User login
Femoral and Saphenous Vein
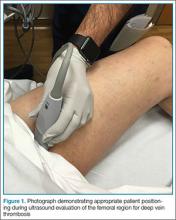
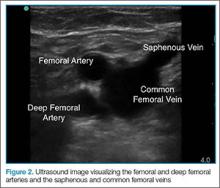
After the appropriate positioning has been achieved, the clinician should identify the common femoral vein and artery, and then slide the probe toward the head or feet until the saphenous vein, which empties into the common femoral vein, is identified
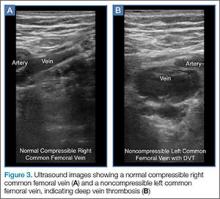
The clinician should take care not to apply too much pressure with the probe as this will compress the saphenous vein; therefore, it is important to use a light touch to ensure proper visualization. Once this key region is identified, the clinician should then use the probe to apply pressure to the vessels. The saphenous vein should compress completely upon application of sufficient pressure to the artery. In a normal vein, the anterior and posterior walls should touch and completely obliterate the lumen of the vein. When a clot is present, the walls of the vein will remain separated (Figure 3). A thrombus can be bright on ultrasound, but some DVTs may appear completely black. In some cases, a lack of compressibility may be the only tip-off to the presence of clot.
After fully evaluating the saphenous vein, the clinician should move the probe toward the feet, keeping the vessels centered in the image, while at the same time applying serial compression approximately every centimeter. As the probe is moved distally, the artery will typically bifurcate first and then the vein will bifurcate into the femoral and deep femoral branches. The femoral vein should be followed until it “dives” into the adductor canal.
Popliteal Region
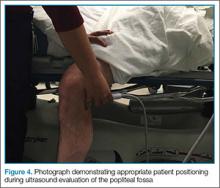
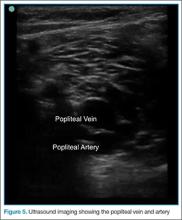
The second zone of the examination is in the popliteal region. It can be helpful to prop the foot up, or hang the foot off the bed to improve access to this region (Figure 4). Similar to the femoral region, maximizing your depth and then decreasing it once the vessels are identified can help to ensure that you are not mistaking superficial vessels
Common Pitfalls
The main pitfall to performing a DVT study is failing to identify the correct vessels. It is important to identify both the artery and vein running together to ensure that the correct location. In larger patients, the relatively shallow depth of the high-frequency
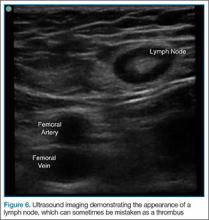
Another common pitfall to keep in mind is that lymph nodes can often be mistaken for clot (Figure 6). A lymph node may be distinguished from a clot by sliding the probe up and down the patient’s leg—lymph nodes will appear as discrete structures, continuous like vasculature. It is essential to evaluate the length of the common femoral, the femoral, and popliteal veins visualized as a recent study by Adhikari et al1 showed that two-point compression studies can miss up to 6% of isolated clots.
Summary
With practice, POC compression ultrasonography of the lower extremities can be used to quickly rule in the diagnosis DVT. Proper patient and probe positioning, as well as the application of appropriate probe pressure at different stages of the examination are essential to accurately visualize and assess the femoral, saphenous, and popliteal veins for the presence of a thrombus.
For a video and more information on performing this scan:
Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
- Emergency Ultrasound: Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Adhikari S, Zeger W, Thom C, Fields JM. Isolated deep venous thrombosis: implications for 2-point compression ultrasonography of the lower extremity. Ann Emerg Med. 2015;66(3):262-266.
Femoral and Saphenous Vein
After the appropriate positioning has been achieved, the clinician should identify the common femoral vein and artery, and then slide the probe toward the head or feet until the saphenous vein, which empties into the common femoral vein, is identified
The clinician should take care not to apply too much pressure with the probe as this will compress the saphenous vein; therefore, it is important to use a light touch to ensure proper visualization. Once this key region is identified, the clinician should then use the probe to apply pressure to the vessels. The saphenous vein should compress completely upon application of sufficient pressure to the artery. In a normal vein, the anterior and posterior walls should touch and completely obliterate the lumen of the vein. When a clot is present, the walls of the vein will remain separated (Figure 3). A thrombus can be bright on ultrasound, but some DVTs may appear completely black. In some cases, a lack of compressibility may be the only tip-off to the presence of clot.
After fully evaluating the saphenous vein, the clinician should move the probe toward the feet, keeping the vessels centered in the image, while at the same time applying serial compression approximately every centimeter. As the probe is moved distally, the artery will typically bifurcate first and then the vein will bifurcate into the femoral and deep femoral branches. The femoral vein should be followed until it “dives” into the adductor canal.
Popliteal Region
The second zone of the examination is in the popliteal region. It can be helpful to prop the foot up, or hang the foot off the bed to improve access to this region (Figure 4). Similar to the femoral region, maximizing your depth and then decreasing it once the vessels are identified can help to ensure that you are not mistaking superficial vessels
Common Pitfalls
The main pitfall to performing a DVT study is failing to identify the correct vessels. It is important to identify both the artery and vein running together to ensure that the correct location. In larger patients, the relatively shallow depth of the high-frequency
Another common pitfall to keep in mind is that lymph nodes can often be mistaken for clot (Figure 6). A lymph node may be distinguished from a clot by sliding the probe up and down the patient’s leg—lymph nodes will appear as discrete structures, continuous like vasculature. It is essential to evaluate the length of the common femoral, the femoral, and popliteal veins visualized as a recent study by Adhikari et al1 showed that two-point compression studies can miss up to 6% of isolated clots.
Summary
With practice, POC compression ultrasonography of the lower extremities can be used to quickly rule in the diagnosis DVT. Proper patient and probe positioning, as well as the application of appropriate probe pressure at different stages of the examination are essential to accurately visualize and assess the femoral, saphenous, and popliteal veins for the presence of a thrombus.
For a video and more information on performing this scan:
Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
Femoral and Saphenous Vein
After the appropriate positioning has been achieved, the clinician should identify the common femoral vein and artery, and then slide the probe toward the head or feet until the saphenous vein, which empties into the common femoral vein, is identified
The clinician should take care not to apply too much pressure with the probe as this will compress the saphenous vein; therefore, it is important to use a light touch to ensure proper visualization. Once this key region is identified, the clinician should then use the probe to apply pressure to the vessels. The saphenous vein should compress completely upon application of sufficient pressure to the artery. In a normal vein, the anterior and posterior walls should touch and completely obliterate the lumen of the vein. When a clot is present, the walls of the vein will remain separated (Figure 3). A thrombus can be bright on ultrasound, but some DVTs may appear completely black. In some cases, a lack of compressibility may be the only tip-off to the presence of clot.
After fully evaluating the saphenous vein, the clinician should move the probe toward the feet, keeping the vessels centered in the image, while at the same time applying serial compression approximately every centimeter. As the probe is moved distally, the artery will typically bifurcate first and then the vein will bifurcate into the femoral and deep femoral branches. The femoral vein should be followed until it “dives” into the adductor canal.
Popliteal Region
The second zone of the examination is in the popliteal region. It can be helpful to prop the foot up, or hang the foot off the bed to improve access to this region (Figure 4). Similar to the femoral region, maximizing your depth and then decreasing it once the vessels are identified can help to ensure that you are not mistaking superficial vessels
Common Pitfalls
The main pitfall to performing a DVT study is failing to identify the correct vessels. It is important to identify both the artery and vein running together to ensure that the correct location. In larger patients, the relatively shallow depth of the high-frequency
Another common pitfall to keep in mind is that lymph nodes can often be mistaken for clot (Figure 6). A lymph node may be distinguished from a clot by sliding the probe up and down the patient’s leg—lymph nodes will appear as discrete structures, continuous like vasculature. It is essential to evaluate the length of the common femoral, the femoral, and popliteal veins visualized as a recent study by Adhikari et al1 showed that two-point compression studies can miss up to 6% of isolated clots.
Summary
With practice, POC compression ultrasonography of the lower extremities can be used to quickly rule in the diagnosis DVT. Proper patient and probe positioning, as well as the application of appropriate probe pressure at different stages of the examination are essential to accurately visualize and assess the femoral, saphenous, and popliteal veins for the presence of a thrombus.
For a video and more information on performing this scan:
Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
- Emergency Ultrasound: Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Adhikari S, Zeger W, Thom C, Fields JM. Isolated deep venous thrombosis: implications for 2-point compression ultrasonography of the lower extremity. Ann Emerg Med. 2015;66(3):262-266.
- Emergency Ultrasound: Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Adhikari S, Zeger W, Thom C, Fields JM. Isolated deep venous thrombosis: implications for 2-point compression ultrasonography of the lower extremity. Ann Emerg Med. 2015;66(3):262-266.