User login
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
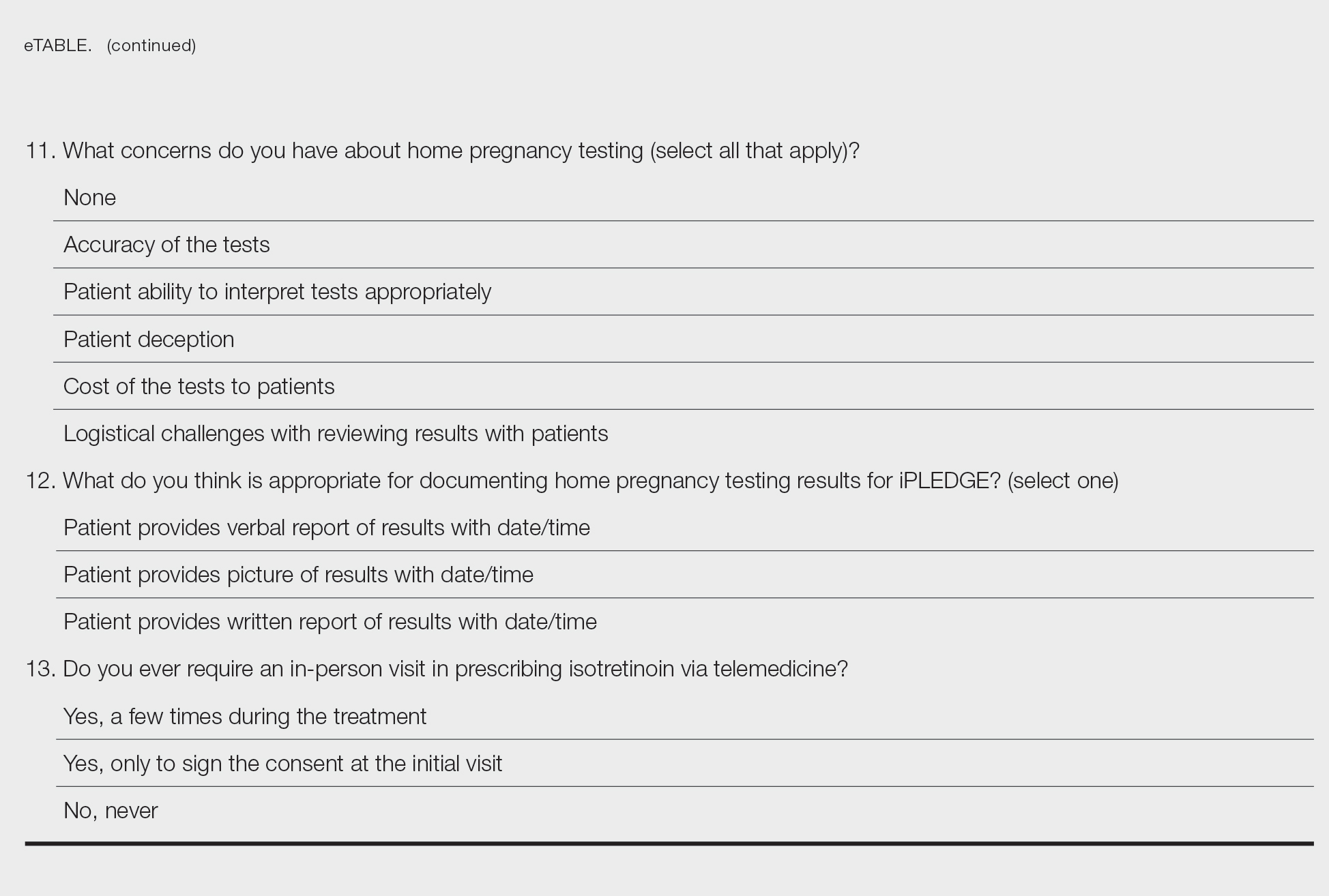
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).
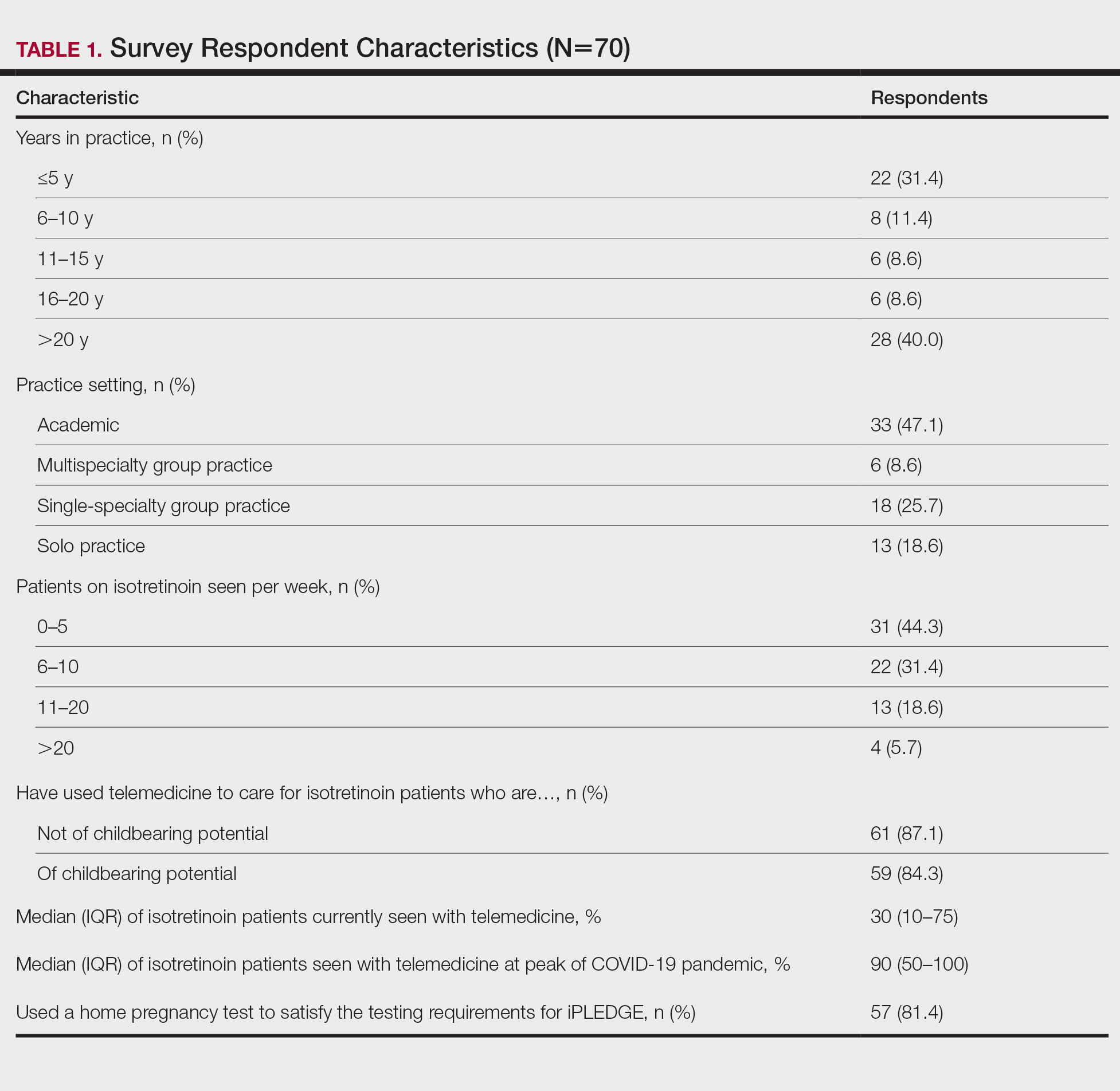
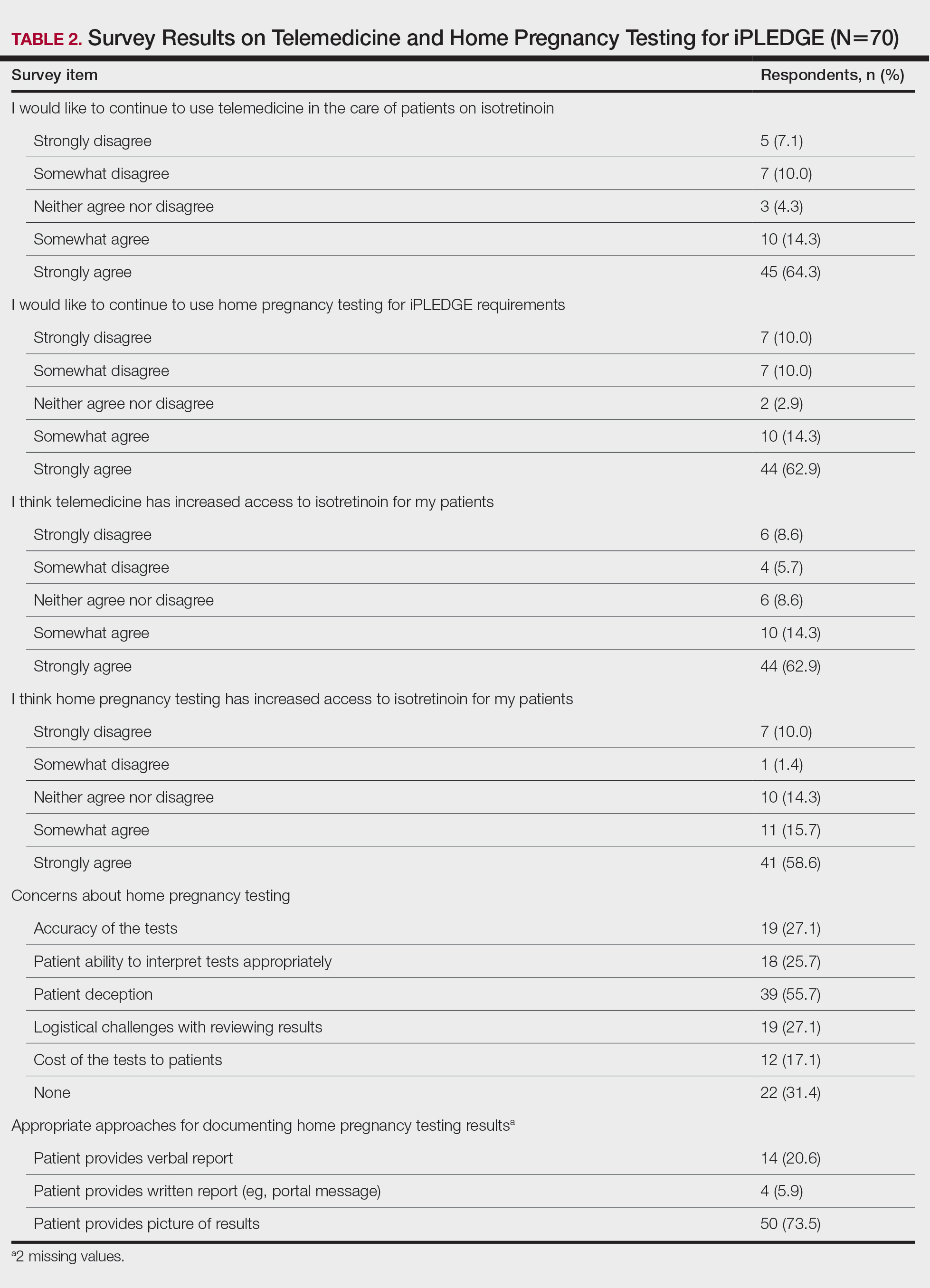
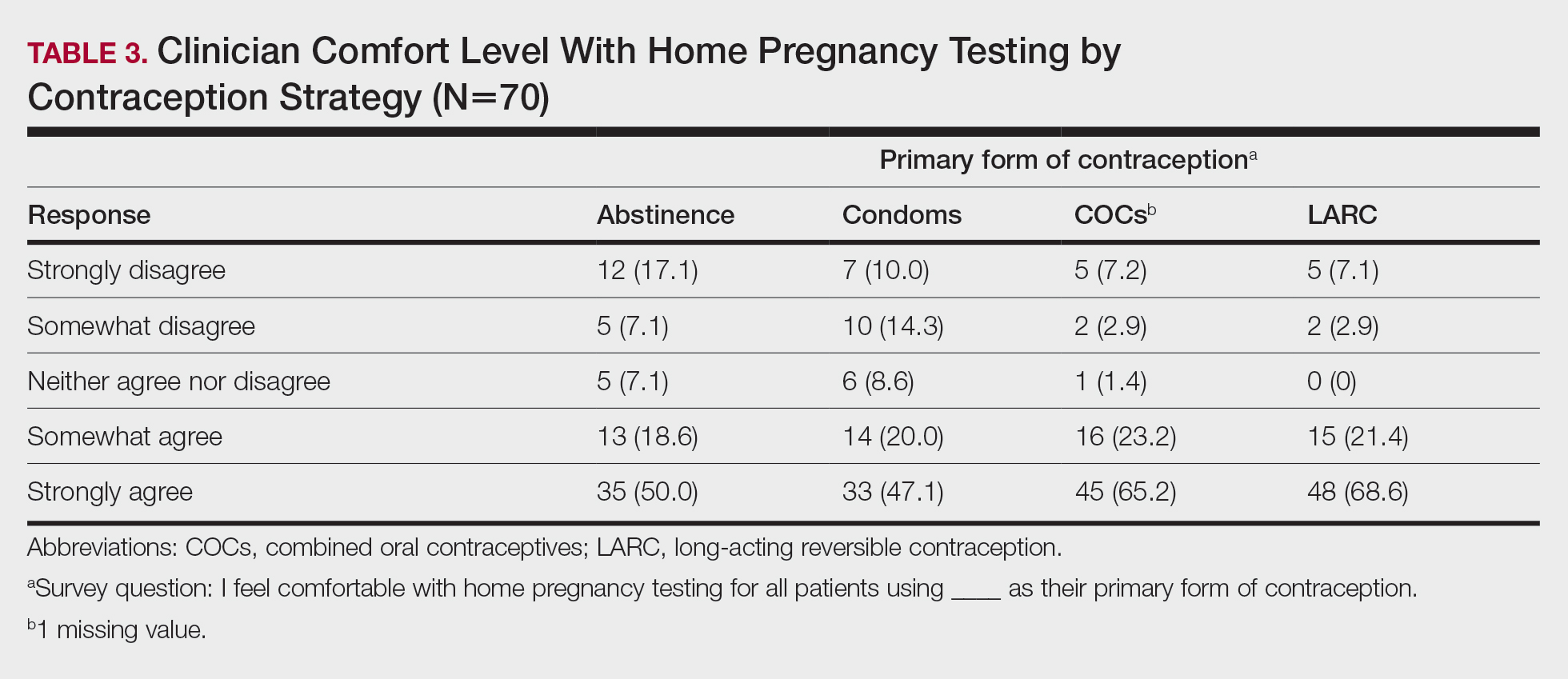
Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).
The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).
In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2
Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).
Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).
The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).
In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2
Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).
Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).
The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).
In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2
Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
PRACTICE POINTS
- The majority of clinicians report that the use of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE has improved access to care and that they would like to continue these practices.
- Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care for patients treated with isotretinoin.