User login
New consensus guidelines strongly recommend screening colonoscopy for individuals who have at least one first-degree relative with nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.
Published in the November issue of Gastroenterology, the guideline cites moderate-quality evidence for this recommendation and reserves fecal immunochemical testing for individuals who refuse colonoscopy, are at increased risk for complications, or face barriers accessing the procedure.
Most colorectal cancer screening guidelines have focused on average-risk individuals or those at highest risk because of heritable germline mutations. However, hereditary syndromes comprise only about 5% of colorectal cancers, noted Desmond Leddin, MB, MSc, FRCPC, FRCPI, of the University of Limerick, Ireland, and David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, FACG, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, with their associates from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Banff Consensus.
To develop the guideline, they searched the literature for studies of family history and colorectal cancer risk apart from hereditary Lynch syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis, attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis, MUTYH-associated polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, Cowden syndrome, serrated (hyperplastic) polyposis syndrome, hereditary pancreatic cancer, and hereditary gastric cancer.
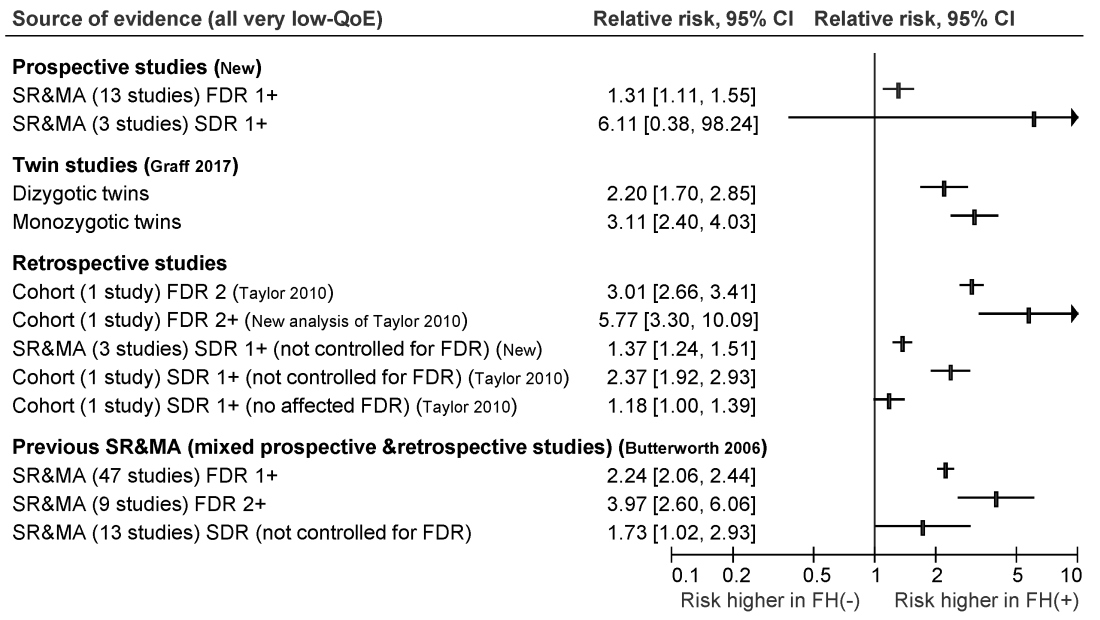
The ensuant guideline cites two new systematic reviews and meta-analyses of 16 prospective studies, as well as one twin study, four retrospective cohort studies, one new systematic review of retrospective studies, and three prior systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The authors note that this is the first guideline to use the GRADE (Grading of Recommendation Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach to make screening recommendations for individuals who have a family history of nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.
For those with one first-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends screening colonoscopy or fecal immunochemical testing beginning at age 40-50 years, or 10 years before the age of diagnosis of the first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. The authors recommend spacing subsequent screening colonoscopies by 5-10 years and spacing fecal immunochemical testing by 1-2 years. They offer the same recommendation for individuals with one or more first-degree relatives with confirmed advanced adenoma.
For individuals whose family history includes at least two first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends an initial screening colonoscopy at age 40, or 10 years earlier than the age of earliest-diagnosed first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. Screenings should occur every 5 years.
For persons with at least one second-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline authors strongly recommend screening starting at age 50 with tests and intervals based on guidelines for average-risk individuals. Their recommendation is the same for individuals with at least one first-degree relative with nonadvanced adenoma or a polyp of unknown histology.
Given the low-quality evidence supporting most of these recommendations, the guideline calls for well designed observational studies to better quantify the risk of colorectal cancer among individuals with a family history of nonheritable disease. Studies should especially focus on the optimal age of first screening and appropriate screening intervals, the guideline authors wrote. Also, they call for randomized controlled trials to assess whether colonoscopy, fecal immunochemical testing, or fecal occult blood screening might significantly reduce long-term risk for colorectal cancer and improve survival in this population.
Merck provided unrestricted funding for the work. Dr. Leddin reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lieberman and several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with companies other than Merck. One coauthor disclosed advisory and consulting relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Leddin D et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Aug 16. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.017.
New consensus guidelines strongly recommend screening colonoscopy for individuals who have at least one first-degree relative with nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.

Published in the November issue of Gastroenterology, the guideline cites moderate-quality evidence for this recommendation and reserves fecal immunochemical testing for individuals who refuse colonoscopy, are at increased risk for complications, or face barriers accessing the procedure.
Most colorectal cancer screening guidelines have focused on average-risk individuals or those at highest risk because of heritable germline mutations. However, hereditary syndromes comprise only about 5% of colorectal cancers, noted Desmond Leddin, MB, MSc, FRCPC, FRCPI, of the University of Limerick, Ireland, and David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, FACG, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, with their associates from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Banff Consensus.
To develop the guideline, they searched the literature for studies of family history and colorectal cancer risk apart from hereditary Lynch syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis, attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis, MUTYH-associated polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, Cowden syndrome, serrated (hyperplastic) polyposis syndrome, hereditary pancreatic cancer, and hereditary gastric cancer.
The ensuant guideline cites two new systematic reviews and meta-analyses of 16 prospective studies, as well as one twin study, four retrospective cohort studies, one new systematic review of retrospective studies, and three prior systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The authors note that this is the first guideline to use the GRADE (Grading of Recommendation Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach to make screening recommendations for individuals who have a family history of nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.
For those with one first-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends screening colonoscopy or fecal immunochemical testing beginning at age 40-50 years, or 10 years before the age of diagnosis of the first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. The authors recommend spacing subsequent screening colonoscopies by 5-10 years and spacing fecal immunochemical testing by 1-2 years. They offer the same recommendation for individuals with one or more first-degree relatives with confirmed advanced adenoma.
For individuals whose family history includes at least two first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends an initial screening colonoscopy at age 40, or 10 years earlier than the age of earliest-diagnosed first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. Screenings should occur every 5 years.
For persons with at least one second-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline authors strongly recommend screening starting at age 50 with tests and intervals based on guidelines for average-risk individuals. Their recommendation is the same for individuals with at least one first-degree relative with nonadvanced adenoma or a polyp of unknown histology.
Given the low-quality evidence supporting most of these recommendations, the guideline calls for well designed observational studies to better quantify the risk of colorectal cancer among individuals with a family history of nonheritable disease. Studies should especially focus on the optimal age of first screening and appropriate screening intervals, the guideline authors wrote. Also, they call for randomized controlled trials to assess whether colonoscopy, fecal immunochemical testing, or fecal occult blood screening might significantly reduce long-term risk for colorectal cancer and improve survival in this population.
Merck provided unrestricted funding for the work. Dr. Leddin reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lieberman and several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with companies other than Merck. One coauthor disclosed advisory and consulting relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Leddin D et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Aug 16. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.017.
New consensus guidelines strongly recommend screening colonoscopy for individuals who have at least one first-degree relative with nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.

Published in the November issue of Gastroenterology, the guideline cites moderate-quality evidence for this recommendation and reserves fecal immunochemical testing for individuals who refuse colonoscopy, are at increased risk for complications, or face barriers accessing the procedure.
Most colorectal cancer screening guidelines have focused on average-risk individuals or those at highest risk because of heritable germline mutations. However, hereditary syndromes comprise only about 5% of colorectal cancers, noted Desmond Leddin, MB, MSc, FRCPC, FRCPI, of the University of Limerick, Ireland, and David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, FACG, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, with their associates from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Banff Consensus.
To develop the guideline, they searched the literature for studies of family history and colorectal cancer risk apart from hereditary Lynch syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis, attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis, MUTYH-associated polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, Cowden syndrome, serrated (hyperplastic) polyposis syndrome, hereditary pancreatic cancer, and hereditary gastric cancer.
The ensuant guideline cites two new systematic reviews and meta-analyses of 16 prospective studies, as well as one twin study, four retrospective cohort studies, one new systematic review of retrospective studies, and three prior systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The authors note that this is the first guideline to use the GRADE (Grading of Recommendation Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach to make screening recommendations for individuals who have a family history of nonhereditary colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma.
For those with one first-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends screening colonoscopy or fecal immunochemical testing beginning at age 40-50 years, or 10 years before the age of diagnosis of the first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. The authors recommend spacing subsequent screening colonoscopies by 5-10 years and spacing fecal immunochemical testing by 1-2 years. They offer the same recommendation for individuals with one or more first-degree relatives with confirmed advanced adenoma.
For individuals whose family history includes at least two first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer, the guideline recommends an initial screening colonoscopy at age 40, or 10 years earlier than the age of earliest-diagnosed first-degree relative, whichever is earlier. Screenings should occur every 5 years.
For persons with at least one second-degree relative with colorectal cancer, the guideline authors strongly recommend screening starting at age 50 with tests and intervals based on guidelines for average-risk individuals. Their recommendation is the same for individuals with at least one first-degree relative with nonadvanced adenoma or a polyp of unknown histology.
Given the low-quality evidence supporting most of these recommendations, the guideline calls for well designed observational studies to better quantify the risk of colorectal cancer among individuals with a family history of nonheritable disease. Studies should especially focus on the optimal age of first screening and appropriate screening intervals, the guideline authors wrote. Also, they call for randomized controlled trials to assess whether colonoscopy, fecal immunochemical testing, or fecal occult blood screening might significantly reduce long-term risk for colorectal cancer and improve survival in this population.
Merck provided unrestricted funding for the work. Dr. Leddin reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lieberman and several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with companies other than Merck. One coauthor disclosed advisory and consulting relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Leddin D et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Aug 16. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.017.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY