User login
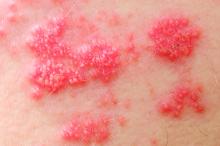
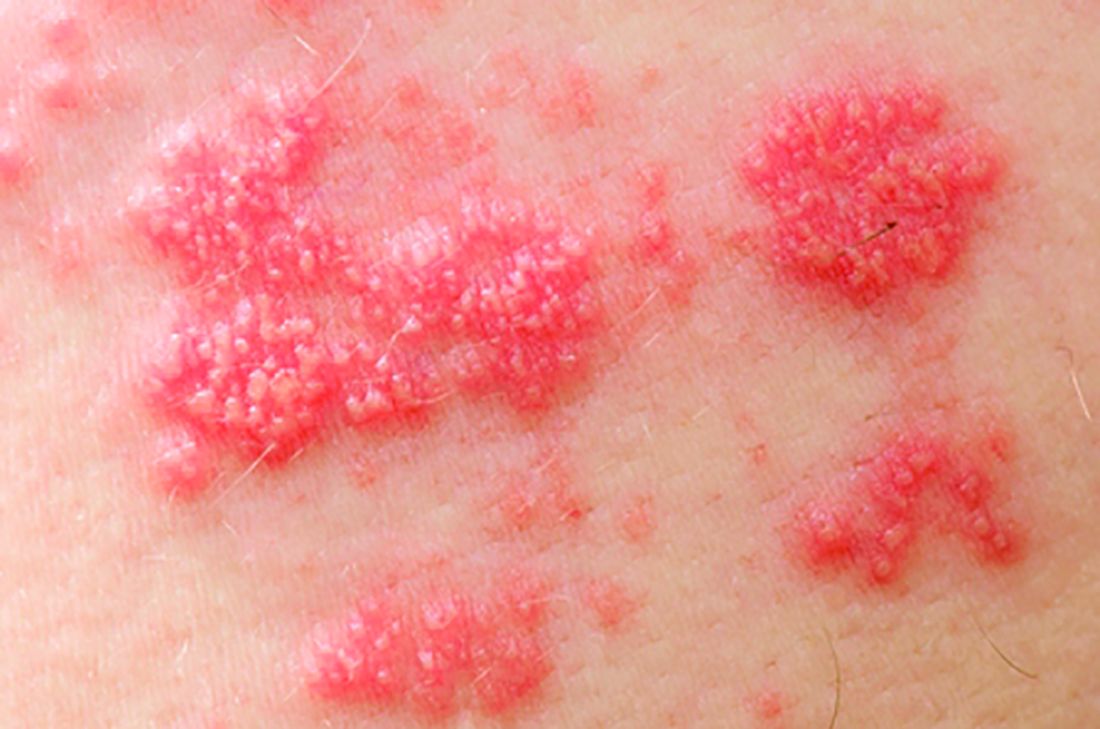
Among patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, a median of 1.4 years and up to 4.4 years of tofacitinib therapy was safe apart from a dose-related increase in risk of herpes zoster infection, according to an integrated analysis of data from five clinical trials.
Compared with placebo, a 5-mg twice-daily maintenance dose of tofacitinib (Xeljanz) produced a 2.1-fold greater risk of herpes zoster infection (95% confidence interval, 0.4-6.0), while a 10-mg, twice-daily dose produced a statistically significant 6.6-fold increase in incidence (95% CI, 3.2-12.2).
With the exception of the higher incidence rate of herpes zoster, “in the overall cohort, the safety profile of tofacitinib was generally similar to that of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies,” wrote William J. Sandborn, MD, director of the inflammatory bowel disease center and professor of medicine, at the University of California, San Diego, and associates. The findings were published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecular Janus kinase inhibitor approved in the United States for treating moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, as well as rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. The recommended ulcerative colitis dose is 10 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks (induction therapy) followed by 5 or 10 mg twice daily (maintenance). The safety of tofacitinib has been studied in patients with rheumatoid arthritis through 9 years of treatment. To begin a similar undertaking in ulcerative colitis, Dr. Sandborn and associates pooled data from three 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled induction trials, as well as one 52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled maintenance trial and one ongoing open-label trial. All patients received twice-daily tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) or placebo.
Among 1,157 tofacitinib recipients in the pooled analysis, 84% received an average of 10 mg twice daily. For every 100 person-years of tofacitinib exposure, there were an estimated 2.0 serious infections, 1.3 opportunistic infections, 4.1 herpes zoster infections, 1.4 malignancies (including nonmelanoma skin cancer, which had an incidence of 0.7), 0.2 major adverse cardiovascular events, and 0.2 gastrointestinal perforations. The likelihood of these events did not increase with time on tofacitinib, the researchers said.
Worsening ulcerative colitis was the most common serious adverse event for patients who received both induction and maintenance therapy. For patients on maintenance therapy, only herpes zoster infection had a higher incidence than placebo, which reached statistical significance at the 10-mg dose. These safety findings resemble those in rheumatoid arthritis trials of tofacitinib, and apart from herpes zoster, they also resemble safety data for vedolizumab (an integrin receptor antagonist), and anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in ulcerative colitis, the researchers wrote.
There were four deaths during the entire tofacitinib ulcerative colitis program, for an incidence rate of 0.2 per 100 person-years of exposure. All occurred in patients receiving 10 mg twice daily. Causes of death were dissecting aortic aneurysm, hepatic angiosarcoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and pulmonary embolism in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma that had metastasized to the peritoneum. Recently, concerns about pulmonary embolism have led the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to recommend against the use of 10-mg twice daily tofacitinib dose in patients at increased risk for pulmonary embolism.
“Compared with prior experience with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis, no new or unexpected safety signals were identified,” the researchers concluded. “These
Pfizer makes tofacitinib, funded the individual trials, and paid for medical writing. Dr. Sandborn disclosed grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Pfizer and many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.035.
As new mechanisms of action become available for ulcerative colitis (UC) drugs, clinicians must weigh the risks versus benefits (i.e., safety vs. efficacy). In this article, Sandborn and colleagues provide additional information on the safety profile of tofacitinib. They report an increased risk of herpes zoster that was dose dependent (sixfold increase on 10 mg twice daily). The overall safety profile was reassuring, is similar to the rheumatoid arthritis population treated with tofacitinib, and is in line with the safety profile of anti-TNF antibodies (excluding the increase risk of zoster). With a nonlive zoster vaccine now available, some have advocated vaccinating all patients being started on tofacitinib. However, there is a theoretical risk of disease exacerbation and ongoing studies that will hopefully answer this important question.
David A. Schwartz, MD, professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Vanderbilt University, Nashville.
As new mechanisms of action become available for ulcerative colitis (UC) drugs, clinicians must weigh the risks versus benefits (i.e., safety vs. efficacy). In this article, Sandborn and colleagues provide additional information on the safety profile of tofacitinib. They report an increased risk of herpes zoster that was dose dependent (sixfold increase on 10 mg twice daily). The overall safety profile was reassuring, is similar to the rheumatoid arthritis population treated with tofacitinib, and is in line with the safety profile of anti-TNF antibodies (excluding the increase risk of zoster). With a nonlive zoster vaccine now available, some have advocated vaccinating all patients being started on tofacitinib. However, there is a theoretical risk of disease exacerbation and ongoing studies that will hopefully answer this important question.
David A. Schwartz, MD, professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Vanderbilt University, Nashville.
As new mechanisms of action become available for ulcerative colitis (UC) drugs, clinicians must weigh the risks versus benefits (i.e., safety vs. efficacy). In this article, Sandborn and colleagues provide additional information on the safety profile of tofacitinib. They report an increased risk of herpes zoster that was dose dependent (sixfold increase on 10 mg twice daily). The overall safety profile was reassuring, is similar to the rheumatoid arthritis population treated with tofacitinib, and is in line with the safety profile of anti-TNF antibodies (excluding the increase risk of zoster). With a nonlive zoster vaccine now available, some have advocated vaccinating all patients being started on tofacitinib. However, there is a theoretical risk of disease exacerbation and ongoing studies that will hopefully answer this important question.
David A. Schwartz, MD, professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Vanderbilt University, Nashville.
Among patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, a median of 1.4 years and up to 4.4 years of tofacitinib therapy was safe apart from a dose-related increase in risk of herpes zoster infection, according to an integrated analysis of data from five clinical trials.
Compared with placebo, a 5-mg twice-daily maintenance dose of tofacitinib (Xeljanz) produced a 2.1-fold greater risk of herpes zoster infection (95% confidence interval, 0.4-6.0), while a 10-mg, twice-daily dose produced a statistically significant 6.6-fold increase in incidence (95% CI, 3.2-12.2).
With the exception of the higher incidence rate of herpes zoster, “in the overall cohort, the safety profile of tofacitinib was generally similar to that of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies,” wrote William J. Sandborn, MD, director of the inflammatory bowel disease center and professor of medicine, at the University of California, San Diego, and associates. The findings were published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecular Janus kinase inhibitor approved in the United States for treating moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, as well as rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. The recommended ulcerative colitis dose is 10 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks (induction therapy) followed by 5 or 10 mg twice daily (maintenance). The safety of tofacitinib has been studied in patients with rheumatoid arthritis through 9 years of treatment. To begin a similar undertaking in ulcerative colitis, Dr. Sandborn and associates pooled data from three 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled induction trials, as well as one 52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled maintenance trial and one ongoing open-label trial. All patients received twice-daily tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) or placebo.
Among 1,157 tofacitinib recipients in the pooled analysis, 84% received an average of 10 mg twice daily. For every 100 person-years of tofacitinib exposure, there were an estimated 2.0 serious infections, 1.3 opportunistic infections, 4.1 herpes zoster infections, 1.4 malignancies (including nonmelanoma skin cancer, which had an incidence of 0.7), 0.2 major adverse cardiovascular events, and 0.2 gastrointestinal perforations. The likelihood of these events did not increase with time on tofacitinib, the researchers said.
Worsening ulcerative colitis was the most common serious adverse event for patients who received both induction and maintenance therapy. For patients on maintenance therapy, only herpes zoster infection had a higher incidence than placebo, which reached statistical significance at the 10-mg dose. These safety findings resemble those in rheumatoid arthritis trials of tofacitinib, and apart from herpes zoster, they also resemble safety data for vedolizumab (an integrin receptor antagonist), and anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in ulcerative colitis, the researchers wrote.
There were four deaths during the entire tofacitinib ulcerative colitis program, for an incidence rate of 0.2 per 100 person-years of exposure. All occurred in patients receiving 10 mg twice daily. Causes of death were dissecting aortic aneurysm, hepatic angiosarcoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and pulmonary embolism in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma that had metastasized to the peritoneum. Recently, concerns about pulmonary embolism have led the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to recommend against the use of 10-mg twice daily tofacitinib dose in patients at increased risk for pulmonary embolism.
“Compared with prior experience with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis, no new or unexpected safety signals were identified,” the researchers concluded. “These
Pfizer makes tofacitinib, funded the individual trials, and paid for medical writing. Dr. Sandborn disclosed grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Pfizer and many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.035.
Among patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, a median of 1.4 years and up to 4.4 years of tofacitinib therapy was safe apart from a dose-related increase in risk of herpes zoster infection, according to an integrated analysis of data from five clinical trials.
Compared with placebo, a 5-mg twice-daily maintenance dose of tofacitinib (Xeljanz) produced a 2.1-fold greater risk of herpes zoster infection (95% confidence interval, 0.4-6.0), while a 10-mg, twice-daily dose produced a statistically significant 6.6-fold increase in incidence (95% CI, 3.2-12.2).
With the exception of the higher incidence rate of herpes zoster, “in the overall cohort, the safety profile of tofacitinib was generally similar to that of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies,” wrote William J. Sandborn, MD, director of the inflammatory bowel disease center and professor of medicine, at the University of California, San Diego, and associates. The findings were published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecular Janus kinase inhibitor approved in the United States for treating moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, as well as rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. The recommended ulcerative colitis dose is 10 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks (induction therapy) followed by 5 or 10 mg twice daily (maintenance). The safety of tofacitinib has been studied in patients with rheumatoid arthritis through 9 years of treatment. To begin a similar undertaking in ulcerative colitis, Dr. Sandborn and associates pooled data from three 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled induction trials, as well as one 52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled maintenance trial and one ongoing open-label trial. All patients received twice-daily tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) or placebo.
Among 1,157 tofacitinib recipients in the pooled analysis, 84% received an average of 10 mg twice daily. For every 100 person-years of tofacitinib exposure, there were an estimated 2.0 serious infections, 1.3 opportunistic infections, 4.1 herpes zoster infections, 1.4 malignancies (including nonmelanoma skin cancer, which had an incidence of 0.7), 0.2 major adverse cardiovascular events, and 0.2 gastrointestinal perforations. The likelihood of these events did not increase with time on tofacitinib, the researchers said.
Worsening ulcerative colitis was the most common serious adverse event for patients who received both induction and maintenance therapy. For patients on maintenance therapy, only herpes zoster infection had a higher incidence than placebo, which reached statistical significance at the 10-mg dose. These safety findings resemble those in rheumatoid arthritis trials of tofacitinib, and apart from herpes zoster, they also resemble safety data for vedolizumab (an integrin receptor antagonist), and anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in ulcerative colitis, the researchers wrote.
There were four deaths during the entire tofacitinib ulcerative colitis program, for an incidence rate of 0.2 per 100 person-years of exposure. All occurred in patients receiving 10 mg twice daily. Causes of death were dissecting aortic aneurysm, hepatic angiosarcoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and pulmonary embolism in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma that had metastasized to the peritoneum. Recently, concerns about pulmonary embolism have led the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to recommend against the use of 10-mg twice daily tofacitinib dose in patients at increased risk for pulmonary embolism.
“Compared with prior experience with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis, no new or unexpected safety signals were identified,” the researchers concluded. “These
Pfizer makes tofacitinib, funded the individual trials, and paid for medical writing. Dr. Sandborn disclosed grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Pfizer and many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.035.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Tofacitinib therapy shows a dose-related increase in risk of herpes zoster in patients with ulcerative colitis.
Major finding: Compared with placebo, a 5-mg twice-daily maintenance dose of tofacitinib produced a 2.1-fold greater risk of herpes zoster infection (95% CI, 0.4-6.0), while a 10-mg twice-daily dose produced a statistically significant 6.6-fold increase in incidence (95% CI, 3.2–12.2).
Study details: Integrated safety analysis of five clinical trials (four randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled) with 1,612.8 total years of exposure (median treatment duration, 1.4 years).
Disclosures: Pfizer makes tofacitinib, funded the individual trials, and paid for medical writing. Dr. Sandborn disclosed grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Pfizer and many other pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.035.