User login
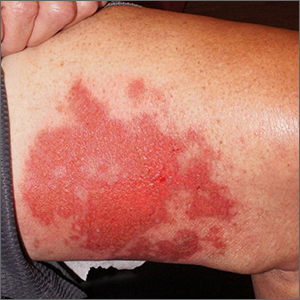
Punch biopsies for standard pathology and direct immunofluorescence were performed and ruled out vesiculobullous disease. Further conversation with the patient revealed that this was a phototoxic drug eruption that resulted from a medication mix-up. The patient had intended to treat an eczema flare with a topical steroid but had inadvertently applied 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), which he had left over from a previous bout of actinic keratosis. While selective to precancerous cells with rapid DNA replication, 5-FU can trigger a significant photodermatitis when applied to heavily sun-exposed skin.
Phototoxic skin reactions can be an adverse result of multiple systemic and topical therapies. Common systemic examples include amiodarone, chlorpromazine, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide, isotretinoin, nalidixic acid, naproxen, piroxicam, tetracycline, thioridazine, vemurafenib, and voriconazole.1 Topical examples include retinoids, levulinic acid, and 5-FU. Treatment requires that the patient stop the offending medication and use photoprotection. The patient followed this protocol and his erosions resolved over the course of a few weeks.
This case demonstrates that topical therapies, like systemic medications, can have chemical names that are confusing to patients. Further complicating matters can be the practice of folding metal tubes of cream over their life of use, thus obscuring the label.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF. Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: culprit drugs, prevention, and management. Drug Saf. 2019;42:827-847. doi: 10.1007/s40264-019-00806-5

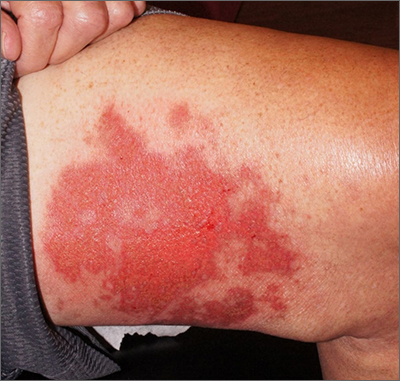
Punch biopsies for standard pathology and direct immunofluorescence were performed and ruled out vesiculobullous disease. Further conversation with the patient revealed that this was a phototoxic drug eruption that resulted from a medication mix-up. The patient had intended to treat an eczema flare with a topical steroid but had inadvertently applied 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), which he had left over from a previous bout of actinic keratosis. While selective to precancerous cells with rapid DNA replication, 5-FU can trigger a significant photodermatitis when applied to heavily sun-exposed skin.
Phototoxic skin reactions can be an adverse result of multiple systemic and topical therapies. Common systemic examples include amiodarone, chlorpromazine, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide, isotretinoin, nalidixic acid, naproxen, piroxicam, tetracycline, thioridazine, vemurafenib, and voriconazole.1 Topical examples include retinoids, levulinic acid, and 5-FU. Treatment requires that the patient stop the offending medication and use photoprotection. The patient followed this protocol and his erosions resolved over the course of a few weeks.
This case demonstrates that topical therapies, like systemic medications, can have chemical names that are confusing to patients. Further complicating matters can be the practice of folding metal tubes of cream over their life of use, thus obscuring the label.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

Punch biopsies for standard pathology and direct immunofluorescence were performed and ruled out vesiculobullous disease. Further conversation with the patient revealed that this was a phototoxic drug eruption that resulted from a medication mix-up. The patient had intended to treat an eczema flare with a topical steroid but had inadvertently applied 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), which he had left over from a previous bout of actinic keratosis. While selective to precancerous cells with rapid DNA replication, 5-FU can trigger a significant photodermatitis when applied to heavily sun-exposed skin.
Phototoxic skin reactions can be an adverse result of multiple systemic and topical therapies. Common systemic examples include amiodarone, chlorpromazine, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide, isotretinoin, nalidixic acid, naproxen, piroxicam, tetracycline, thioridazine, vemurafenib, and voriconazole.1 Topical examples include retinoids, levulinic acid, and 5-FU. Treatment requires that the patient stop the offending medication and use photoprotection. The patient followed this protocol and his erosions resolved over the course of a few weeks.
This case demonstrates that topical therapies, like systemic medications, can have chemical names that are confusing to patients. Further complicating matters can be the practice of folding metal tubes of cream over their life of use, thus obscuring the label.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF. Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: culprit drugs, prevention, and management. Drug Saf. 2019;42:827-847. doi: 10.1007/s40264-019-00806-5
1. Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF. Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: culprit drugs, prevention, and management. Drug Saf. 2019;42:827-847. doi: 10.1007/s40264-019-00806-5