User login
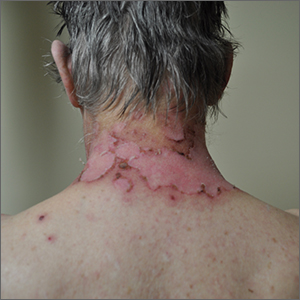
The photo distribution and annular quality of this patient’s rash, combined with his positive autoimmune work-up, led to a diagnosis of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), a nonscarring subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
SCLE is a chronic and relapsing condition that may manifest as either a papulosquamous or annular eruption.1 It most commonly affects areas of sun exposure such as the shoulders, upper back, and extensor surfaces of the arms. This disorder typically affects young or middle-aged women between the ages of 30 and 40 years.
The differential diagnosis of this eruption includes dermatomyositis, polymorphous light eruption, psoriasis, tinea corporis, and other photodermatoses. The etiology of SCLE is multifactorial and may include a genetic susceptibility in combination with environmental triggers that provoke an autoimmune response to sunlight.1 There is strong evidence linking drug-induced SCLE with proton pump inhibitors, anticonvulsants, beta-blockers, terbinafine, and immune modulators.2
As many as 70% of patients with SCLE have positive anti-Ro/SSA autoantibodies, and this is most often associated with Sjogren syndrome.1 Interestingly, SCLE patients often exhibit symptoms that overlap with Sjogren syndrome. Systemic involvement is rare in SCLE, and if present, these symptoms are usually limited to arthritis and myalgia.
Treatment of SCLE includes photo-protective behaviors, topical corticosteroids/calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic therapies such as hydroxychloroquine (first-line), methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil (second-line).2
Our patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg orally bid, with complete resolution of the lesions at his 2 month–follow-up appointment. This case emphasizes the importance of distinguishing SCLE from other subtypes of lupus erythematosus as the prognostic course and treatment varies between these conditions.
Photos courtesy of Kriti Mishra, MD. Text courtesy of Jaimie Lin, BS, Kriti Mishra, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Okon LG, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:391-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2013.07.008
2. Jatwani S, Hearth Holmes MP. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. 2021. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
The photo distribution and annular quality of this patient’s rash, combined with his positive autoimmune work-up, led to a diagnosis of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), a nonscarring subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
SCLE is a chronic and relapsing condition that may manifest as either a papulosquamous or annular eruption.1 It most commonly affects areas of sun exposure such as the shoulders, upper back, and extensor surfaces of the arms. This disorder typically affects young or middle-aged women between the ages of 30 and 40 years.
The differential diagnosis of this eruption includes dermatomyositis, polymorphous light eruption, psoriasis, tinea corporis, and other photodermatoses. The etiology of SCLE is multifactorial and may include a genetic susceptibility in combination with environmental triggers that provoke an autoimmune response to sunlight.1 There is strong evidence linking drug-induced SCLE with proton pump inhibitors, anticonvulsants, beta-blockers, terbinafine, and immune modulators.2
As many as 70% of patients with SCLE have positive anti-Ro/SSA autoantibodies, and this is most often associated with Sjogren syndrome.1 Interestingly, SCLE patients often exhibit symptoms that overlap with Sjogren syndrome. Systemic involvement is rare in SCLE, and if present, these symptoms are usually limited to arthritis and myalgia.
Treatment of SCLE includes photo-protective behaviors, topical corticosteroids/calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic therapies such as hydroxychloroquine (first-line), methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil (second-line).2
Our patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg orally bid, with complete resolution of the lesions at his 2 month–follow-up appointment. This case emphasizes the importance of distinguishing SCLE from other subtypes of lupus erythematosus as the prognostic course and treatment varies between these conditions.
Photos courtesy of Kriti Mishra, MD. Text courtesy of Jaimie Lin, BS, Kriti Mishra, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
The photo distribution and annular quality of this patient’s rash, combined with his positive autoimmune work-up, led to a diagnosis of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), a nonscarring subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
SCLE is a chronic and relapsing condition that may manifest as either a papulosquamous or annular eruption.1 It most commonly affects areas of sun exposure such as the shoulders, upper back, and extensor surfaces of the arms. This disorder typically affects young or middle-aged women between the ages of 30 and 40 years.
The differential diagnosis of this eruption includes dermatomyositis, polymorphous light eruption, psoriasis, tinea corporis, and other photodermatoses. The etiology of SCLE is multifactorial and may include a genetic susceptibility in combination with environmental triggers that provoke an autoimmune response to sunlight.1 There is strong evidence linking drug-induced SCLE with proton pump inhibitors, anticonvulsants, beta-blockers, terbinafine, and immune modulators.2
As many as 70% of patients with SCLE have positive anti-Ro/SSA autoantibodies, and this is most often associated with Sjogren syndrome.1 Interestingly, SCLE patients often exhibit symptoms that overlap with Sjogren syndrome. Systemic involvement is rare in SCLE, and if present, these symptoms are usually limited to arthritis and myalgia.
Treatment of SCLE includes photo-protective behaviors, topical corticosteroids/calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic therapies such as hydroxychloroquine (first-line), methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil (second-line).2
Our patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg orally bid, with complete resolution of the lesions at his 2 month–follow-up appointment. This case emphasizes the importance of distinguishing SCLE from other subtypes of lupus erythematosus as the prognostic course and treatment varies between these conditions.
Photos courtesy of Kriti Mishra, MD. Text courtesy of Jaimie Lin, BS, Kriti Mishra, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Okon LG, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:391-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2013.07.008
2. Jatwani S, Hearth Holmes MP. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. 2021. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
1. Okon LG, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:391-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2013.07.008
2. Jatwani S, Hearth Holmes MP. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. 2021. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.