User login
ORLANDO – Botulinum toxin may have a place in treating psoriasis and rosacea.
There is not a huge body of literature supporting the use of neuromodulators for these conditions, but a smattering of case reports have shown positive results and some clinicians are exploring their off label use, Erin Gilbert, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Her own interest was originally piqued when she began working with Nicole Ward, PhD, director of the morphology core of the Skin Diseases Research Center in the department of dermatology at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, who developed a transgenic mouse model of psoriasis. Dr. Ward discovered that transecting the thoracic-level cutaneous nerves at their entry site into back skin resulted in rapid and significant changes in the psoriatic phenotype (J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Jul;131[7]:1530–8). These included decreases of up to 40% in various immune cell populations and a 30% improvement in acanthosis relative to sham surgery sites on the same animals.
This gave rise to a new thought, Dr. Gilbert said. Could chemical denervation produce similar improvements?
Using the same mouse model, she and Dr. Ward evaluated the effect of injecting botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) 9 units/kg diluted in 1 ml saline at one site, and saline control at another site (J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Jul;132[7]:1927–30). The mice were euthanized at 2 and 6 weeks after treatment. The results were similar to those of the surgical denervation: At 6 weeks, a 25% reduction in acanthosis was observed relative to the control site, with decreases in immune cells and inflammatory markers.
BoNT-A inhibits the release of neurotransmitters by cleaving the SPAP25 protein, an inhibitor of acetylcholine, at the neuromuscular junction. This is the root of the toxin’s ability to relax muscle spasm and decrease hyperhidrosis. The investigators also suggested that BoNT-A inhibits nerve-derived release of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P – important peptides in pain and itch sensation.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Ward also published a case report in which abobotulinumtoxinA was used off label to treat a recalcitrant psoriatic plaque in a 75-year-old woman (J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13[11]:1407-8).
“This patient had psoriatic plaques concentrated on her trunk, arms, buttocks, and legs. She had been using strong topical corticosteroids for quite a long time with incomplete relief. I asked her to withdraw from all steroids for 3 months and then treated one lesion.”
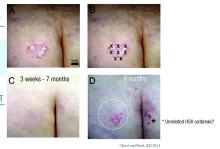
The treated plaque was on the patient’s buttock. Dr. Gilbert injected a total of 30 units of abobotulinumtoxinA intradermally at eight points, about 1 cm apart. Within 3 weeks, there was complete remission of that plaque, sustained for 7 months. During this time, new lesions formed on other areas of her body. At 8 months, the treated plaque returned in the same place.
“Some of my patients had been completely recalcitrant to other therapies, and, following off label injection with neuromodulators, they have had life-changing results. In my experience, the key to consistently successful treatment is using adequate doses of toxin.”
This practice is supported by case reports in 2012 and 2015 (J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11[12]:e76-e79; Dermatology 2015;230:299-301). Some investigators seem to think that, along with the anti-inflammatory and neurotransmitter effects, the toxin alters vascular tone.
Dr. Gilbert acknowledged that these treatments are expensive and cannot, in the case of psoriasis, be used in disseminated disease. However, she said that, for many patients, the relief is so profound and the benefit so long-lasting, that the expense is worth it. An argument in favor of this approach is that, where effective, BoNT-A could be used as a steroid-sparing agent and one that might reduce the need for systemic therapies.
“I will tell you that, sometimes, we get only partial relief and still need adjunctive therapies. Ultimately, neuromodulators may be especially useful for psoriatic plaques that are of cosmetic concern, such as those in the scalp or on the face. Limitations to their use include cost, the need for further studies, and safety concerns, such as muscle weakness.”
Dr. Gilbert had no relevant financial disclosures.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @alz_gal
ORLANDO – Botulinum toxin may have a place in treating psoriasis and rosacea.
There is not a huge body of literature supporting the use of neuromodulators for these conditions, but a smattering of case reports have shown positive results and some clinicians are exploring their off label use, Erin Gilbert, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Her own interest was originally piqued when she began working with Nicole Ward, PhD, director of the morphology core of the Skin Diseases Research Center in the department of dermatology at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, who developed a transgenic mouse model of psoriasis. Dr. Ward discovered that transecting the thoracic-level cutaneous nerves at their entry site into back skin resulted in rapid and significant changes in the psoriatic phenotype (J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Jul;131[7]:1530–8). These included decreases of up to 40% in various immune cell populations and a 30% improvement in acanthosis relative to sham surgery sites on the same animals.
This gave rise to a new thought, Dr. Gilbert said. Could chemical denervation produce similar improvements?
Using the same mouse model, she and Dr. Ward evaluated the effect of injecting botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) 9 units/kg diluted in 1 ml saline at one site, and saline control at another site (J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Jul;132[7]:1927–30). The mice were euthanized at 2 and 6 weeks after treatment. The results were similar to those of the surgical denervation: At 6 weeks, a 25% reduction in acanthosis was observed relative to the control site, with decreases in immune cells and inflammatory markers.
BoNT-A inhibits the release of neurotransmitters by cleaving the SPAP25 protein, an inhibitor of acetylcholine, at the neuromuscular junction. This is the root of the toxin’s ability to relax muscle spasm and decrease hyperhidrosis. The investigators also suggested that BoNT-A inhibits nerve-derived release of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P – important peptides in pain and itch sensation.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Ward also published a case report in which abobotulinumtoxinA was used off label to treat a recalcitrant psoriatic plaque in a 75-year-old woman (J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13[11]:1407-8).
“This patient had psoriatic plaques concentrated on her trunk, arms, buttocks, and legs. She had been using strong topical corticosteroids for quite a long time with incomplete relief. I asked her to withdraw from all steroids for 3 months and then treated one lesion.”
The treated plaque was on the patient’s buttock. Dr. Gilbert injected a total of 30 units of abobotulinumtoxinA intradermally at eight points, about 1 cm apart. Within 3 weeks, there was complete remission of that plaque, sustained for 7 months. During this time, new lesions formed on other areas of her body. At 8 months, the treated plaque returned in the same place.
“Some of my patients had been completely recalcitrant to other therapies, and, following off label injection with neuromodulators, they have had life-changing results. In my experience, the key to consistently successful treatment is using adequate doses of toxin.”
This practice is supported by case reports in 2012 and 2015 (J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11[12]:e76-e79; Dermatology 2015;230:299-301). Some investigators seem to think that, along with the anti-inflammatory and neurotransmitter effects, the toxin alters vascular tone.
Dr. Gilbert acknowledged that these treatments are expensive and cannot, in the case of psoriasis, be used in disseminated disease. However, she said that, for many patients, the relief is so profound and the benefit so long-lasting, that the expense is worth it. An argument in favor of this approach is that, where effective, BoNT-A could be used as a steroid-sparing agent and one that might reduce the need for systemic therapies.
“I will tell you that, sometimes, we get only partial relief and still need adjunctive therapies. Ultimately, neuromodulators may be especially useful for psoriatic plaques that are of cosmetic concern, such as those in the scalp or on the face. Limitations to their use include cost, the need for further studies, and safety concerns, such as muscle weakness.”
Dr. Gilbert had no relevant financial disclosures.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @alz_gal
ORLANDO – Botulinum toxin may have a place in treating psoriasis and rosacea.
There is not a huge body of literature supporting the use of neuromodulators for these conditions, but a smattering of case reports have shown positive results and some clinicians are exploring their off label use, Erin Gilbert, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Her own interest was originally piqued when she began working with Nicole Ward, PhD, director of the morphology core of the Skin Diseases Research Center in the department of dermatology at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, who developed a transgenic mouse model of psoriasis. Dr. Ward discovered that transecting the thoracic-level cutaneous nerves at their entry site into back skin resulted in rapid and significant changes in the psoriatic phenotype (J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Jul;131[7]:1530–8). These included decreases of up to 40% in various immune cell populations and a 30% improvement in acanthosis relative to sham surgery sites on the same animals.
This gave rise to a new thought, Dr. Gilbert said. Could chemical denervation produce similar improvements?
Using the same mouse model, she and Dr. Ward evaluated the effect of injecting botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) 9 units/kg diluted in 1 ml saline at one site, and saline control at another site (J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Jul;132[7]:1927–30). The mice were euthanized at 2 and 6 weeks after treatment. The results were similar to those of the surgical denervation: At 6 weeks, a 25% reduction in acanthosis was observed relative to the control site, with decreases in immune cells and inflammatory markers.
BoNT-A inhibits the release of neurotransmitters by cleaving the SPAP25 protein, an inhibitor of acetylcholine, at the neuromuscular junction. This is the root of the toxin’s ability to relax muscle spasm and decrease hyperhidrosis. The investigators also suggested that BoNT-A inhibits nerve-derived release of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P – important peptides in pain and itch sensation.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Ward also published a case report in which abobotulinumtoxinA was used off label to treat a recalcitrant psoriatic plaque in a 75-year-old woman (J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13[11]:1407-8).
“This patient had psoriatic plaques concentrated on her trunk, arms, buttocks, and legs. She had been using strong topical corticosteroids for quite a long time with incomplete relief. I asked her to withdraw from all steroids for 3 months and then treated one lesion.”
The treated plaque was on the patient’s buttock. Dr. Gilbert injected a total of 30 units of abobotulinumtoxinA intradermally at eight points, about 1 cm apart. Within 3 weeks, there was complete remission of that plaque, sustained for 7 months. During this time, new lesions formed on other areas of her body. At 8 months, the treated plaque returned in the same place.
“Some of my patients had been completely recalcitrant to other therapies, and, following off label injection with neuromodulators, they have had life-changing results. In my experience, the key to consistently successful treatment is using adequate doses of toxin.”
This practice is supported by case reports in 2012 and 2015 (J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11[12]:e76-e79; Dermatology 2015;230:299-301). Some investigators seem to think that, along with the anti-inflammatory and neurotransmitter effects, the toxin alters vascular tone.
Dr. Gilbert acknowledged that these treatments are expensive and cannot, in the case of psoriasis, be used in disseminated disease. However, she said that, for many patients, the relief is so profound and the benefit so long-lasting, that the expense is worth it. An argument in favor of this approach is that, where effective, BoNT-A could be used as a steroid-sparing agent and one that might reduce the need for systemic therapies.
“I will tell you that, sometimes, we get only partial relief and still need adjunctive therapies. Ultimately, neuromodulators may be especially useful for psoriatic plaques that are of cosmetic concern, such as those in the scalp or on the face. Limitations to their use include cost, the need for further studies, and safety concerns, such as muscle weakness.”
Dr. Gilbert had no relevant financial disclosures.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @alz_gal
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAD 17