User login
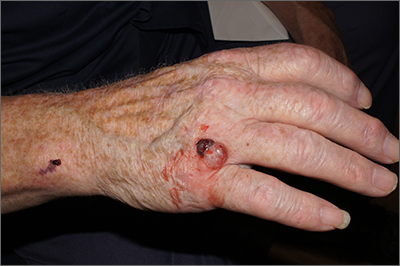
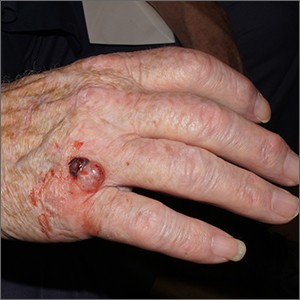
A broad shave biopsy was performed at the base of the lesion and the results were consistent with a thick nodular melanoma with a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm.
Melanoma is the deadliest skin cancer in the United States with mortality risk corresponding with the depth of the tumor.1 Nodular melanomas grow faster than all other types of melanoma. For this reason, a concerning raised lesion with a risk of melanoma should not be observed for change over time; it should be biopsied promptly. In this case, a depth of 5.5 mm was cause for quick action. Patients with tumors > 1 mm in depth (and some tumors > 0.8 mm) should be offered sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) along with wide local excision to evaluate for lymphatic spread. Patients with thinner tumors may undergo wide local excision without SLNB.
In this case, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines would dictate a 2-cm margin for a wide local incision; the patient underwent a modified version of this with Surgical Oncology to accommodate maintenance of hand function. This patient’s SLNB was negative, so the melanoma was classified as Stage IIC.
In the recent past, there were no additional treatments for patients with late Stage II disease (thick tumors without evidence of metastasis). However, in December 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab in patients with node-negative late Stage II melanoma after demonstration of improved recurrence-free survival in the KEYNOTE trial.2 Evidence of improved long-term survival is mixed with adjuvant therapy, and studies evaluating the best role of adjuvant therapy are ongoing.
This patient was started on a regimen of pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks, which he will continue for as long as 1 year. He has tolerated this regimen without difficulty and has no evidence of disease.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Epstein DS, Lange JR, Gruber SB, et al. Is physician detection associated with thinner melanomas? JAMA. 1999;281:640-643. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.7.640
2. Luke JJ, Rutkowski P, Queirolo P, et al; KEYNOTE-716 Investigators. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma (KEYNOTE-716): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399:1718-1729. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00562-1

A broad shave biopsy was performed at the base of the lesion and the results were consistent with a thick nodular melanoma with a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm.
Melanoma is the deadliest skin cancer in the United States with mortality risk corresponding with the depth of the tumor.1 Nodular melanomas grow faster than all other types of melanoma. For this reason, a concerning raised lesion with a risk of melanoma should not be observed for change over time; it should be biopsied promptly. In this case, a depth of 5.5 mm was cause for quick action. Patients with tumors > 1 mm in depth (and some tumors > 0.8 mm) should be offered sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) along with wide local excision to evaluate for lymphatic spread. Patients with thinner tumors may undergo wide local excision without SLNB.
In this case, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines would dictate a 2-cm margin for a wide local incision; the patient underwent a modified version of this with Surgical Oncology to accommodate maintenance of hand function. This patient’s SLNB was negative, so the melanoma was classified as Stage IIC.
In the recent past, there were no additional treatments for patients with late Stage II disease (thick tumors without evidence of metastasis). However, in December 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab in patients with node-negative late Stage II melanoma after demonstration of improved recurrence-free survival in the KEYNOTE trial.2 Evidence of improved long-term survival is mixed with adjuvant therapy, and studies evaluating the best role of adjuvant therapy are ongoing.
This patient was started on a regimen of pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks, which he will continue for as long as 1 year. He has tolerated this regimen without difficulty and has no evidence of disease.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

A broad shave biopsy was performed at the base of the lesion and the results were consistent with a thick nodular melanoma with a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm.
Melanoma is the deadliest skin cancer in the United States with mortality risk corresponding with the depth of the tumor.1 Nodular melanomas grow faster than all other types of melanoma. For this reason, a concerning raised lesion with a risk of melanoma should not be observed for change over time; it should be biopsied promptly. In this case, a depth of 5.5 mm was cause for quick action. Patients with tumors > 1 mm in depth (and some tumors > 0.8 mm) should be offered sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) along with wide local excision to evaluate for lymphatic spread. Patients with thinner tumors may undergo wide local excision without SLNB.
In this case, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines would dictate a 2-cm margin for a wide local incision; the patient underwent a modified version of this with Surgical Oncology to accommodate maintenance of hand function. This patient’s SLNB was negative, so the melanoma was classified as Stage IIC.
In the recent past, there were no additional treatments for patients with late Stage II disease (thick tumors without evidence of metastasis). However, in December 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab in patients with node-negative late Stage II melanoma after demonstration of improved recurrence-free survival in the KEYNOTE trial.2 Evidence of improved long-term survival is mixed with adjuvant therapy, and studies evaluating the best role of adjuvant therapy are ongoing.
This patient was started on a regimen of pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks, which he will continue for as long as 1 year. He has tolerated this regimen without difficulty and has no evidence of disease.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Epstein DS, Lange JR, Gruber SB, et al. Is physician detection associated with thinner melanomas? JAMA. 1999;281:640-643. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.7.640
2. Luke JJ, Rutkowski P, Queirolo P, et al; KEYNOTE-716 Investigators. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma (KEYNOTE-716): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399:1718-1729. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00562-1
1. Epstein DS, Lange JR, Gruber SB, et al. Is physician detection associated with thinner melanomas? JAMA. 1999;281:640-643. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.7.640
2. Luke JJ, Rutkowski P, Queirolo P, et al; KEYNOTE-716 Investigators. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma (KEYNOTE-716): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399:1718-1729. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00562-1