User login
A 54-year-old man presented to our hospital with acute-onset left-sided weakness and right facial droop. Three days earlier he had also had migraine-like headaches, which he had never experienced before. He also reported a change in behavior during the past week, which his family had described as inappropriate laughter.
He had no history of hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. He did not smoke or drink alcohol. However, he had an extensive family history of stroke. His mother had a stroke at age 50, his brother a stroke at age 57, and his sister had been admitted for a stroke 1 month earlier at the age of 52.
On examination, he had weakness of the left arm and leg, right facial droop, and hyperactive reflexes on the left side. He had no sensory or cerebellar deficits. He had episodes of laughter during the examination.
We learned that the patient’s sister had undergone a workup showing mutations in the NOTCH3 gene and a skin biopsy study consistent with CADASIL.
Our patient was started on antiplatelet and high-intensity statin therapy. His symptoms improved, and he was discharged to an acute inpatient rehabilitation facility. He was referred to a CADASIL registry.
STROKE AND HEREDITY
CADASIL is a rare hereditary vascular disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is the most common inherited form of small-vessel disease and results from a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene that leads to degeneration of smooth muscle in cerebral blood vessels. It can manifest as migraine with aura, vascular dementia, cognitive impairment, or ischemic stroke.
The diagnosis is based on a clinical picture that typically includes stroke at a young age (age 40 to 50) in the absence of stroke risk factors, or frequent lacunar infarction episodes that can manifest as migraine, lacunar infarct, or dementia.1 Some patients, such as ours, may have subtle nonspecific behavioral changes such as inappropriate laughter, which may herald the development of an infarct.
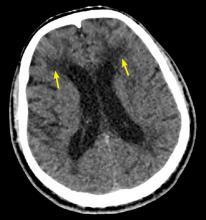
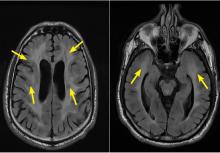
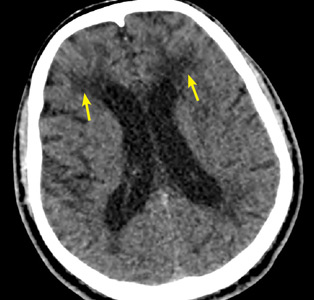
Characteristic findings on MRI are white matter hyperintensities that tend to be bilateral and symmetrical in the periventricular areas. Symmetrical involvement in the temporal lobes has high sensitivity and specificity for CADASIL.2 Biopsy study of the skin, muscle, or sural nerve shows small-vessel changes that include thickening of the media, granular material positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining, and narrowing of the lumen. However, the gold standard for diagnosis is confirmation of the NOTCH3 mutation on chromosome 19.1,2
There is no known treatment for CADASIL.
- Davous P. CADASIL: a review with proposed diagnostic criteria. Eur J Neurol 1998; 5(3):219–233. pmid:10210836
- Stojanov D, Vojinovic S, Aracki-Trenkic A, et al. Imaging characteristics of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2015; 15(1):1–8. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2015.247
A 54-year-old man presented to our hospital with acute-onset left-sided weakness and right facial droop. Three days earlier he had also had migraine-like headaches, which he had never experienced before. He also reported a change in behavior during the past week, which his family had described as inappropriate laughter.
He had no history of hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. He did not smoke or drink alcohol. However, he had an extensive family history of stroke. His mother had a stroke at age 50, his brother a stroke at age 57, and his sister had been admitted for a stroke 1 month earlier at the age of 52.
On examination, he had weakness of the left arm and leg, right facial droop, and hyperactive reflexes on the left side. He had no sensory or cerebellar deficits. He had episodes of laughter during the examination.
We learned that the patient’s sister had undergone a workup showing mutations in the NOTCH3 gene and a skin biopsy study consistent with CADASIL.
Our patient was started on antiplatelet and high-intensity statin therapy. His symptoms improved, and he was discharged to an acute inpatient rehabilitation facility. He was referred to a CADASIL registry.
STROKE AND HEREDITY
CADASIL is a rare hereditary vascular disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is the most common inherited form of small-vessel disease and results from a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene that leads to degeneration of smooth muscle in cerebral blood vessels. It can manifest as migraine with aura, vascular dementia, cognitive impairment, or ischemic stroke.
The diagnosis is based on a clinical picture that typically includes stroke at a young age (age 40 to 50) in the absence of stroke risk factors, or frequent lacunar infarction episodes that can manifest as migraine, lacunar infarct, or dementia.1 Some patients, such as ours, may have subtle nonspecific behavioral changes such as inappropriate laughter, which may herald the development of an infarct.
Characteristic findings on MRI are white matter hyperintensities that tend to be bilateral and symmetrical in the periventricular areas. Symmetrical involvement in the temporal lobes has high sensitivity and specificity for CADASIL.2 Biopsy study of the skin, muscle, or sural nerve shows small-vessel changes that include thickening of the media, granular material positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining, and narrowing of the lumen. However, the gold standard for diagnosis is confirmation of the NOTCH3 mutation on chromosome 19.1,2
There is no known treatment for CADASIL.
A 54-year-old man presented to our hospital with acute-onset left-sided weakness and right facial droop. Three days earlier he had also had migraine-like headaches, which he had never experienced before. He also reported a change in behavior during the past week, which his family had described as inappropriate laughter.
He had no history of hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. He did not smoke or drink alcohol. However, he had an extensive family history of stroke. His mother had a stroke at age 50, his brother a stroke at age 57, and his sister had been admitted for a stroke 1 month earlier at the age of 52.
On examination, he had weakness of the left arm and leg, right facial droop, and hyperactive reflexes on the left side. He had no sensory or cerebellar deficits. He had episodes of laughter during the examination.
We learned that the patient’s sister had undergone a workup showing mutations in the NOTCH3 gene and a skin biopsy study consistent with CADASIL.
Our patient was started on antiplatelet and high-intensity statin therapy. His symptoms improved, and he was discharged to an acute inpatient rehabilitation facility. He was referred to a CADASIL registry.
STROKE AND HEREDITY
CADASIL is a rare hereditary vascular disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is the most common inherited form of small-vessel disease and results from a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene that leads to degeneration of smooth muscle in cerebral blood vessels. It can manifest as migraine with aura, vascular dementia, cognitive impairment, or ischemic stroke.
The diagnosis is based on a clinical picture that typically includes stroke at a young age (age 40 to 50) in the absence of stroke risk factors, or frequent lacunar infarction episodes that can manifest as migraine, lacunar infarct, or dementia.1 Some patients, such as ours, may have subtle nonspecific behavioral changes such as inappropriate laughter, which may herald the development of an infarct.
Characteristic findings on MRI are white matter hyperintensities that tend to be bilateral and symmetrical in the periventricular areas. Symmetrical involvement in the temporal lobes has high sensitivity and specificity for CADASIL.2 Biopsy study of the skin, muscle, or sural nerve shows small-vessel changes that include thickening of the media, granular material positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining, and narrowing of the lumen. However, the gold standard for diagnosis is confirmation of the NOTCH3 mutation on chromosome 19.1,2
There is no known treatment for CADASIL.
- Davous P. CADASIL: a review with proposed diagnostic criteria. Eur J Neurol 1998; 5(3):219–233. pmid:10210836
- Stojanov D, Vojinovic S, Aracki-Trenkic A, et al. Imaging characteristics of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2015; 15(1):1–8. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2015.247
- Davous P. CADASIL: a review with proposed diagnostic criteria. Eur J Neurol 1998; 5(3):219–233. pmid:10210836
- Stojanov D, Vojinovic S, Aracki-Trenkic A, et al. Imaging characteristics of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2015; 15(1):1–8. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2015.247