User login
Moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) is a familiar and established approach to reducing cardiovascular (CV) risk, but it’s often believed that the exercise should be spread out across the week rather than concentrated within a couple of days.
A challenge to that view comes from an observational study of accelerometer-confirmed exercise in almost 90,000 people in their 60s. It suggests,
Researchers compared three patterns of MVPA in their subjects who wore accelerometers on their wrists for 1 week. Active WW subjects obtained at least 2.5 hours of exercise weekly, with at least half the amount completed over 1-2 days; “active regular” subjects achieved that exercise level but not mostly during 1 or 2 days; and those who were “inactive” fell short of 2.5 hours of exercise during the week. The group used a median exercise threshold of 3 hours, 50 minutes in a separate analysis.
The “active” groups, compared with inactive subjects, achieved similar and significant reductions in risk for incident atrial fibrillation (AF), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and heart failure (HF) over a median follow-up of 6.3 years at both weekly exercise thresholds, the group reported.
“The take-home [message] is that efforts to optimize activity, even if concentrated within just a day or 2 each week, should be expected to result in improved cardiovascular risk profiles,” lead author Shaan Khurshid, MD, MPH, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA.
The research “provides novel data on patterns of physical activity accumulation and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases,” observed Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview. He was not involved with the research. Its “marked strengths,” he noted, include a large sample population and “use of accelerometers to measure physical activity levels and patterns.”
Moreover, Dr. Katzmarzyk said, its findings are “important” for showing that physical activity “can be accumulated throughout the week in different ways, which opens up more options for busy people to get their physical activity in.”
Current guidelines from the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association recommend at least 150 minutes of MVPA weekly to lower risk for cardiovascular disease and death, but do not specify an optimal exercise time frame. The U.K. National Health Service recommends MVPA daily or spread evenly over perhaps 4-5 days.
“The weekend warrior pattern has been studied previously, but typically relying on self-reported data, which may be biased, or [in studies] too small to look at specific cardiovascular outcomes,” Dr. Khurshid explained.
In the UK Biobank database, he said, “We saw the opportunity to leverage the largest sample of measured activity to date” to address the question of whether exercise time pattern “affects specific major cardiovascular diseases differently,” Dr. Khurshid said
The primary analysis assessed exercise amount in a week based on the guideline-recommended threshold of at least 2.5 hours; a 3-hour, 50-minutes threshold was used in a secondary analysis. The group assessed multiple thresholds because optimal MVPS levels derived from wrist-based accelerometers are “unclear,” he said.
The sample consisted of 89,573 participants with a mean age 62; slightly more than half (56%) were women. Based on the weekly MVPA threshold of 2.5 hours , the WW, active regular, and inactive groups made up 42.2%, 24%, and 33.7% of the population, respectively.
Compared with the inactive group, the two active groups both showed significant risk reductions for the four clinical outcomes, to similar degrees, in multivariate analysis. The results were similar at the 230-minute weekly exercise threshold for incident AF, MI, and HF but not for stroke.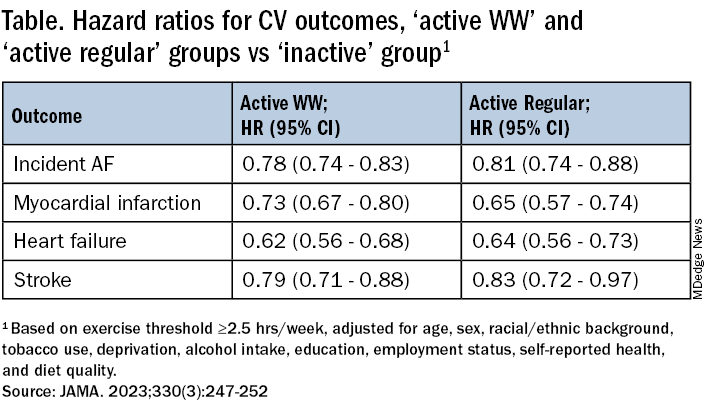
The findings were similarly consistent at the 3-hour, 50-minutes median threshold, although stroke differences were no longer significant.
Patients should be encouraged to exercise at recommended levels, “and should not be discouraged if, for whatever reasons, they are able to focus exercise within only 1 or a few days of the week,” said Dr. Khurshid. “Our findings suggest that it is the volume of activity, rather than the pattern, that matters most.”
The report notes several limitations of the study, including the exercise observation period limited to 1 week and that participants could have modified their behavior during the observation period. Also, the participants were almost all White, so the results may not be generalizable to other populations.
Clinicians should familiarize themselves with the “full range of recommendations” presented in the “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition” “and personalize prescriptions by setting achievable physical activity goals” based on age, physical abilities, and activity levels, states an accompanying editorial from Dr. Katzmarzyk and John M. Jakicic, PhD, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
Although MVPA at the recommended level of at least 2.5 hours per week will certainly be beneficial, they write, “the public health message should also clearly convey that every minute counts, especially among the three-quarters of U.S. adults who do not achieve that goal.”
Dr. Khurshid reported no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the original article. Dr. Katzmarzyk reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jakicic discloses receiving personal fees from Wondr Health, WW International (formerly Weight Watchers), and Educational Initiatives and grants from Epitomee Medical.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) is a familiar and established approach to reducing cardiovascular (CV) risk, but it’s often believed that the exercise should be spread out across the week rather than concentrated within a couple of days.
A challenge to that view comes from an observational study of accelerometer-confirmed exercise in almost 90,000 people in their 60s. It suggests,
Researchers compared three patterns of MVPA in their subjects who wore accelerometers on their wrists for 1 week. Active WW subjects obtained at least 2.5 hours of exercise weekly, with at least half the amount completed over 1-2 days; “active regular” subjects achieved that exercise level but not mostly during 1 or 2 days; and those who were “inactive” fell short of 2.5 hours of exercise during the week. The group used a median exercise threshold of 3 hours, 50 minutes in a separate analysis.
The “active” groups, compared with inactive subjects, achieved similar and significant reductions in risk for incident atrial fibrillation (AF), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and heart failure (HF) over a median follow-up of 6.3 years at both weekly exercise thresholds, the group reported.
“The take-home [message] is that efforts to optimize activity, even if concentrated within just a day or 2 each week, should be expected to result in improved cardiovascular risk profiles,” lead author Shaan Khurshid, MD, MPH, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA.
The research “provides novel data on patterns of physical activity accumulation and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases,” observed Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview. He was not involved with the research. Its “marked strengths,” he noted, include a large sample population and “use of accelerometers to measure physical activity levels and patterns.”
Moreover, Dr. Katzmarzyk said, its findings are “important” for showing that physical activity “can be accumulated throughout the week in different ways, which opens up more options for busy people to get their physical activity in.”
Current guidelines from the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association recommend at least 150 minutes of MVPA weekly to lower risk for cardiovascular disease and death, but do not specify an optimal exercise time frame. The U.K. National Health Service recommends MVPA daily or spread evenly over perhaps 4-5 days.
“The weekend warrior pattern has been studied previously, but typically relying on self-reported data, which may be biased, or [in studies] too small to look at specific cardiovascular outcomes,” Dr. Khurshid explained.
In the UK Biobank database, he said, “We saw the opportunity to leverage the largest sample of measured activity to date” to address the question of whether exercise time pattern “affects specific major cardiovascular diseases differently,” Dr. Khurshid said
The primary analysis assessed exercise amount in a week based on the guideline-recommended threshold of at least 2.5 hours; a 3-hour, 50-minutes threshold was used in a secondary analysis. The group assessed multiple thresholds because optimal MVPS levels derived from wrist-based accelerometers are “unclear,” he said.
The sample consisted of 89,573 participants with a mean age 62; slightly more than half (56%) were women. Based on the weekly MVPA threshold of 2.5 hours , the WW, active regular, and inactive groups made up 42.2%, 24%, and 33.7% of the population, respectively.
Compared with the inactive group, the two active groups both showed significant risk reductions for the four clinical outcomes, to similar degrees, in multivariate analysis. The results were similar at the 230-minute weekly exercise threshold for incident AF, MI, and HF but not for stroke.
The findings were similarly consistent at the 3-hour, 50-minutes median threshold, although stroke differences were no longer significant.
Patients should be encouraged to exercise at recommended levels, “and should not be discouraged if, for whatever reasons, they are able to focus exercise within only 1 or a few days of the week,” said Dr. Khurshid. “Our findings suggest that it is the volume of activity, rather than the pattern, that matters most.”
The report notes several limitations of the study, including the exercise observation period limited to 1 week and that participants could have modified their behavior during the observation period. Also, the participants were almost all White, so the results may not be generalizable to other populations.
Clinicians should familiarize themselves with the “full range of recommendations” presented in the “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition” “and personalize prescriptions by setting achievable physical activity goals” based on age, physical abilities, and activity levels, states an accompanying editorial from Dr. Katzmarzyk and John M. Jakicic, PhD, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
Although MVPA at the recommended level of at least 2.5 hours per week will certainly be beneficial, they write, “the public health message should also clearly convey that every minute counts, especially among the three-quarters of U.S. adults who do not achieve that goal.”
Dr. Khurshid reported no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the original article. Dr. Katzmarzyk reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jakicic discloses receiving personal fees from Wondr Health, WW International (formerly Weight Watchers), and Educational Initiatives and grants from Epitomee Medical.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) is a familiar and established approach to reducing cardiovascular (CV) risk, but it’s often believed that the exercise should be spread out across the week rather than concentrated within a couple of days.
A challenge to that view comes from an observational study of accelerometer-confirmed exercise in almost 90,000 people in their 60s. It suggests,
Researchers compared three patterns of MVPA in their subjects who wore accelerometers on their wrists for 1 week. Active WW subjects obtained at least 2.5 hours of exercise weekly, with at least half the amount completed over 1-2 days; “active regular” subjects achieved that exercise level but not mostly during 1 or 2 days; and those who were “inactive” fell short of 2.5 hours of exercise during the week. The group used a median exercise threshold of 3 hours, 50 minutes in a separate analysis.
The “active” groups, compared with inactive subjects, achieved similar and significant reductions in risk for incident atrial fibrillation (AF), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and heart failure (HF) over a median follow-up of 6.3 years at both weekly exercise thresholds, the group reported.
“The take-home [message] is that efforts to optimize activity, even if concentrated within just a day or 2 each week, should be expected to result in improved cardiovascular risk profiles,” lead author Shaan Khurshid, MD, MPH, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA.
The research “provides novel data on patterns of physical activity accumulation and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases,” observed Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview. He was not involved with the research. Its “marked strengths,” he noted, include a large sample population and “use of accelerometers to measure physical activity levels and patterns.”
Moreover, Dr. Katzmarzyk said, its findings are “important” for showing that physical activity “can be accumulated throughout the week in different ways, which opens up more options for busy people to get their physical activity in.”
Current guidelines from the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association recommend at least 150 minutes of MVPA weekly to lower risk for cardiovascular disease and death, but do not specify an optimal exercise time frame. The U.K. National Health Service recommends MVPA daily or spread evenly over perhaps 4-5 days.
“The weekend warrior pattern has been studied previously, but typically relying on self-reported data, which may be biased, or [in studies] too small to look at specific cardiovascular outcomes,” Dr. Khurshid explained.
In the UK Biobank database, he said, “We saw the opportunity to leverage the largest sample of measured activity to date” to address the question of whether exercise time pattern “affects specific major cardiovascular diseases differently,” Dr. Khurshid said
The primary analysis assessed exercise amount in a week based on the guideline-recommended threshold of at least 2.5 hours; a 3-hour, 50-minutes threshold was used in a secondary analysis. The group assessed multiple thresholds because optimal MVPS levels derived from wrist-based accelerometers are “unclear,” he said.
The sample consisted of 89,573 participants with a mean age 62; slightly more than half (56%) were women. Based on the weekly MVPA threshold of 2.5 hours , the WW, active regular, and inactive groups made up 42.2%, 24%, and 33.7% of the population, respectively.
Compared with the inactive group, the two active groups both showed significant risk reductions for the four clinical outcomes, to similar degrees, in multivariate analysis. The results were similar at the 230-minute weekly exercise threshold for incident AF, MI, and HF but not for stroke.
The findings were similarly consistent at the 3-hour, 50-minutes median threshold, although stroke differences were no longer significant.
Patients should be encouraged to exercise at recommended levels, “and should not be discouraged if, for whatever reasons, they are able to focus exercise within only 1 or a few days of the week,” said Dr. Khurshid. “Our findings suggest that it is the volume of activity, rather than the pattern, that matters most.”
The report notes several limitations of the study, including the exercise observation period limited to 1 week and that participants could have modified their behavior during the observation period. Also, the participants were almost all White, so the results may not be generalizable to other populations.
Clinicians should familiarize themselves with the “full range of recommendations” presented in the “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition” “and personalize prescriptions by setting achievable physical activity goals” based on age, physical abilities, and activity levels, states an accompanying editorial from Dr. Katzmarzyk and John M. Jakicic, PhD, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
Although MVPA at the recommended level of at least 2.5 hours per week will certainly be beneficial, they write, “the public health message should also clearly convey that every minute counts, especially among the three-quarters of U.S. adults who do not achieve that goal.”
Dr. Khurshid reported no relevant financial relationships; disclosures for the other authors are in the original article. Dr. Katzmarzyk reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jakicic discloses receiving personal fees from Wondr Health, WW International (formerly Weight Watchers), and Educational Initiatives and grants from Epitomee Medical.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA