User login

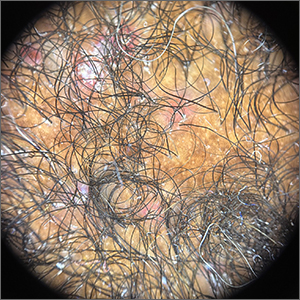
Dermoscopy showed not only the erythema, inflammation, and crusting visible during the initial examination, but it also revealed that each lesion had a hair growing through it. This pointed to a diagnosis of superficial folliculitis of the scalp.
The physician ruled out tinea capitis, acne keloidalis nuchae, and scarring alopecia based on the dermoscopic exam. There were no broken hairs that one would expect with tinea capitis. Also, there was no polytrichia (multiple hairs pushed into a single follicular opening due to scarring of the skin) that would be expected with acne keloidalis nuchae and scarring alopecias.
There are multiple types of scalp folliculitis. This patient had superficial folliculitis, in which pustules develop at the ostium of the hair follicles. Deep folliculitis is more severe and includes furuncles and carbuncles.1
Folliculitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection and, less commonly, fungal infection. In addition to superficial and deep folliculitis, inflammation with scarring of the follicles occurs with folliculitis decalvans, which is one of the scarring alopecias.1
Mild cases of superficial bacterial folliculitis are treated with topical antibiotics (eg, topical clindamycin 1% applied twice daily). Depending on the severity, oral antibiotics including doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days or trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg (double strength) twice daily for 7 days may be used. There is also a chronic nonscarring form of scalp folliculitis that often responds initially to antibiotics but then recurs. This has been treated with longer courses of oral antibiotics and, if the lesions don’t respond or continue to recur, with low-dose isotretinoin.2
Due to the amount of scalp involvement, crusting, and inflammation seen on this patient’s scalp, he was treated with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg twice daily for 7 days. After 1 week, he reported that he was doing much better and that the lesions had nearly resolved. He was told to return for reevaluation if the lesions did not completely resolve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Lugović-Mihić L, Barisić F, Bulat V, et al. Differential diagnosis of the scalp hair folliculitis. Acta Clin Croat. 2011;50:395-402.
2. Romero-Maté A, Arias-Palomo D, Hernández-Núñez A, et al. Chronic nonscarring scalp folliculitis: retrospective case series study of 34 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1023-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.065

Dermoscopy showed not only the erythema, inflammation, and crusting visible during the initial examination, but it also revealed that each lesion had a hair growing through it. This pointed to a diagnosis of superficial folliculitis of the scalp.
The physician ruled out tinea capitis, acne keloidalis nuchae, and scarring alopecia based on the dermoscopic exam. There were no broken hairs that one would expect with tinea capitis. Also, there was no polytrichia (multiple hairs pushed into a single follicular opening due to scarring of the skin) that would be expected with acne keloidalis nuchae and scarring alopecias.
There are multiple types of scalp folliculitis. This patient had superficial folliculitis, in which pustules develop at the ostium of the hair follicles. Deep folliculitis is more severe and includes furuncles and carbuncles.1
Folliculitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection and, less commonly, fungal infection. In addition to superficial and deep folliculitis, inflammation with scarring of the follicles occurs with folliculitis decalvans, which is one of the scarring alopecias.1
Mild cases of superficial bacterial folliculitis are treated with topical antibiotics (eg, topical clindamycin 1% applied twice daily). Depending on the severity, oral antibiotics including doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days or trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg (double strength) twice daily for 7 days may be used. There is also a chronic nonscarring form of scalp folliculitis that often responds initially to antibiotics but then recurs. This has been treated with longer courses of oral antibiotics and, if the lesions don’t respond or continue to recur, with low-dose isotretinoin.2
Due to the amount of scalp involvement, crusting, and inflammation seen on this patient’s scalp, he was treated with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg twice daily for 7 days. After 1 week, he reported that he was doing much better and that the lesions had nearly resolved. He was told to return for reevaluation if the lesions did not completely resolve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

Dermoscopy showed not only the erythema, inflammation, and crusting visible during the initial examination, but it also revealed that each lesion had a hair growing through it. This pointed to a diagnosis of superficial folliculitis of the scalp.
The physician ruled out tinea capitis, acne keloidalis nuchae, and scarring alopecia based on the dermoscopic exam. There were no broken hairs that one would expect with tinea capitis. Also, there was no polytrichia (multiple hairs pushed into a single follicular opening due to scarring of the skin) that would be expected with acne keloidalis nuchae and scarring alopecias.
There are multiple types of scalp folliculitis. This patient had superficial folliculitis, in which pustules develop at the ostium of the hair follicles. Deep folliculitis is more severe and includes furuncles and carbuncles.1
Folliculitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection and, less commonly, fungal infection. In addition to superficial and deep folliculitis, inflammation with scarring of the follicles occurs with folliculitis decalvans, which is one of the scarring alopecias.1
Mild cases of superficial bacterial folliculitis are treated with topical antibiotics (eg, topical clindamycin 1% applied twice daily). Depending on the severity, oral antibiotics including doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days or trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg (double strength) twice daily for 7 days may be used. There is also a chronic nonscarring form of scalp folliculitis that often responds initially to antibiotics but then recurs. This has been treated with longer courses of oral antibiotics and, if the lesions don’t respond or continue to recur, with low-dose isotretinoin.2
Due to the amount of scalp involvement, crusting, and inflammation seen on this patient’s scalp, he was treated with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg twice daily for 7 days. After 1 week, he reported that he was doing much better and that the lesions had nearly resolved. He was told to return for reevaluation if the lesions did not completely resolve.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Lugović-Mihić L, Barisić F, Bulat V, et al. Differential diagnosis of the scalp hair folliculitis. Acta Clin Croat. 2011;50:395-402.
2. Romero-Maté A, Arias-Palomo D, Hernández-Núñez A, et al. Chronic nonscarring scalp folliculitis: retrospective case series study of 34 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1023-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.065
1. Lugović-Mihić L, Barisić F, Bulat V, et al. Differential diagnosis of the scalp hair folliculitis. Acta Clin Croat. 2011;50:395-402.
2. Romero-Maté A, Arias-Palomo D, Hernández-Núñez A, et al. Chronic nonscarring scalp folliculitis: retrospective case series study of 34 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1023-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.065