User login
CHICAGO – Efforts to encourage even modest amounts of physical activity in sedentary patients with atrial fibrillation are likely to pay off in reduced risks of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, according to a report from the EurObservational Research Program Pilot Survey on Atrial Fibrillation General Registry.
“Clearly we would recommend regular physical activity for patients with atrial fibrillation on the basis of the mortality benefit we see in the registry. If we give patients with atrial fibrillation oral anticoagulation, they are protected against stroke risk, but clearly they are still dying a lot,” Dr. Marco Proietti said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented 1-year follow-up data on 2,442 “real world” patients enrolled in the nine-country, observational, prospective registry, known as EORP-AF, shortly after being diagnosed with AF. One of the goals of EORP-AF is to learn whether physical exercise protects against cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in AF patients, as has been well established in the general population and in patients at high cardiovascular risk.
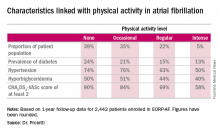
One striking finding was that nearly 40% of patients in EORP-AF reported engaging in no physical activity, defined for study purposes as zero to less than 3 hours of physical activity per week for less than 2 years.
The other three categories employed by investigators were “occasional,” meaning less than 3 hours per week but for 2 years or more; “regular,” defined as at least 3 hours weekly for at least 2 years; and “intense,” which required more than 7 hours of physical activity per week for at least 2 years. Levels of cardiovascular and stroke risk factors decreased progressively with increasing levels of physical activity. Only 5% of the AF patients met the ‘intense’ standard, noted Dr. Proietti of the University of Birmingham (England).
The 1-year cardiovascular mortality rate approached 6% in the no physical activity group and hovered around 1% in the other three groups. The 1-year all-cause mortality rate exceeded 12% in the no-exercise group, was 4%% in the occasional exercisers, and 1%-2% in the groups reporting regular or intense physical activity.
The 1-year composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, any thromboembolism, or a bleeding event occurred in 12% of the sedentary patients, a rate two-to-three times higher than in the others.
Updated outcomes are to be reported from the EORP-AF pilot registry after 2 and 3 years of follow-up. Meanwhile, on the basis of the success of the pilot registry, more than 10,000 patients with AF have been enrolled in the EORP-AF main registry, according to Dr. Proietti.
A study limitation, he conceded, is that the registry includes no objective measure of physical capacity, such as METS.
Session co-chair Dr. Brian Olshansky, emeritus professor of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, observed that the registry data raise a classic chicken-versus-egg issue: Do the sedentary patients do worse because they’re inactive, or are they inactive because they are sicker and hence have worse outcomes?
Dr. Proietti said the registry data provide some support for the latter idea, since the no-physical-activity group had higher prevalences of coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Dr. Olshansky raised another point: “It’s interesting to me that there’s a whole bunch of literature showing that elite endurance athletes – bike racers, cross country skiers – have a very high incidence of atrial fibrillation. It seems to be either an inflammatory or an autonomic issue.”
Dr. Proietti replied that he’s familiar with that extensive literature, but the EORP-AF data through 1 year don’t provide validation. While the intense physical activity group tended to have more symptomatic AF than the other groups, they were no more likely to show progression from paroxysmal to permanent AF. The much larger main registry now underway may be able to better clarify the relationship between physical activity and incidence and progression of AF, including the possibility of a U-shaped dose-response curve.
The EORP-AF registry is supported by the European Society of Cardiology. Dr. Proietti reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – Efforts to encourage even modest amounts of physical activity in sedentary patients with atrial fibrillation are likely to pay off in reduced risks of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, according to a report from the EurObservational Research Program Pilot Survey on Atrial Fibrillation General Registry.
“Clearly we would recommend regular physical activity for patients with atrial fibrillation on the basis of the mortality benefit we see in the registry. If we give patients with atrial fibrillation oral anticoagulation, they are protected against stroke risk, but clearly they are still dying a lot,” Dr. Marco Proietti said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented 1-year follow-up data on 2,442 “real world” patients enrolled in the nine-country, observational, prospective registry, known as EORP-AF, shortly after being diagnosed with AF. One of the goals of EORP-AF is to learn whether physical exercise protects against cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in AF patients, as has been well established in the general population and in patients at high cardiovascular risk.
One striking finding was that nearly 40% of patients in EORP-AF reported engaging in no physical activity, defined for study purposes as zero to less than 3 hours of physical activity per week for less than 2 years.
The other three categories employed by investigators were “occasional,” meaning less than 3 hours per week but for 2 years or more; “regular,” defined as at least 3 hours weekly for at least 2 years; and “intense,” which required more than 7 hours of physical activity per week for at least 2 years. Levels of cardiovascular and stroke risk factors decreased progressively with increasing levels of physical activity. Only 5% of the AF patients met the ‘intense’ standard, noted Dr. Proietti of the University of Birmingham (England).
The 1-year cardiovascular mortality rate approached 6% in the no physical activity group and hovered around 1% in the other three groups. The 1-year all-cause mortality rate exceeded 12% in the no-exercise group, was 4%% in the occasional exercisers, and 1%-2% in the groups reporting regular or intense physical activity.
The 1-year composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, any thromboembolism, or a bleeding event occurred in 12% of the sedentary patients, a rate two-to-three times higher than in the others.
Updated outcomes are to be reported from the EORP-AF pilot registry after 2 and 3 years of follow-up. Meanwhile, on the basis of the success of the pilot registry, more than 10,000 patients with AF have been enrolled in the EORP-AF main registry, according to Dr. Proietti.
A study limitation, he conceded, is that the registry includes no objective measure of physical capacity, such as METS.
Session co-chair Dr. Brian Olshansky, emeritus professor of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, observed that the registry data raise a classic chicken-versus-egg issue: Do the sedentary patients do worse because they’re inactive, or are they inactive because they are sicker and hence have worse outcomes?
Dr. Proietti said the registry data provide some support for the latter idea, since the no-physical-activity group had higher prevalences of coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Dr. Olshansky raised another point: “It’s interesting to me that there’s a whole bunch of literature showing that elite endurance athletes – bike racers, cross country skiers – have a very high incidence of atrial fibrillation. It seems to be either an inflammatory or an autonomic issue.”
Dr. Proietti replied that he’s familiar with that extensive literature, but the EORP-AF data through 1 year don’t provide validation. While the intense physical activity group tended to have more symptomatic AF than the other groups, they were no more likely to show progression from paroxysmal to permanent AF. The much larger main registry now underway may be able to better clarify the relationship between physical activity and incidence and progression of AF, including the possibility of a U-shaped dose-response curve.
The EORP-AF registry is supported by the European Society of Cardiology. Dr. Proietti reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – Efforts to encourage even modest amounts of physical activity in sedentary patients with atrial fibrillation are likely to pay off in reduced risks of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, according to a report from the EurObservational Research Program Pilot Survey on Atrial Fibrillation General Registry.
“Clearly we would recommend regular physical activity for patients with atrial fibrillation on the basis of the mortality benefit we see in the registry. If we give patients with atrial fibrillation oral anticoagulation, they are protected against stroke risk, but clearly they are still dying a lot,” Dr. Marco Proietti said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented 1-year follow-up data on 2,442 “real world” patients enrolled in the nine-country, observational, prospective registry, known as EORP-AF, shortly after being diagnosed with AF. One of the goals of EORP-AF is to learn whether physical exercise protects against cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in AF patients, as has been well established in the general population and in patients at high cardiovascular risk.
One striking finding was that nearly 40% of patients in EORP-AF reported engaging in no physical activity, defined for study purposes as zero to less than 3 hours of physical activity per week for less than 2 years.
The other three categories employed by investigators were “occasional,” meaning less than 3 hours per week but for 2 years or more; “regular,” defined as at least 3 hours weekly for at least 2 years; and “intense,” which required more than 7 hours of physical activity per week for at least 2 years. Levels of cardiovascular and stroke risk factors decreased progressively with increasing levels of physical activity. Only 5% of the AF patients met the ‘intense’ standard, noted Dr. Proietti of the University of Birmingham (England).
The 1-year cardiovascular mortality rate approached 6% in the no physical activity group and hovered around 1% in the other three groups. The 1-year all-cause mortality rate exceeded 12% in the no-exercise group, was 4%% in the occasional exercisers, and 1%-2% in the groups reporting regular or intense physical activity.
The 1-year composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, any thromboembolism, or a bleeding event occurred in 12% of the sedentary patients, a rate two-to-three times higher than in the others.
Updated outcomes are to be reported from the EORP-AF pilot registry after 2 and 3 years of follow-up. Meanwhile, on the basis of the success of the pilot registry, more than 10,000 patients with AF have been enrolled in the EORP-AF main registry, according to Dr. Proietti.
A study limitation, he conceded, is that the registry includes no objective measure of physical capacity, such as METS.
Session co-chair Dr. Brian Olshansky, emeritus professor of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, observed that the registry data raise a classic chicken-versus-egg issue: Do the sedentary patients do worse because they’re inactive, or are they inactive because they are sicker and hence have worse outcomes?
Dr. Proietti said the registry data provide some support for the latter idea, since the no-physical-activity group had higher prevalences of coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Dr. Olshansky raised another point: “It’s interesting to me that there’s a whole bunch of literature showing that elite endurance athletes – bike racers, cross country skiers – have a very high incidence of atrial fibrillation. It seems to be either an inflammatory or an autonomic issue.”
Dr. Proietti replied that he’s familiar with that extensive literature, but the EORP-AF data through 1 year don’t provide validation. While the intense physical activity group tended to have more symptomatic AF than the other groups, they were no more likely to show progression from paroxysmal to permanent AF. The much larger main registry now underway may be able to better clarify the relationship between physical activity and incidence and progression of AF, including the possibility of a U-shaped dose-response curve.
The EORP-AF registry is supported by the European Society of Cardiology. Dr. Proietti reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
AT ACC 16