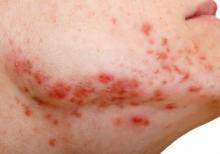
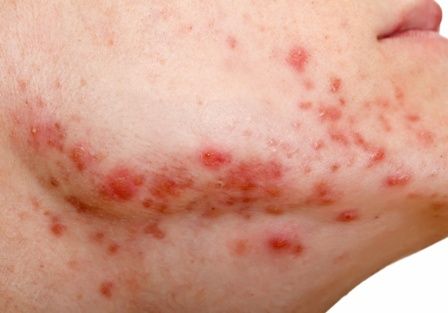
The investigators utilized software to analyze the contents of more than 8,000 digitized letters exchanged between NHS Tayside dermatologists and general practitioners during 2005-2018, zeroing in on 3,151 consecutive patients on isotretinoin for acne and 158 on the drug for other conditions, most often rosacea or folliculitis. They then drilled down further through the letters, electronically searching for key words such as suicide, depression, and anxiety. In this way, they ultimately identified 30 patients who discontinued the drug because they developed depressive symptoms. All 30 were on the drug for acne.
The annual incidence of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was 0.96%, a figure that remained steady over the 13-year study period, even though prescribing of isotretinoin increased over time. This flat incidence rate effectively rules out the potential for confounding because of assessor bias, especially since many different NHS dermatologists were prescribing the drug, Dr. Butt said.
Half of acne patients prescribed isotretinoin were female and 50% were male. And 15 cases of treatment discontinuation caused by development of depressive symptoms occurred in females, 15 in males. A history of past depressive illness was present in 9.3% of females who started on isotretinoin and in 4.5% of the males. The relative risk of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was increased 790% among females with a prior history of depressive illness and 440% in males with such a history.
Dr. Butt reported having no financial conflicts regarding her NHS-funded study.
A Sanaa Butt, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This was, however, the sole identifiable risk factor for treatment-limiting depressive symptoms in acne patients on isotretinoin in the study of 3,151 consecutive acne patients taking isotretinoin. There was no significant difference between those who did or did not develop depression on the oral retinoid in terms of age, gender, or daily dose of the drug at the time it was discontinued.
“Depressive symptoms occurred at any time from the date of initiation of isotretinoin up to 6 months into therapy, with no identifiable peak time period,” said Dr. Butt, a dermatologist with the U.K. National Health Service Tayside district at Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, Scotland. “Lower doses appear not to be protective,” she added.
The Tayside district has a catchment of roughly 450,000 people. The local population tends to stay put because Tayside is an economically disadvantaged and remote part of Scotland. There are very few private practice dermatologists in the area, so Dr. Butt and coinvestigators are confident their observational study of NHS patients captured the great majority of isotretinoin users in northern Scotland.
The investigators utilized software to analyze the contents of more than 8,000 digitized letters exchanged between NHS Tayside dermatologists and general practitioners during 2005-2018, zeroing in on 3,151 consecutive patients on isotretinoin for acne and 158 on the drug for other conditions, most often rosacea or folliculitis. They then drilled down further through the letters, electronically searching for key words such as suicide, depression, and anxiety. In this way, they ultimately identified 30 patients who discontinued the drug because they developed depressive symptoms. All 30 were on the drug for acne.
The annual incidence of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was 0.96%, a figure that remained steady over the 13-year study period, even though prescribing of isotretinoin increased over time. This flat incidence rate effectively rules out the potential for confounding because of assessor bias, especially since many different NHS dermatologists were prescribing the drug, Dr. Butt said.
Half of acne patients prescribed isotretinoin were female and 50% were male. And 15 cases of treatment discontinuation caused by development of depressive symptoms occurred in females, 15 in males. A history of past depressive illness was present in 9.3% of females who started on isotretinoin and in 4.5% of the males. The relative risk of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was increased 790% among females with a prior history of depressive illness and 440% in males with such a history.
Dr. Butt reported having no financial conflicts regarding her NHS-funded study.
A Sanaa Butt, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This was, however, the sole identifiable risk factor for treatment-limiting depressive symptoms in acne patients on isotretinoin in the study of 3,151 consecutive acne patients taking isotretinoin. There was no significant difference between those who did or did not develop depression on the oral retinoid in terms of age, gender, or daily dose of the drug at the time it was discontinued.
“Depressive symptoms occurred at any time from the date of initiation of isotretinoin up to 6 months into therapy, with no identifiable peak time period,” said Dr. Butt, a dermatologist with the U.K. National Health Service Tayside district at Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, Scotland. “Lower doses appear not to be protective,” she added.
The Tayside district has a catchment of roughly 450,000 people. The local population tends to stay put because Tayside is an economically disadvantaged and remote part of Scotland. There are very few private practice dermatologists in the area, so Dr. Butt and coinvestigators are confident their observational study of NHS patients captured the great majority of isotretinoin users in northern Scotland.
The investigators utilized software to analyze the contents of more than 8,000 digitized letters exchanged between NHS Tayside dermatologists and general practitioners during 2005-2018, zeroing in on 3,151 consecutive patients on isotretinoin for acne and 158 on the drug for other conditions, most often rosacea or folliculitis. They then drilled down further through the letters, electronically searching for key words such as suicide, depression, and anxiety. In this way, they ultimately identified 30 patients who discontinued the drug because they developed depressive symptoms. All 30 were on the drug for acne.
The annual incidence of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was 0.96%, a figure that remained steady over the 13-year study period, even though prescribing of isotretinoin increased over time. This flat incidence rate effectively rules out the potential for confounding because of assessor bias, especially since many different NHS dermatologists were prescribing the drug, Dr. Butt said.
Half of acne patients prescribed isotretinoin were female and 50% were male. And 15 cases of treatment discontinuation caused by development of depressive symptoms occurred in females, 15 in males. A history of past depressive illness was present in 9.3% of females who started on isotretinoin and in 4.5% of the males. The relative risk of treatment-limiting depressive mood changes was increased 790% among females with a prior history of depressive illness and 440% in males with such a history.
Dr. Butt reported having no financial conflicts regarding her NHS-funded study.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS