User login
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
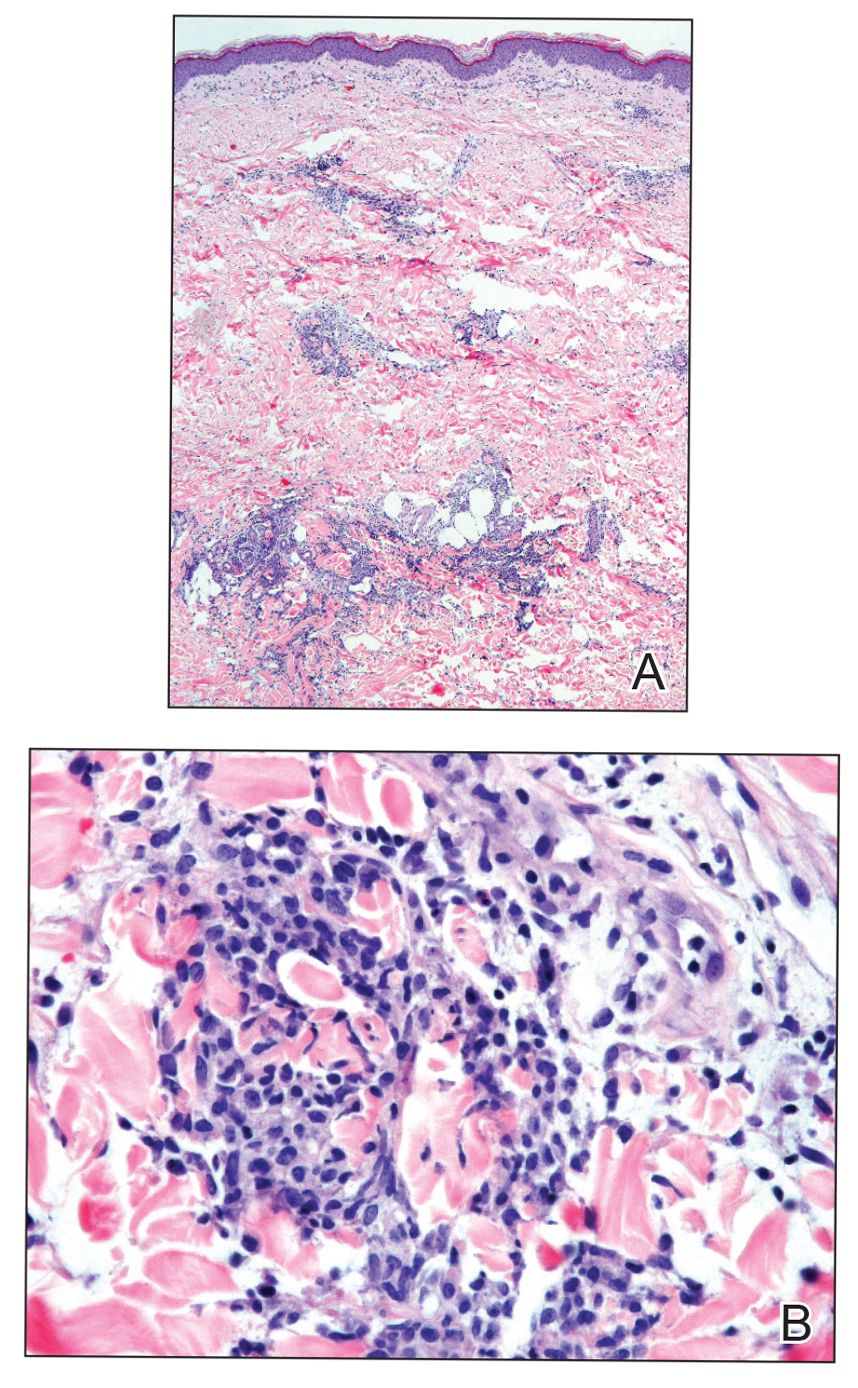
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.
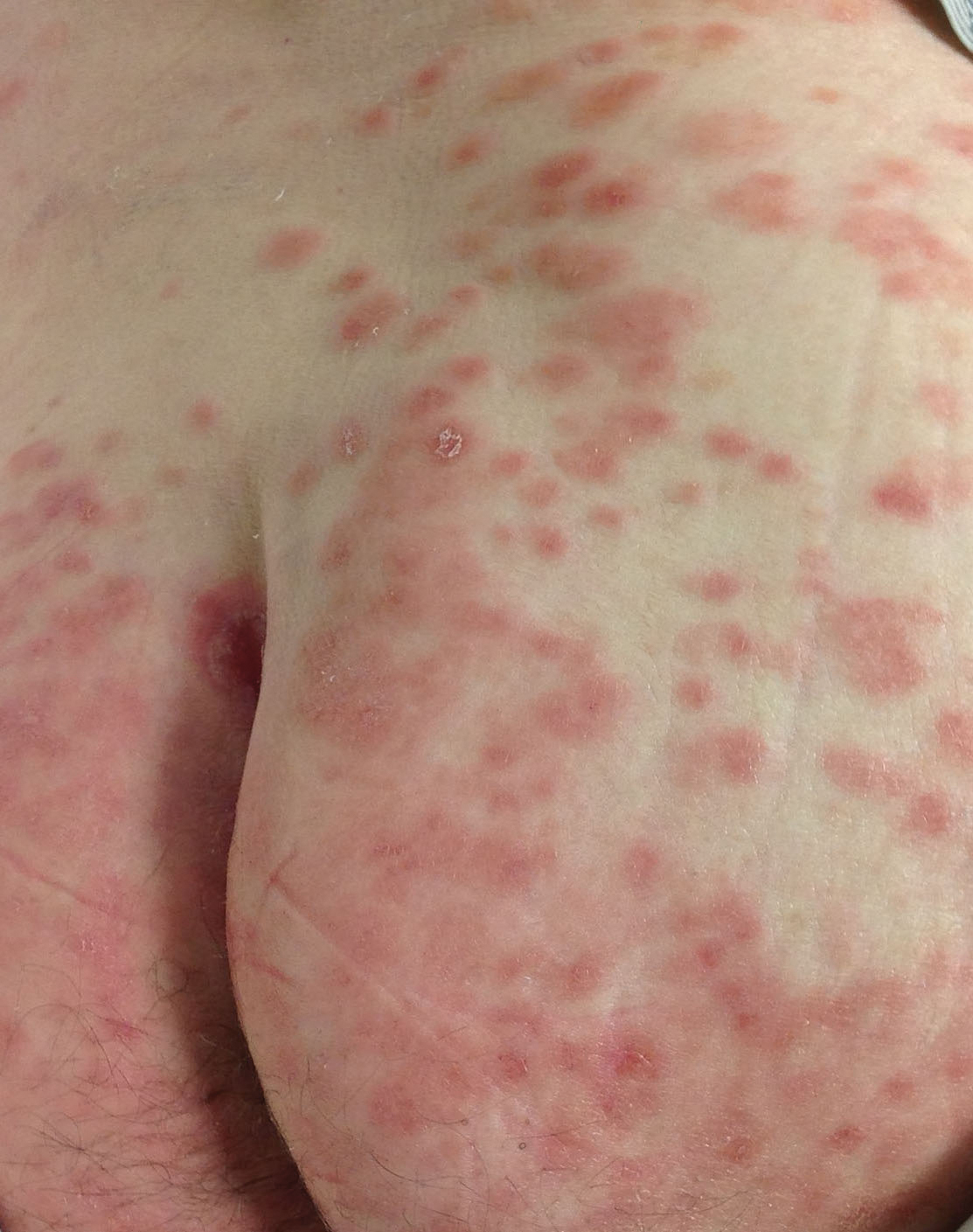
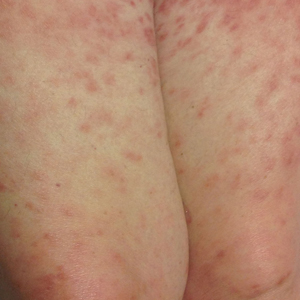
Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.

Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.

Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.