User login
Six different clinical tests used to identify peripheral arterial disease (PAD) were found to be significantly different in their ability to detect PAD in a population of 50 patients with diabetes, according to a report published online in Primary Care Diabetes.
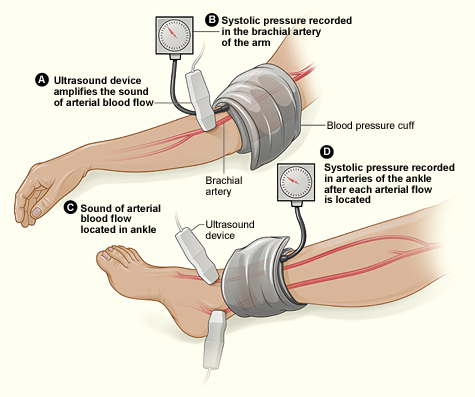
This study assessed the same group of participants with each of the following six tests: Doppler Waveform, toe-brachial pressure index (TBPI), ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI), posterior tibial artery pulse (ATP), transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TCPO), and pulse palpation. The right and left foot were assessed in each participant, yeilding100 limbs for analysis, according to Yvonne Midolo Azzopardi, MD, of the University of Malta in Msida and her colleagues.
The highest percent of participants who were found to have PAD was 93%, as detected by Doppler Waveform, followed by TBPI (72%), ABPI (57%), ATP (35%), TCPO (30%), and pulse palpation (23%). The difference between these percentages was significant at P less than .0005.
“The reported observations suggest that use of only one screening tool in isolation could yield high false results since it is clear that these tests do not concur with each other to a large extent,” the authors stated.
Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues pointed out that the use of more specialized tools, such as duplex scanning, could be compared with these six modalities to detect PAD but that such methods were unlikely to be routinely available to primary care physicians who are at the front lines of making the determination of PAD in patients with diabetes.
“The authors advocate for urgent, more robust studies utilizing a gold standard modality for the diagnosis of PAD in order to provide evidence regarding which noninvasive screening modalities would yield the most valid results. This would significantly reduce the proportion of patients with diabetes who would be falsely identified as having no PAD and subsequently denied beneficial and effective secondary risk factor control,” Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Azzopardi YM et al. 2018. Prim Care Diabetes.. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.08.005.
Six different clinical tests used to identify peripheral arterial disease (PAD) were found to be significantly different in their ability to detect PAD in a population of 50 patients with diabetes, according to a report published online in Primary Care Diabetes.

This study assessed the same group of participants with each of the following six tests: Doppler Waveform, toe-brachial pressure index (TBPI), ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI), posterior tibial artery pulse (ATP), transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TCPO), and pulse palpation. The right and left foot were assessed in each participant, yeilding100 limbs for analysis, according to Yvonne Midolo Azzopardi, MD, of the University of Malta in Msida and her colleagues.
The highest percent of participants who were found to have PAD was 93%, as detected by Doppler Waveform, followed by TBPI (72%), ABPI (57%), ATP (35%), TCPO (30%), and pulse palpation (23%). The difference between these percentages was significant at P less than .0005.
“The reported observations suggest that use of only one screening tool in isolation could yield high false results since it is clear that these tests do not concur with each other to a large extent,” the authors stated.
Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues pointed out that the use of more specialized tools, such as duplex scanning, could be compared with these six modalities to detect PAD but that such methods were unlikely to be routinely available to primary care physicians who are at the front lines of making the determination of PAD in patients with diabetes.
“The authors advocate for urgent, more robust studies utilizing a gold standard modality for the diagnosis of PAD in order to provide evidence regarding which noninvasive screening modalities would yield the most valid results. This would significantly reduce the proportion of patients with diabetes who would be falsely identified as having no PAD and subsequently denied beneficial and effective secondary risk factor control,” Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Azzopardi YM et al. 2018. Prim Care Diabetes.. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.08.005.
Six different clinical tests used to identify peripheral arterial disease (PAD) were found to be significantly different in their ability to detect PAD in a population of 50 patients with diabetes, according to a report published online in Primary Care Diabetes.

This study assessed the same group of participants with each of the following six tests: Doppler Waveform, toe-brachial pressure index (TBPI), ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI), posterior tibial artery pulse (ATP), transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TCPO), and pulse palpation. The right and left foot were assessed in each participant, yeilding100 limbs for analysis, according to Yvonne Midolo Azzopardi, MD, of the University of Malta in Msida and her colleagues.
The highest percent of participants who were found to have PAD was 93%, as detected by Doppler Waveform, followed by TBPI (72%), ABPI (57%), ATP (35%), TCPO (30%), and pulse palpation (23%). The difference between these percentages was significant at P less than .0005.
“The reported observations suggest that use of only one screening tool in isolation could yield high false results since it is clear that these tests do not concur with each other to a large extent,” the authors stated.
Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues pointed out that the use of more specialized tools, such as duplex scanning, could be compared with these six modalities to detect PAD but that such methods were unlikely to be routinely available to primary care physicians who are at the front lines of making the determination of PAD in patients with diabetes.
“The authors advocate for urgent, more robust studies utilizing a gold standard modality for the diagnosis of PAD in order to provide evidence regarding which noninvasive screening modalities would yield the most valid results. This would significantly reduce the proportion of patients with diabetes who would be falsely identified as having no PAD and subsequently denied beneficial and effective secondary risk factor control,” Dr. Azzopardi and her colleagues concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Azzopardi YM et al. 2018. Prim Care Diabetes.. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.08.005.
FROM PRIMARY CARE DIABETES
Key clinical point: Six different tests used to identify PAD differed significantly in their ability to detect the disease.
Major finding: Detection ranged from 93% to 23% in the same group of patients.
Study details: Both legs of 50 patients with diabetes were assessed for PAD using six screening modalities.
Disclosures: The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
Source: Azzopardi YM et al. 2018. Prim Care Diabetes. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.08.005.