User login
A novel five-strain probiotic blend could provide relief for patients with functional GI disorders, a new study shows.
The combination “improved patient’s functional GI symptoms and displayed a favorable safety profile,” said lead study investigator Lucinda A. Harris, MD, MS, from the Mayo Clinic School of Medicine in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Results of this study are promising, and additional studies would support the novel probiotic blend’s efficacy, safety, and durability of effect,” said Dr. Harris during her presentation at the virtual American College of Gastroenterology 2020 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Treatment with probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium lactis strains Bl-04, Bi-07, and HN019 and Lactobacillus strains L. acidophilus NCFM and L. paracasei Lpc-37 – administered alone or in multistrain blends – has been shown to improve diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation symptoms in patients with GI disturbances, she reported.
“Multiple pathophysiologic processes may cause functional GI symptoms, including altered gut microbiota,” she said. “The administration of probiotics can impact intestinal microbial balance, thereby contributing to improvement in functional GI symptoms.”
In their study, Dr. Harris and her colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of a five-strain probiotic blend – composed of Bl-04, Bi-07, HN019, NCFM, and Lpc-37 – in people with functional GI disturbances.
In the open-label, multicenter study, all 188 adult participants (mean age, 44.1 years; 72.3% female) demonstrated symptoms of functional GI disturbances. Each received an oral capsule of the probiotic blend once daily for 30 days.
Patients were assessed at multiple time points: screening (days –15 to –1), baseline (day 1), day 14, day 30, and a follow-up visit (day 42). The study’s primary efficacy endpoint was patient-reported improvement in overall GI well-being at day 30. Secondary outcomes included changes in GI symptoms, assessed with the 11-point GI Health Symptom Questionnaire. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was assessed during all patient visits.
By day 30, 85.1% of patients had achieved the primary endpoint and indicated a positive response when asked about their overall GI well-being. All of the improvements reported at day 30 were generally observed at day 14 as well.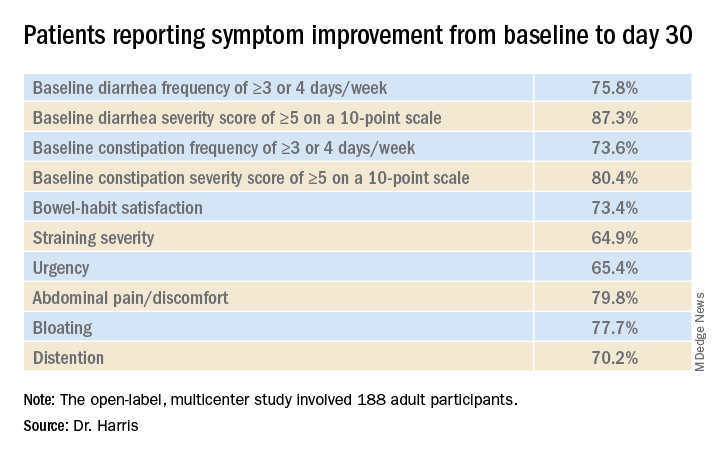
“In addition, we observed a mean decrease in I-FABP [intestinal fatty-acid binding protein] of 32.7% in patients with the highest quartile of baseline I-FABP levels,” Dr. Harris reported.
With respect to tolerability, adverse events were reported by 18.6% of participants and treatment-related adverse events were reported by 8.0%.
“Overall, 35 patients experienced a treatment-emergent adverse event,” she said. “Six patients experienced flatulence and five patients had a cough.” There were no deaths, no serious treatment-emergent adverse events, and no drug-related discontinuations
Placebo effect?
“We know that the biome has a role in modulating a number of physiologic processes, so looking at biomic influence for functional disease makes sense,” said David A. Johnson, MD, from the Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, who was not involved in the study.
However, one of the limitations of this study is the potential for a marked placebo effect, he said in an interview. “When you do an open-label trial in functional diseases, there’s a high placebo rate response. This effect is less pronounced in longer trials, but shorter trials like this one definitely carry the risk of increased placebo responses.”
“Although promising, a randomized control trial evaluating the microbiome as a response to the treatment intervention would be extremely helpful in defining the true role of effect,” he added.
This study was funded by Bausch Health Americas, Inc. Harris reports financial relationships with Allergan, Ironwood, and Takeda. Johnson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships; he writes the Johnson on Gastroenterology blog on Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel five-strain probiotic blend could provide relief for patients with functional GI disorders, a new study shows.
The combination “improved patient’s functional GI symptoms and displayed a favorable safety profile,” said lead study investigator Lucinda A. Harris, MD, MS, from the Mayo Clinic School of Medicine in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Results of this study are promising, and additional studies would support the novel probiotic blend’s efficacy, safety, and durability of effect,” said Dr. Harris during her presentation at the virtual American College of Gastroenterology 2020 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Treatment with probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium lactis strains Bl-04, Bi-07, and HN019 and Lactobacillus strains L. acidophilus NCFM and L. paracasei Lpc-37 – administered alone or in multistrain blends – has been shown to improve diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation symptoms in patients with GI disturbances, she reported.
“Multiple pathophysiologic processes may cause functional GI symptoms, including altered gut microbiota,” she said. “The administration of probiotics can impact intestinal microbial balance, thereby contributing to improvement in functional GI symptoms.”
In their study, Dr. Harris and her colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of a five-strain probiotic blend – composed of Bl-04, Bi-07, HN019, NCFM, and Lpc-37 – in people with functional GI disturbances.
In the open-label, multicenter study, all 188 adult participants (mean age, 44.1 years; 72.3% female) demonstrated symptoms of functional GI disturbances. Each received an oral capsule of the probiotic blend once daily for 30 days.
Patients were assessed at multiple time points: screening (days –15 to –1), baseline (day 1), day 14, day 30, and a follow-up visit (day 42). The study’s primary efficacy endpoint was patient-reported improvement in overall GI well-being at day 30. Secondary outcomes included changes in GI symptoms, assessed with the 11-point GI Health Symptom Questionnaire. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was assessed during all patient visits.
By day 30, 85.1% of patients had achieved the primary endpoint and indicated a positive response when asked about their overall GI well-being. All of the improvements reported at day 30 were generally observed at day 14 as well.
“In addition, we observed a mean decrease in I-FABP [intestinal fatty-acid binding protein] of 32.7% in patients with the highest quartile of baseline I-FABP levels,” Dr. Harris reported.
With respect to tolerability, adverse events were reported by 18.6% of participants and treatment-related adverse events were reported by 8.0%.
“Overall, 35 patients experienced a treatment-emergent adverse event,” she said. “Six patients experienced flatulence and five patients had a cough.” There were no deaths, no serious treatment-emergent adverse events, and no drug-related discontinuations
Placebo effect?
“We know that the biome has a role in modulating a number of physiologic processes, so looking at biomic influence for functional disease makes sense,” said David A. Johnson, MD, from the Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, who was not involved in the study.
However, one of the limitations of this study is the potential for a marked placebo effect, he said in an interview. “When you do an open-label trial in functional diseases, there’s a high placebo rate response. This effect is less pronounced in longer trials, but shorter trials like this one definitely carry the risk of increased placebo responses.”
“Although promising, a randomized control trial evaluating the microbiome as a response to the treatment intervention would be extremely helpful in defining the true role of effect,” he added.
This study was funded by Bausch Health Americas, Inc. Harris reports financial relationships with Allergan, Ironwood, and Takeda. Johnson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships; he writes the Johnson on Gastroenterology blog on Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel five-strain probiotic blend could provide relief for patients with functional GI disorders, a new study shows.
The combination “improved patient’s functional GI symptoms and displayed a favorable safety profile,” said lead study investigator Lucinda A. Harris, MD, MS, from the Mayo Clinic School of Medicine in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Results of this study are promising, and additional studies would support the novel probiotic blend’s efficacy, safety, and durability of effect,” said Dr. Harris during her presentation at the virtual American College of Gastroenterology 2020 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Treatment with probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium lactis strains Bl-04, Bi-07, and HN019 and Lactobacillus strains L. acidophilus NCFM and L. paracasei Lpc-37 – administered alone or in multistrain blends – has been shown to improve diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation symptoms in patients with GI disturbances, she reported.
“Multiple pathophysiologic processes may cause functional GI symptoms, including altered gut microbiota,” she said. “The administration of probiotics can impact intestinal microbial balance, thereby contributing to improvement in functional GI symptoms.”
In their study, Dr. Harris and her colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of a five-strain probiotic blend – composed of Bl-04, Bi-07, HN019, NCFM, and Lpc-37 – in people with functional GI disturbances.
In the open-label, multicenter study, all 188 adult participants (mean age, 44.1 years; 72.3% female) demonstrated symptoms of functional GI disturbances. Each received an oral capsule of the probiotic blend once daily for 30 days.
Patients were assessed at multiple time points: screening (days –15 to –1), baseline (day 1), day 14, day 30, and a follow-up visit (day 42). The study’s primary efficacy endpoint was patient-reported improvement in overall GI well-being at day 30. Secondary outcomes included changes in GI symptoms, assessed with the 11-point GI Health Symptom Questionnaire. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was assessed during all patient visits.
By day 30, 85.1% of patients had achieved the primary endpoint and indicated a positive response when asked about their overall GI well-being. All of the improvements reported at day 30 were generally observed at day 14 as well.
“In addition, we observed a mean decrease in I-FABP [intestinal fatty-acid binding protein] of 32.7% in patients with the highest quartile of baseline I-FABP levels,” Dr. Harris reported.
With respect to tolerability, adverse events were reported by 18.6% of participants and treatment-related adverse events were reported by 8.0%.
“Overall, 35 patients experienced a treatment-emergent adverse event,” she said. “Six patients experienced flatulence and five patients had a cough.” There were no deaths, no serious treatment-emergent adverse events, and no drug-related discontinuations
Placebo effect?
“We know that the biome has a role in modulating a number of physiologic processes, so looking at biomic influence for functional disease makes sense,” said David A. Johnson, MD, from the Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, who was not involved in the study.
However, one of the limitations of this study is the potential for a marked placebo effect, he said in an interview. “When you do an open-label trial in functional diseases, there’s a high placebo rate response. This effect is less pronounced in longer trials, but shorter trials like this one definitely carry the risk of increased placebo responses.”
“Although promising, a randomized control trial evaluating the microbiome as a response to the treatment intervention would be extremely helpful in defining the true role of effect,” he added.
This study was funded by Bausch Health Americas, Inc. Harris reports financial relationships with Allergan, Ironwood, and Takeda. Johnson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships; he writes the Johnson on Gastroenterology blog on Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.