User login
Medical professional liability claims (claims) are a major cause of worry and agony for physicians who are dedicated to optimizing the health of all their patients. Among physicians, those who practice neurosurgery, thoracic surgery, plastic surgery, and obstetrics and gynecology have the greatest rate of making a payment on a claim per year of practice.1 Physicians who practice psychiatry, pediatrics, pathology, and internal medicine have the lowest rate of making a payment on a claim. Among the physicians in high-risk specialties, greater than 90% will have a claim filed against them during their career.2 Although professional liability exposure reached a crisis during the 1980s and 1990s, recent data have shown a decrease in overall professional liability risk.
The good news: Paid claims per 1,000 ObGyns have decreased greatly
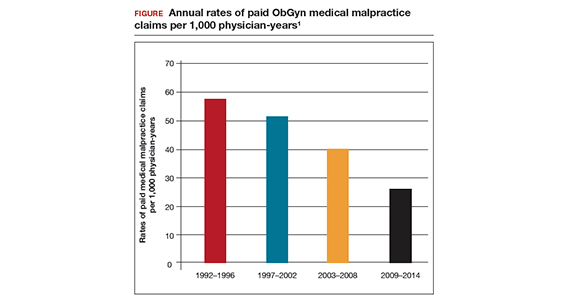
In a review of all paid claims reported to the National Practitioner Data Bank from 1992 to 2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was determined.1 For the time periods 1992–1996, 1997–2002, 2003–2008,and 2009–2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was 57.6, 51.5, 40.0, and 25.9, representing an astounding 55% decrease in paid claims from 1992 to 2014 (FIGURE).1
The majority of claims result in no payment
In a review of the experience of a nationwide professional liability insurer from 1991 to 2005, only 22% of claims resulted in a payment.2 In this study, for obstetrics and gynecology and gynecologic surgery, only 11% and 8% of claims, respectively, resulted in a payment.2 However, being named in a malpractice claim results in significant stress for a physician and requires a great deal of work and time to defend.
In another study using data from the Physician Insurer’s Association of America, among 10,915 claims closed from 2005 to 2014, 59.5% were dropped, withdrawn, or dismissed; 27.7% were settled; 2.5% were resolved using an alternative dispute resolution process; 1.8% were uncategorized; and 8.6% went to trial.3 Of the cases that went to trial, 87% resulted in a verdict for the physician and 13% resulted in a verdict for the plaintiff.3
Not as good news: Payments per claim and claims settling for a payment > $1 million are increasing
In the period 1992–1996, the average payment per paid claim in the field of obstetrics and gynecology was $387,186, rising to $447,034 in 2009–2014—a 16% increase.1 From 2004 to 2010, million dollar payments occurred in about 8% of cases of paid claims, but they represent 36% of the total of all paid claims.4 In the time periods 1992–1996 and 2009–2014, payments greater than $1 million occurred in 6% and 8% of paid claims, respectively.1
Claims settled for much more than $1 million are of great concern to physicians because the payment may exceed their policy limit, creating a complex legal problem that may take time to resolve. In some cases, where the award is greater than the insurance policy limit, aggressive plaintiff attorneys have obtained a lien on the defendant physician’s home pending settlement of the case. When a multimillion dollar payment is made to settle a professional liability claim, it can greatly influence physician practice and change hospital policies. Frequently, following a multimillion dollar payment a physician may decide to limit their practice to low-risk cases or retire from the practice of medicine.
Liability premiums are stable or decreasing
From 2014 to 2019, my ObGyn professional liability insurance premiums decreased by 18%. During the same time period, my colleagues who practice surgical gynecology (no obstetrics) had a premium decrease of 22%. Insurers use a complex algorithm to determine annual liability insurance premiums, and premiums for ObGyns may not have stabilized or decreased in all regions. Take this Instant Poll:
Create your own user feedback survey
Reform of the liability tort system
Litigation policies and practices that reduce liability risk reduce total medical liability losses. Policies that have helped to constrain medical liability risk include state constitutional amendments limiting payments for pain and suffering, caps on compensation to plaintiff attorneys, increased early resolution programs that compensate patients who experience an adverse event and no-fault conflict resolution programs.5 In 2003, Texas implemented a comprehensive package of tort reform laws. Experts believe the reforms decreased the financial burden of professional liability insurance6 and led to less defensive medical practices, reducing excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests.
Medical factors contributing to a decrease in claims
In 1999, the Institute of Medicine released the report, “To Err is Human,” which galvanized health care systems to deploy systems of care that reduce the rate of adverse patient outcomes.7 Over the past 20 years, health systems have implemented quality improvement programs in obstetrics and gynecology that have contributed to a reduction in the rate of adverse patient outcomes. This may have contributed to the decrease in the rate of paid claims.
In a quasi-experimental study performed in 13 health systems, 7 interventions were implemented with the goal of improving outcomes and reducing medical liability. The 7 interventions included8:
- an elective induction bundle focused on the safe use of oxytocin
- an augmentation bundle focused on early intervention for possible fetal metabolic acidosis
- an operative vaginal delivery bundle
- TeamSTEPPS teamwork training to improve the quality of communication
- best practices education with a focus on electronic fetal monitoring
- regular performance feedback to hospitals and clinicians
- implementation of a quality improvement collaboration to support implementation of the interventions.
During the two-year baseline period prior to the intervention there were 185,373 deliveries with 6.7 perinatal claims made per 10,000 deliveries and 1.3 claims paid per 10,000 deliveries. Following the intervention, the rate of claims made and claims paid per 10,000 deliveries decreased by 22% and 37%, respectively. In addition there was a marked decrease in claims over $1 million paid, greatly limiting total financial liability losses.
Experts with vast experience in obstetrics and obstetric liability litigation have identified 4 priority interventions that may improve outcomes and mitigate liability risk, including: 1) 24-hour in-house physician coverage of an obstetrics service, 2) a conservative approach to trial of labor after a prior cesarean delivery, 3) utilization of a comprehensive, standardized event note in cases of a shoulder dystocia, and 4) judicious use of oxytocin, misoprostol, and magnesium sulfate.9
Other health system interventions that may contribute to a reduction in claims include:
- systematic improvement in the quality of communication among physicians and nurses through the use of team training, preprocedure huddles, and time-out processes10
- rapid response systems to rescue hospital patients with worrisome vital signs11
- standardized responses to a worrisome category 2 or 3 fetal heart-rate tracing12
- rapid recognition, evaluation, and treatment of women with hemorrhage, severe hypertension, sepsis, and venous thromboembolism13
- identification and referral of high-risk patients to tertiary centers14
- closed loop communication of critical imaging and laboratory results15
- universal insurance coverage for health care including contraception, obstetrics, and pediatric care.
Medical liability risk is an important practice issue because it causes excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests and often traumatizes clinicians, which can result in burnout. In the 1980s and 1990s, medical liability litigation reached a crescendo and was a prominent concern among obstetrician-gynecologists. The good news is that, for ObGyns, liability risk has stabilized. Hopefully our resolute efforts to continuously improve the quality of care will result in a long-term reduction in medical liability risk.
- Schaffer AC, Jena AB, Seabury SA, et al. Rates and characteristics of paid malpractice claims among US physicians by specialty, 1992–2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:710-718.
- Jena AB, Seabury S, Lakdawalla D, et al. Malpractice risk according to physician specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:629-636.
- Glaser LM, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Trends in malpractice claims for obstetric and gynecologic procedures, 2005 through 2014. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:340.e1-e6.
- Bixenstine PJ, Shore AD, Mehtsun WT, et al. Catastrophic medical malpractice payouts in the United States. J Healthc Quality. 2014;36:43-53.
- Cardoso R, Zarin W, Nincic V, et al. Evaluative reports on medical malpractice policies in obstetrics: a rapid scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6:181.
- Stewart RM, Geoghegan K, Myers JG, et al. Malpractice risk and costs are significantly reduced after tort reform. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:463-467.
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, eds. To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Riley W, Meredith LW, Price R, et al. Decreasing malpractice claims by reducing preventable perinatal harm. Health Serv Res. 2016;51(suppl 3):2453-2471.
- Clark SL, Belfort MA, Dildy GA, et al. Reducing obstetric litigation through alterations in practice patterns. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:1279-1283.
- Haynes AB, Weiser TG, Berry WR, et al; Safe Surgery Saves Lives Study Group. A surgical safety checklist to reduce morbidity and mortality in a global population. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:491-499.
- Patel S, Gillon SA, Jones DA. Rapid response systems: recognition and rescue of the deteriorating hospital patient. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2017;78:143-148.
- Clark SL, Hamilton EF, Garite TJ, et al. The limits of electronic fetal heart rate monitoring in the prevention of neonatal metabolic acidemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216:163.e1-163.e6.
- The Council on Patient Safety in Women’s Healthcare website. www.safehealthcareforeverywoman.org. Accessed April 12, 2019.
- Zahn CM, Remick A, Catalano A, et al. Levels of maternal care verification pilot: translating guidance into practice. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1401-1406.
- Zuccotti G, Maloney FL, Feblowitz J, et al. Reducing risk with clinical decision support: a study of closed malpractice claims. Appl Clin Inform. 2014;5:746-756.
Medical professional liability claims (claims) are a major cause of worry and agony for physicians who are dedicated to optimizing the health of all their patients. Among physicians, those who practice neurosurgery, thoracic surgery, plastic surgery, and obstetrics and gynecology have the greatest rate of making a payment on a claim per year of practice.1 Physicians who practice psychiatry, pediatrics, pathology, and internal medicine have the lowest rate of making a payment on a claim. Among the physicians in high-risk specialties, greater than 90% will have a claim filed against them during their career.2 Although professional liability exposure reached a crisis during the 1980s and 1990s, recent data have shown a decrease in overall professional liability risk.
The good news: Paid claims per 1,000 ObGyns have decreased greatly
In a review of all paid claims reported to the National Practitioner Data Bank from 1992 to 2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was determined.1 For the time periods 1992–1996, 1997–2002, 2003–2008,and 2009–2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was 57.6, 51.5, 40.0, and 25.9, representing an astounding 55% decrease in paid claims from 1992 to 2014 (FIGURE).1
The majority of claims result in no payment
In a review of the experience of a nationwide professional liability insurer from 1991 to 2005, only 22% of claims resulted in a payment.2 In this study, for obstetrics and gynecology and gynecologic surgery, only 11% and 8% of claims, respectively, resulted in a payment.2 However, being named in a malpractice claim results in significant stress for a physician and requires a great deal of work and time to defend.
In another study using data from the Physician Insurer’s Association of America, among 10,915 claims closed from 2005 to 2014, 59.5% were dropped, withdrawn, or dismissed; 27.7% were settled; 2.5% were resolved using an alternative dispute resolution process; 1.8% were uncategorized; and 8.6% went to trial.3 Of the cases that went to trial, 87% resulted in a verdict for the physician and 13% resulted in a verdict for the plaintiff.3
Not as good news: Payments per claim and claims settling for a payment > $1 million are increasing
In the period 1992–1996, the average payment per paid claim in the field of obstetrics and gynecology was $387,186, rising to $447,034 in 2009–2014—a 16% increase.1 From 2004 to 2010, million dollar payments occurred in about 8% of cases of paid claims, but they represent 36% of the total of all paid claims.4 In the time periods 1992–1996 and 2009–2014, payments greater than $1 million occurred in 6% and 8% of paid claims, respectively.1
Claims settled for much more than $1 million are of great concern to physicians because the payment may exceed their policy limit, creating a complex legal problem that may take time to resolve. In some cases, where the award is greater than the insurance policy limit, aggressive plaintiff attorneys have obtained a lien on the defendant physician’s home pending settlement of the case. When a multimillion dollar payment is made to settle a professional liability claim, it can greatly influence physician practice and change hospital policies. Frequently, following a multimillion dollar payment a physician may decide to limit their practice to low-risk cases or retire from the practice of medicine.
Liability premiums are stable or decreasing
From 2014 to 2019, my ObGyn professional liability insurance premiums decreased by 18%. During the same time period, my colleagues who practice surgical gynecology (no obstetrics) had a premium decrease of 22%. Insurers use a complex algorithm to determine annual liability insurance premiums, and premiums for ObGyns may not have stabilized or decreased in all regions. Take this Instant Poll:
Create your own user feedback survey
Reform of the liability tort system
Litigation policies and practices that reduce liability risk reduce total medical liability losses. Policies that have helped to constrain medical liability risk include state constitutional amendments limiting payments for pain and suffering, caps on compensation to plaintiff attorneys, increased early resolution programs that compensate patients who experience an adverse event and no-fault conflict resolution programs.5 In 2003, Texas implemented a comprehensive package of tort reform laws. Experts believe the reforms decreased the financial burden of professional liability insurance6 and led to less defensive medical practices, reducing excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests.
Medical factors contributing to a decrease in claims
In 1999, the Institute of Medicine released the report, “To Err is Human,” which galvanized health care systems to deploy systems of care that reduce the rate of adverse patient outcomes.7 Over the past 20 years, health systems have implemented quality improvement programs in obstetrics and gynecology that have contributed to a reduction in the rate of adverse patient outcomes. This may have contributed to the decrease in the rate of paid claims.
In a quasi-experimental study performed in 13 health systems, 7 interventions were implemented with the goal of improving outcomes and reducing medical liability. The 7 interventions included8:
- an elective induction bundle focused on the safe use of oxytocin
- an augmentation bundle focused on early intervention for possible fetal metabolic acidosis
- an operative vaginal delivery bundle
- TeamSTEPPS teamwork training to improve the quality of communication
- best practices education with a focus on electronic fetal monitoring
- regular performance feedback to hospitals and clinicians
- implementation of a quality improvement collaboration to support implementation of the interventions.
During the two-year baseline period prior to the intervention there were 185,373 deliveries with 6.7 perinatal claims made per 10,000 deliveries and 1.3 claims paid per 10,000 deliveries. Following the intervention, the rate of claims made and claims paid per 10,000 deliveries decreased by 22% and 37%, respectively. In addition there was a marked decrease in claims over $1 million paid, greatly limiting total financial liability losses.
Experts with vast experience in obstetrics and obstetric liability litigation have identified 4 priority interventions that may improve outcomes and mitigate liability risk, including: 1) 24-hour in-house physician coverage of an obstetrics service, 2) a conservative approach to trial of labor after a prior cesarean delivery, 3) utilization of a comprehensive, standardized event note in cases of a shoulder dystocia, and 4) judicious use of oxytocin, misoprostol, and magnesium sulfate.9
Other health system interventions that may contribute to a reduction in claims include:
- systematic improvement in the quality of communication among physicians and nurses through the use of team training, preprocedure huddles, and time-out processes10
- rapid response systems to rescue hospital patients with worrisome vital signs11
- standardized responses to a worrisome category 2 or 3 fetal heart-rate tracing12
- rapid recognition, evaluation, and treatment of women with hemorrhage, severe hypertension, sepsis, and venous thromboembolism13
- identification and referral of high-risk patients to tertiary centers14
- closed loop communication of critical imaging and laboratory results15
- universal insurance coverage for health care including contraception, obstetrics, and pediatric care.
Medical liability risk is an important practice issue because it causes excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests and often traumatizes clinicians, which can result in burnout. In the 1980s and 1990s, medical liability litigation reached a crescendo and was a prominent concern among obstetrician-gynecologists. The good news is that, for ObGyns, liability risk has stabilized. Hopefully our resolute efforts to continuously improve the quality of care will result in a long-term reduction in medical liability risk.
Medical professional liability claims (claims) are a major cause of worry and agony for physicians who are dedicated to optimizing the health of all their patients. Among physicians, those who practice neurosurgery, thoracic surgery, plastic surgery, and obstetrics and gynecology have the greatest rate of making a payment on a claim per year of practice.1 Physicians who practice psychiatry, pediatrics, pathology, and internal medicine have the lowest rate of making a payment on a claim. Among the physicians in high-risk specialties, greater than 90% will have a claim filed against them during their career.2 Although professional liability exposure reached a crisis during the 1980s and 1990s, recent data have shown a decrease in overall professional liability risk.
The good news: Paid claims per 1,000 ObGyns have decreased greatly
In a review of all paid claims reported to the National Practitioner Data Bank from 1992 to 2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was determined.1 For the time periods 1992–1996, 1997–2002, 2003–2008,and 2009–2014, the annual rate of paid claims per 1,000 ObGyn physician-years was 57.6, 51.5, 40.0, and 25.9, representing an astounding 55% decrease in paid claims from 1992 to 2014 (FIGURE).1
The majority of claims result in no payment
In a review of the experience of a nationwide professional liability insurer from 1991 to 2005, only 22% of claims resulted in a payment.2 In this study, for obstetrics and gynecology and gynecologic surgery, only 11% and 8% of claims, respectively, resulted in a payment.2 However, being named in a malpractice claim results in significant stress for a physician and requires a great deal of work and time to defend.
In another study using data from the Physician Insurer’s Association of America, among 10,915 claims closed from 2005 to 2014, 59.5% were dropped, withdrawn, or dismissed; 27.7% were settled; 2.5% were resolved using an alternative dispute resolution process; 1.8% were uncategorized; and 8.6% went to trial.3 Of the cases that went to trial, 87% resulted in a verdict for the physician and 13% resulted in a verdict for the plaintiff.3
Not as good news: Payments per claim and claims settling for a payment > $1 million are increasing
In the period 1992–1996, the average payment per paid claim in the field of obstetrics and gynecology was $387,186, rising to $447,034 in 2009–2014—a 16% increase.1 From 2004 to 2010, million dollar payments occurred in about 8% of cases of paid claims, but they represent 36% of the total of all paid claims.4 In the time periods 1992–1996 and 2009–2014, payments greater than $1 million occurred in 6% and 8% of paid claims, respectively.1
Claims settled for much more than $1 million are of great concern to physicians because the payment may exceed their policy limit, creating a complex legal problem that may take time to resolve. In some cases, where the award is greater than the insurance policy limit, aggressive plaintiff attorneys have obtained a lien on the defendant physician’s home pending settlement of the case. When a multimillion dollar payment is made to settle a professional liability claim, it can greatly influence physician practice and change hospital policies. Frequently, following a multimillion dollar payment a physician may decide to limit their practice to low-risk cases or retire from the practice of medicine.
Liability premiums are stable or decreasing
From 2014 to 2019, my ObGyn professional liability insurance premiums decreased by 18%. During the same time period, my colleagues who practice surgical gynecology (no obstetrics) had a premium decrease of 22%. Insurers use a complex algorithm to determine annual liability insurance premiums, and premiums for ObGyns may not have stabilized or decreased in all regions. Take this Instant Poll:
Create your own user feedback survey
Reform of the liability tort system
Litigation policies and practices that reduce liability risk reduce total medical liability losses. Policies that have helped to constrain medical liability risk include state constitutional amendments limiting payments for pain and suffering, caps on compensation to plaintiff attorneys, increased early resolution programs that compensate patients who experience an adverse event and no-fault conflict resolution programs.5 In 2003, Texas implemented a comprehensive package of tort reform laws. Experts believe the reforms decreased the financial burden of professional liability insurance6 and led to less defensive medical practices, reducing excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests.
Medical factors contributing to a decrease in claims
In 1999, the Institute of Medicine released the report, “To Err is Human,” which galvanized health care systems to deploy systems of care that reduce the rate of adverse patient outcomes.7 Over the past 20 years, health systems have implemented quality improvement programs in obstetrics and gynecology that have contributed to a reduction in the rate of adverse patient outcomes. This may have contributed to the decrease in the rate of paid claims.
In a quasi-experimental study performed in 13 health systems, 7 interventions were implemented with the goal of improving outcomes and reducing medical liability. The 7 interventions included8:
- an elective induction bundle focused on the safe use of oxytocin
- an augmentation bundle focused on early intervention for possible fetal metabolic acidosis
- an operative vaginal delivery bundle
- TeamSTEPPS teamwork training to improve the quality of communication
- best practices education with a focus on electronic fetal monitoring
- regular performance feedback to hospitals and clinicians
- implementation of a quality improvement collaboration to support implementation of the interventions.
During the two-year baseline period prior to the intervention there were 185,373 deliveries with 6.7 perinatal claims made per 10,000 deliveries and 1.3 claims paid per 10,000 deliveries. Following the intervention, the rate of claims made and claims paid per 10,000 deliveries decreased by 22% and 37%, respectively. In addition there was a marked decrease in claims over $1 million paid, greatly limiting total financial liability losses.
Experts with vast experience in obstetrics and obstetric liability litigation have identified 4 priority interventions that may improve outcomes and mitigate liability risk, including: 1) 24-hour in-house physician coverage of an obstetrics service, 2) a conservative approach to trial of labor after a prior cesarean delivery, 3) utilization of a comprehensive, standardized event note in cases of a shoulder dystocia, and 4) judicious use of oxytocin, misoprostol, and magnesium sulfate.9
Other health system interventions that may contribute to a reduction in claims include:
- systematic improvement in the quality of communication among physicians and nurses through the use of team training, preprocedure huddles, and time-out processes10
- rapid response systems to rescue hospital patients with worrisome vital signs11
- standardized responses to a worrisome category 2 or 3 fetal heart-rate tracing12
- rapid recognition, evaluation, and treatment of women with hemorrhage, severe hypertension, sepsis, and venous thromboembolism13
- identification and referral of high-risk patients to tertiary centers14
- closed loop communication of critical imaging and laboratory results15
- universal insurance coverage for health care including contraception, obstetrics, and pediatric care.
Medical liability risk is an important practice issue because it causes excessive use of imaging and laboratory tests and often traumatizes clinicians, which can result in burnout. In the 1980s and 1990s, medical liability litigation reached a crescendo and was a prominent concern among obstetrician-gynecologists. The good news is that, for ObGyns, liability risk has stabilized. Hopefully our resolute efforts to continuously improve the quality of care will result in a long-term reduction in medical liability risk.
- Schaffer AC, Jena AB, Seabury SA, et al. Rates and characteristics of paid malpractice claims among US physicians by specialty, 1992–2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:710-718.
- Jena AB, Seabury S, Lakdawalla D, et al. Malpractice risk according to physician specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:629-636.
- Glaser LM, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Trends in malpractice claims for obstetric and gynecologic procedures, 2005 through 2014. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:340.e1-e6.
- Bixenstine PJ, Shore AD, Mehtsun WT, et al. Catastrophic medical malpractice payouts in the United States. J Healthc Quality. 2014;36:43-53.
- Cardoso R, Zarin W, Nincic V, et al. Evaluative reports on medical malpractice policies in obstetrics: a rapid scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6:181.
- Stewart RM, Geoghegan K, Myers JG, et al. Malpractice risk and costs are significantly reduced after tort reform. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:463-467.
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, eds. To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Riley W, Meredith LW, Price R, et al. Decreasing malpractice claims by reducing preventable perinatal harm. Health Serv Res. 2016;51(suppl 3):2453-2471.
- Clark SL, Belfort MA, Dildy GA, et al. Reducing obstetric litigation through alterations in practice patterns. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:1279-1283.
- Haynes AB, Weiser TG, Berry WR, et al; Safe Surgery Saves Lives Study Group. A surgical safety checklist to reduce morbidity and mortality in a global population. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:491-499.
- Patel S, Gillon SA, Jones DA. Rapid response systems: recognition and rescue of the deteriorating hospital patient. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2017;78:143-148.
- Clark SL, Hamilton EF, Garite TJ, et al. The limits of electronic fetal heart rate monitoring in the prevention of neonatal metabolic acidemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216:163.e1-163.e6.
- The Council on Patient Safety in Women’s Healthcare website. www.safehealthcareforeverywoman.org. Accessed April 12, 2019.
- Zahn CM, Remick A, Catalano A, et al. Levels of maternal care verification pilot: translating guidance into practice. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1401-1406.
- Zuccotti G, Maloney FL, Feblowitz J, et al. Reducing risk with clinical decision support: a study of closed malpractice claims. Appl Clin Inform. 2014;5:746-756.
- Schaffer AC, Jena AB, Seabury SA, et al. Rates and characteristics of paid malpractice claims among US physicians by specialty, 1992–2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:710-718.
- Jena AB, Seabury S, Lakdawalla D, et al. Malpractice risk according to physician specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:629-636.
- Glaser LM, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Trends in malpractice claims for obstetric and gynecologic procedures, 2005 through 2014. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:340.e1-e6.
- Bixenstine PJ, Shore AD, Mehtsun WT, et al. Catastrophic medical malpractice payouts in the United States. J Healthc Quality. 2014;36:43-53.
- Cardoso R, Zarin W, Nincic V, et al. Evaluative reports on medical malpractice policies in obstetrics: a rapid scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6:181.
- Stewart RM, Geoghegan K, Myers JG, et al. Malpractice risk and costs are significantly reduced after tort reform. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:463-467.
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, eds. To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Riley W, Meredith LW, Price R, et al. Decreasing malpractice claims by reducing preventable perinatal harm. Health Serv Res. 2016;51(suppl 3):2453-2471.
- Clark SL, Belfort MA, Dildy GA, et al. Reducing obstetric litigation through alterations in practice patterns. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:1279-1283.
- Haynes AB, Weiser TG, Berry WR, et al; Safe Surgery Saves Lives Study Group. A surgical safety checklist to reduce morbidity and mortality in a global population. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:491-499.
- Patel S, Gillon SA, Jones DA. Rapid response systems: recognition and rescue of the deteriorating hospital patient. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2017;78:143-148.
- Clark SL, Hamilton EF, Garite TJ, et al. The limits of electronic fetal heart rate monitoring in the prevention of neonatal metabolic acidemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216:163.e1-163.e6.
- The Council on Patient Safety in Women’s Healthcare website. www.safehealthcareforeverywoman.org. Accessed April 12, 2019.
- Zahn CM, Remick A, Catalano A, et al. Levels of maternal care verification pilot: translating guidance into practice. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1401-1406.
- Zuccotti G, Maloney FL, Feblowitz J, et al. Reducing risk with clinical decision support: a study of closed malpractice claims. Appl Clin Inform. 2014;5:746-756.