User login
After more than 10 hours of intense debate, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel gave its support to a premarket approval application (PMA) for the TransMedics Organ Care System (OCS) Heart system.
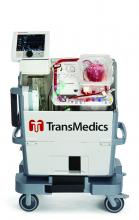
The OCS Heart is a portable extracorporeal perfusion and monitoring system designed to keep a donor heart in a normothermic, beating state. The “heart in a box” technology allows donor hearts to be transported across longer distances than is possible with standard cold storage, which can safely preserve donor hearts for about 4 hours.
The Circulatory System Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee voted 12 to 5, with 1 abstention, that the benefits of the OCS Heart System outweigh its risks.
The panel voted in favor of the OCS Heart being effective (10 yes, 6 no, and 2 abstaining) and safe (9 yes, 7 no, 2 abstaining) but not without mixed feelings.
James Blankenship, MD, a cardiologist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, voted yes to all three questions but said: “If it had been compared to standard of care, I would have voted no to all three. But if it’s compared to getting an [left ventricular assist device] LVAD or not getting a heart at all, I would say the benefits outweigh the risks.”
Marc R. Katz, MD, chief of cardiothoracic surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, also gave universal support, noting that the rate of heart transplantations has been flat for years. “This is a big step forward toward being able to expand that number. Now all that said, it obviously was a less-than-perfect study and I do think there needs to be some constraints put on the utilization.”
The panel reviewed data from the single-arm OCS Heart EXPAND trial and associated EXPAND Continued Access Protocol (CAP), as well the sponsor’s first OCS Heart trial, PROCEED II.
EXPAND met its effectiveness endpoint, with 88% of donor hearts successfully transplanted, an 8% incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction (PGD) 24 hours after transplantation, and 94.6% survival at 30 days.
Data from 41 patients with 30-day follow-up in the ongoing EXPAND CAP show 91% of donor hearts were utilized, a 2.4% incidence of severe PGD, and 100% 30-day survival.
The sponsor and the FDA clashed over changes made to the trial after the PMA was submitted, the appropriateness of the effectiveness outcome, and claims by the FDA that there was substantial overlap in demographic characteristics between the extended criteria donor hearts in the EXPAND trials and the standard criteria donor hearts in PROCEED II.
TransMedics previously submitted a PMA based on PROCEED II but it noted in submitted documents that it was withdrawn because of “fundamental disagreements with FDA” on the interpretation of a post hoc analysis with United Network for Organ Sharing registry data that identified increased all-cause mortality risk but comparable cardiac-related mortality in patients with OCS hearts.
During the marathon hearing, FDA officials presented several post hoc analyses, including one stratified by donor inclusion criteria, in which 30-day survival estimates were worse in recipients of single-criterion organs than for those receiving donor organs with multiple inclusion criteria (85% vs. 91.4%). In a second analysis, 2-year point estimates of survival also trended lower with donor organs having only one extended criterion.
Reported EXPAND CAP 6- and 12-month survival estimates were 100% and 93%, respectively, which was higher than EXPAND (93% and 84%), but there was substantial censoring (>50%) at 6 months and beyond, FDA officials said.
When EXPAND and CAP data were pooled, modeled survival curves shifted upward but there was a substantial site effect, with a single site contributing 46% of data, which may affect generalizability of the results, they noted.
“I voted yes for safety, no for efficacy, and no for approval and I’d just like to say I found this to be the most difficult vote in my experience on this panel,” John Hirshfeld, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “I was very concerned that the PROCEED data suggests a possible harm, and in the absence of an interpretable comparator for the EXPAND trial, it’s really not possible to decide if there’s efficacy.”
Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at Saint Luke’s Hospital of Kansas City (Mo.), said, “I voted no on safety; I’m not going to give the company a pass. I think their animal data was sorely lacking and a lot of issues over the last 10 years could have been addressed with some key animal studies.
“For efficacy and risk/benefit, I voted yes for both,” he said. “Had this been standard of care and only PROCEED II, I would have voted no, but I do think there are a lot of hearts that go in the bucket and this is a challenging population.”
More than a dozen physicians and patients spoke at the open public hearing about the potential for the device to expand donor heart utilization, including a recipient whose own father died while waiting on the transplant list. Only about 3 out of every 10 donated hearts are used for transplant. To ensure fair access, particularly for patients in rural areas, federal changes in 2020 mandate that organs be allocated to the sickest patients first.
Data showed that the OCS Heart System was associated with shorter waiting list times, compared with U.S. averages but longer preservation times than cold static preservation.
In all, 13% of accepted donor organs were subsequently turned down after OCS heart preservation. Lactate levels were cited as the principal reason for turn-down but, FDA officials said, the validity of using lactate as a marker for transplantability is unclear.
Pathologic analysis of OCS Heart turned-down donor hearts with stable antemortem hemodynamics, normal or near-normal anatomy and normal ventricular function by echocardiography, and autopsy findings of acute diffuse or multifocal myocardial damage “suggest that in an important proportion of cases the OCS Heart system did not provide effective organ preservation or its use caused severe myocardial damage to what might have been an acceptable graft for transplant,” said Andrew Farb, MD, chief medical officer of the FDA’s Office of Cardiovascular Devices.
Proposed indication
In the present PMA, the OCS Heart System is indicated for donor hearts with one or more of the following characteristics: an expected cross-clamp or ischemic time of at least 4 hours because of donor or recipient characteristics; or an expected total cross-clamp time of at least 2 hours plus one of the following risk factors: donor age 55 or older, history of cardiac arrest and downtime of at least 20 minutes, history of alcoholism, history of diabetes, donor ejection fraction of 40%-50%,history of left ventricular hypertrophy, and donor angiogram with luminal irregularities but no significant coronary artery disease
Several members voiced concern about “indication creep” should the device be approved by the FDA, and highlighted the 2-hour cross-clamp time plus wide-ranging risk factors.
“I’m a surgeon and I voted no on all three counts,” said Murray H. Kwon, MD, Ronald Reagan University of California, Los Angeles Medical Center. “As far as risk/benefit, if it was just limited to one group – the 4-hour plus – I would say yes, but if you’re going to tell me that there’s a risk/benefit for the 2-hour with the alcoholic, I don’t know how that was proved in anything.”
Dr. Kwon was also troubled by lack of proper controls and by the one quarter of patients who ended up on mechanical circulatory support in the first 30 days after transplant. “I find that highly aberrant.”
Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, head of cardiovascular medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said the unmet need for patients with refractory, end-stage heart failure is challenging and quite emotional, but also voted no across the board, citing concerns about a lack of comparator in the EXPAND trials and overall out-of-body ischemic time.
“As it relates to risk/benefit, I thought long and hard about voting yes despite all the unknowns because of this emotion, but ultimately I voted no because of the secondary 2-hours plus alcoholism, diabetes, or minor coronary disease, in which the ischemic burden and ongoing lactate production concern me,” he said.
Although the panel decision is nonbinding, there was strong support from the committee members for a randomized, postapproval trial and more complete animal studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After more than 10 hours of intense debate, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel gave its support to a premarket approval application (PMA) for the TransMedics Organ Care System (OCS) Heart system.
The OCS Heart is a portable extracorporeal perfusion and monitoring system designed to keep a donor heart in a normothermic, beating state. The “heart in a box” technology allows donor hearts to be transported across longer distances than is possible with standard cold storage, which can safely preserve donor hearts for about 4 hours.
The Circulatory System Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee voted 12 to 5, with 1 abstention, that the benefits of the OCS Heart System outweigh its risks.
The panel voted in favor of the OCS Heart being effective (10 yes, 6 no, and 2 abstaining) and safe (9 yes, 7 no, 2 abstaining) but not without mixed feelings.
James Blankenship, MD, a cardiologist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, voted yes to all three questions but said: “If it had been compared to standard of care, I would have voted no to all three. But if it’s compared to getting an [left ventricular assist device] LVAD or not getting a heart at all, I would say the benefits outweigh the risks.”
Marc R. Katz, MD, chief of cardiothoracic surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, also gave universal support, noting that the rate of heart transplantations has been flat for years. “This is a big step forward toward being able to expand that number. Now all that said, it obviously was a less-than-perfect study and I do think there needs to be some constraints put on the utilization.”
The panel reviewed data from the single-arm OCS Heart EXPAND trial and associated EXPAND Continued Access Protocol (CAP), as well the sponsor’s first OCS Heart trial, PROCEED II.
EXPAND met its effectiveness endpoint, with 88% of donor hearts successfully transplanted, an 8% incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction (PGD) 24 hours after transplantation, and 94.6% survival at 30 days.
Data from 41 patients with 30-day follow-up in the ongoing EXPAND CAP show 91% of donor hearts were utilized, a 2.4% incidence of severe PGD, and 100% 30-day survival.
The sponsor and the FDA clashed over changes made to the trial after the PMA was submitted, the appropriateness of the effectiveness outcome, and claims by the FDA that there was substantial overlap in demographic characteristics between the extended criteria donor hearts in the EXPAND trials and the standard criteria donor hearts in PROCEED II.
TransMedics previously submitted a PMA based on PROCEED II but it noted in submitted documents that it was withdrawn because of “fundamental disagreements with FDA” on the interpretation of a post hoc analysis with United Network for Organ Sharing registry data that identified increased all-cause mortality risk but comparable cardiac-related mortality in patients with OCS hearts.
During the marathon hearing, FDA officials presented several post hoc analyses, including one stratified by donor inclusion criteria, in which 30-day survival estimates were worse in recipients of single-criterion organs than for those receiving donor organs with multiple inclusion criteria (85% vs. 91.4%). In a second analysis, 2-year point estimates of survival also trended lower with donor organs having only one extended criterion.
Reported EXPAND CAP 6- and 12-month survival estimates were 100% and 93%, respectively, which was higher than EXPAND (93% and 84%), but there was substantial censoring (>50%) at 6 months and beyond, FDA officials said.
When EXPAND and CAP data were pooled, modeled survival curves shifted upward but there was a substantial site effect, with a single site contributing 46% of data, which may affect generalizability of the results, they noted.
“I voted yes for safety, no for efficacy, and no for approval and I’d just like to say I found this to be the most difficult vote in my experience on this panel,” John Hirshfeld, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “I was very concerned that the PROCEED data suggests a possible harm, and in the absence of an interpretable comparator for the EXPAND trial, it’s really not possible to decide if there’s efficacy.”
Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at Saint Luke’s Hospital of Kansas City (Mo.), said, “I voted no on safety; I’m not going to give the company a pass. I think their animal data was sorely lacking and a lot of issues over the last 10 years could have been addressed with some key animal studies.
“For efficacy and risk/benefit, I voted yes for both,” he said. “Had this been standard of care and only PROCEED II, I would have voted no, but I do think there are a lot of hearts that go in the bucket and this is a challenging population.”
More than a dozen physicians and patients spoke at the open public hearing about the potential for the device to expand donor heart utilization, including a recipient whose own father died while waiting on the transplant list. Only about 3 out of every 10 donated hearts are used for transplant. To ensure fair access, particularly for patients in rural areas, federal changes in 2020 mandate that organs be allocated to the sickest patients first.
Data showed that the OCS Heart System was associated with shorter waiting list times, compared with U.S. averages but longer preservation times than cold static preservation.
In all, 13% of accepted donor organs were subsequently turned down after OCS heart preservation. Lactate levels were cited as the principal reason for turn-down but, FDA officials said, the validity of using lactate as a marker for transplantability is unclear.
Pathologic analysis of OCS Heart turned-down donor hearts with stable antemortem hemodynamics, normal or near-normal anatomy and normal ventricular function by echocardiography, and autopsy findings of acute diffuse or multifocal myocardial damage “suggest that in an important proportion of cases the OCS Heart system did not provide effective organ preservation or its use caused severe myocardial damage to what might have been an acceptable graft for transplant,” said Andrew Farb, MD, chief medical officer of the FDA’s Office of Cardiovascular Devices.
Proposed indication
In the present PMA, the OCS Heart System is indicated for donor hearts with one or more of the following characteristics: an expected cross-clamp or ischemic time of at least 4 hours because of donor or recipient characteristics; or an expected total cross-clamp time of at least 2 hours plus one of the following risk factors: donor age 55 or older, history of cardiac arrest and downtime of at least 20 minutes, history of alcoholism, history of diabetes, donor ejection fraction of 40%-50%,history of left ventricular hypertrophy, and donor angiogram with luminal irregularities but no significant coronary artery disease
Several members voiced concern about “indication creep” should the device be approved by the FDA, and highlighted the 2-hour cross-clamp time plus wide-ranging risk factors.
“I’m a surgeon and I voted no on all three counts,” said Murray H. Kwon, MD, Ronald Reagan University of California, Los Angeles Medical Center. “As far as risk/benefit, if it was just limited to one group – the 4-hour plus – I would say yes, but if you’re going to tell me that there’s a risk/benefit for the 2-hour with the alcoholic, I don’t know how that was proved in anything.”
Dr. Kwon was also troubled by lack of proper controls and by the one quarter of patients who ended up on mechanical circulatory support in the first 30 days after transplant. “I find that highly aberrant.”
Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, head of cardiovascular medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said the unmet need for patients with refractory, end-stage heart failure is challenging and quite emotional, but also voted no across the board, citing concerns about a lack of comparator in the EXPAND trials and overall out-of-body ischemic time.
“As it relates to risk/benefit, I thought long and hard about voting yes despite all the unknowns because of this emotion, but ultimately I voted no because of the secondary 2-hours plus alcoholism, diabetes, or minor coronary disease, in which the ischemic burden and ongoing lactate production concern me,” he said.
Although the panel decision is nonbinding, there was strong support from the committee members for a randomized, postapproval trial and more complete animal studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After more than 10 hours of intense debate, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel gave its support to a premarket approval application (PMA) for the TransMedics Organ Care System (OCS) Heart system.
The OCS Heart is a portable extracorporeal perfusion and monitoring system designed to keep a donor heart in a normothermic, beating state. The “heart in a box” technology allows donor hearts to be transported across longer distances than is possible with standard cold storage, which can safely preserve donor hearts for about 4 hours.
The Circulatory System Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee voted 12 to 5, with 1 abstention, that the benefits of the OCS Heart System outweigh its risks.
The panel voted in favor of the OCS Heart being effective (10 yes, 6 no, and 2 abstaining) and safe (9 yes, 7 no, 2 abstaining) but not without mixed feelings.
James Blankenship, MD, a cardiologist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, voted yes to all three questions but said: “If it had been compared to standard of care, I would have voted no to all three. But if it’s compared to getting an [left ventricular assist device] LVAD or not getting a heart at all, I would say the benefits outweigh the risks.”
Marc R. Katz, MD, chief of cardiothoracic surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, also gave universal support, noting that the rate of heart transplantations has been flat for years. “This is a big step forward toward being able to expand that number. Now all that said, it obviously was a less-than-perfect study and I do think there needs to be some constraints put on the utilization.”
The panel reviewed data from the single-arm OCS Heart EXPAND trial and associated EXPAND Continued Access Protocol (CAP), as well the sponsor’s first OCS Heart trial, PROCEED II.
EXPAND met its effectiveness endpoint, with 88% of donor hearts successfully transplanted, an 8% incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction (PGD) 24 hours after transplantation, and 94.6% survival at 30 days.
Data from 41 patients with 30-day follow-up in the ongoing EXPAND CAP show 91% of donor hearts were utilized, a 2.4% incidence of severe PGD, and 100% 30-day survival.
The sponsor and the FDA clashed over changes made to the trial after the PMA was submitted, the appropriateness of the effectiveness outcome, and claims by the FDA that there was substantial overlap in demographic characteristics between the extended criteria donor hearts in the EXPAND trials and the standard criteria donor hearts in PROCEED II.
TransMedics previously submitted a PMA based on PROCEED II but it noted in submitted documents that it was withdrawn because of “fundamental disagreements with FDA” on the interpretation of a post hoc analysis with United Network for Organ Sharing registry data that identified increased all-cause mortality risk but comparable cardiac-related mortality in patients with OCS hearts.
During the marathon hearing, FDA officials presented several post hoc analyses, including one stratified by donor inclusion criteria, in which 30-day survival estimates were worse in recipients of single-criterion organs than for those receiving donor organs with multiple inclusion criteria (85% vs. 91.4%). In a second analysis, 2-year point estimates of survival also trended lower with donor organs having only one extended criterion.
Reported EXPAND CAP 6- and 12-month survival estimates were 100% and 93%, respectively, which was higher than EXPAND (93% and 84%), but there was substantial censoring (>50%) at 6 months and beyond, FDA officials said.
When EXPAND and CAP data were pooled, modeled survival curves shifted upward but there was a substantial site effect, with a single site contributing 46% of data, which may affect generalizability of the results, they noted.
“I voted yes for safety, no for efficacy, and no for approval and I’d just like to say I found this to be the most difficult vote in my experience on this panel,” John Hirshfeld, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “I was very concerned that the PROCEED data suggests a possible harm, and in the absence of an interpretable comparator for the EXPAND trial, it’s really not possible to decide if there’s efficacy.”
Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at Saint Luke’s Hospital of Kansas City (Mo.), said, “I voted no on safety; I’m not going to give the company a pass. I think their animal data was sorely lacking and a lot of issues over the last 10 years could have been addressed with some key animal studies.
“For efficacy and risk/benefit, I voted yes for both,” he said. “Had this been standard of care and only PROCEED II, I would have voted no, but I do think there are a lot of hearts that go in the bucket and this is a challenging population.”
More than a dozen physicians and patients spoke at the open public hearing about the potential for the device to expand donor heart utilization, including a recipient whose own father died while waiting on the transplant list. Only about 3 out of every 10 donated hearts are used for transplant. To ensure fair access, particularly for patients in rural areas, federal changes in 2020 mandate that organs be allocated to the sickest patients first.
Data showed that the OCS Heart System was associated with shorter waiting list times, compared with U.S. averages but longer preservation times than cold static preservation.
In all, 13% of accepted donor organs were subsequently turned down after OCS heart preservation. Lactate levels were cited as the principal reason for turn-down but, FDA officials said, the validity of using lactate as a marker for transplantability is unclear.
Pathologic analysis of OCS Heart turned-down donor hearts with stable antemortem hemodynamics, normal or near-normal anatomy and normal ventricular function by echocardiography, and autopsy findings of acute diffuse or multifocal myocardial damage “suggest that in an important proportion of cases the OCS Heart system did not provide effective organ preservation or its use caused severe myocardial damage to what might have been an acceptable graft for transplant,” said Andrew Farb, MD, chief medical officer of the FDA’s Office of Cardiovascular Devices.
Proposed indication
In the present PMA, the OCS Heart System is indicated for donor hearts with one or more of the following characteristics: an expected cross-clamp or ischemic time of at least 4 hours because of donor or recipient characteristics; or an expected total cross-clamp time of at least 2 hours plus one of the following risk factors: donor age 55 or older, history of cardiac arrest and downtime of at least 20 minutes, history of alcoholism, history of diabetes, donor ejection fraction of 40%-50%,history of left ventricular hypertrophy, and donor angiogram with luminal irregularities but no significant coronary artery disease
Several members voiced concern about “indication creep” should the device be approved by the FDA, and highlighted the 2-hour cross-clamp time plus wide-ranging risk factors.
“I’m a surgeon and I voted no on all three counts,” said Murray H. Kwon, MD, Ronald Reagan University of California, Los Angeles Medical Center. “As far as risk/benefit, if it was just limited to one group – the 4-hour plus – I would say yes, but if you’re going to tell me that there’s a risk/benefit for the 2-hour with the alcoholic, I don’t know how that was proved in anything.”
Dr. Kwon was also troubled by lack of proper controls and by the one quarter of patients who ended up on mechanical circulatory support in the first 30 days after transplant. “I find that highly aberrant.”
Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, head of cardiovascular medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said the unmet need for patients with refractory, end-stage heart failure is challenging and quite emotional, but also voted no across the board, citing concerns about a lack of comparator in the EXPAND trials and overall out-of-body ischemic time.
“As it relates to risk/benefit, I thought long and hard about voting yes despite all the unknowns because of this emotion, but ultimately I voted no because of the secondary 2-hours plus alcoholism, diabetes, or minor coronary disease, in which the ischemic burden and ongoing lactate production concern me,” he said.
Although the panel decision is nonbinding, there was strong support from the committee members for a randomized, postapproval trial and more complete animal studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.