User login
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.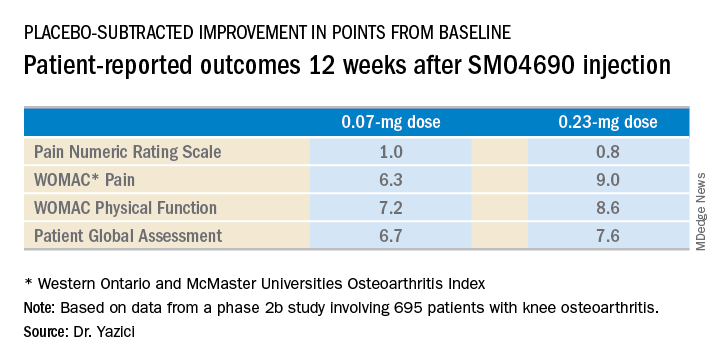
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 proved superior to placebo for four key patient-reported outcomes.
Study details: This was a 24-week, randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study in 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA.
Disclosures: The presenter is chief medical officer at Samumed, the study sponsor.
Source: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.

