User login
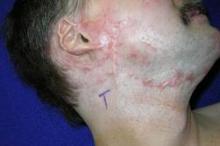
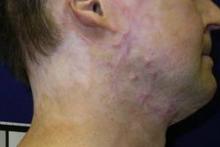
PHOENIX – A fractional carbon dioxide laser at 10,600 nm was the only one of three laser treatments for hypertrophic scars that produced significant overall improvements in a comparison of data on 141 scars in 66 patients.
Less successful were treatments using a vascular KTP laser at 532 nm or a 1,550-nm nonablative fractional erbium glass laser.
"The only one that showed significant improvement compared with the control scar, adjusted for the baseline scar, was the fractional CO2 laser," Dr. Sigrid Blome-Eberwein said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
The data came from three prospective controlled studies at one institution. The patients were burn survivors who had at least two scars of similar appearance and physiologic function in the same body area that were at least 6 months from wound healing. Patients underwent a series of at least three treatments at 4-week intervals on one or more scars, with a similar scar left untreated as the control scar.
Subjective assessments of the scars showed statistically significant improvements in scores on the Vancouver Scar Scale with all three treatments compared with control scars, but fewer changes were seen in objective measurements of scar qualities. "Measurements of these improvements are really difficult to tackle. We tried to add some objective measurement instruments to our evaluations," reported Dr. Blome-Eberwein of Lehigh Valley Regional Burn Center, Allentown, Pa.
None of the treatments produced significant changes in elasticity as measured by the Cutometer device. "It’s really a complete mix of results in this value," she said.
The fractional erbium laser produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars, in thickness as measured by high-resolution ultrasound used to assess scar thickness (so that patients could avoid biopsies). The KTP laser also produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars: improved sensation as assessed by Semmes Weinstein monofilaments.
The CO2 laser, however, produced greater improvements in scar thickness and sensation, as well as significant improvements in erythema and pigment (both measured by spectrometry), compared with control scars. Measurements of pain and pruritus did not differ significantly between treated and control scars in any of the studies; pain levels tended to improve in both the treated and control areas and pruritus tended to remain steady.
The KTP laser caused blisters in some patients. The fractional CO2 and fractional erbium lasers produced minimal damage. Increased power was more likely to produce collateral damage and blisters, Dr. Blome-Eberwein said.
Any results were persistent and additive. Because penetration of these lasers is limited, multiple treatments are needed for thick scars, she noted.
Based on these findings and her experience at the burn center, Dr. Blome-Eberwein recommended treating scars that seem to turn hypertrophic early (within 4 weeks of wound healing) and frequently (every 3 weeks) with a nonablative fractional erbium glass laser or pulsed dye laser. The erbium glass laser does seem to prevent "some degree of hypertrophy early on," she said. Either of these early treatments may decrease hypertrophic activity and prevent hypertrophy with no dermal damage.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein said she treats hypertrophic scars 3-12 months after healing with fractional CO2 laser. Treating scar pigment remains a challenge, she added.
"In the future, there will be handheld devices" to treat scars at home "because a lot of people are affected by this problem," she said.
Most of the scars in the studies were from burns, with a few from trauma.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein reported having no financial disclosures.
On Twitter @sherryboschert
PHOENIX – A fractional carbon dioxide laser at 10,600 nm was the only one of three laser treatments for hypertrophic scars that produced significant overall improvements in a comparison of data on 141 scars in 66 patients.
Less successful were treatments using a vascular KTP laser at 532 nm or a 1,550-nm nonablative fractional erbium glass laser.
"The only one that showed significant improvement compared with the control scar, adjusted for the baseline scar, was the fractional CO2 laser," Dr. Sigrid Blome-Eberwein said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
The data came from three prospective controlled studies at one institution. The patients were burn survivors who had at least two scars of similar appearance and physiologic function in the same body area that were at least 6 months from wound healing. Patients underwent a series of at least three treatments at 4-week intervals on one or more scars, with a similar scar left untreated as the control scar.
Subjective assessments of the scars showed statistically significant improvements in scores on the Vancouver Scar Scale with all three treatments compared with control scars, but fewer changes were seen in objective measurements of scar qualities. "Measurements of these improvements are really difficult to tackle. We tried to add some objective measurement instruments to our evaluations," reported Dr. Blome-Eberwein of Lehigh Valley Regional Burn Center, Allentown, Pa.
None of the treatments produced significant changes in elasticity as measured by the Cutometer device. "It’s really a complete mix of results in this value," she said.
The fractional erbium laser produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars, in thickness as measured by high-resolution ultrasound used to assess scar thickness (so that patients could avoid biopsies). The KTP laser also produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars: improved sensation as assessed by Semmes Weinstein monofilaments.
The CO2 laser, however, produced greater improvements in scar thickness and sensation, as well as significant improvements in erythema and pigment (both measured by spectrometry), compared with control scars. Measurements of pain and pruritus did not differ significantly between treated and control scars in any of the studies; pain levels tended to improve in both the treated and control areas and pruritus tended to remain steady.
The KTP laser caused blisters in some patients. The fractional CO2 and fractional erbium lasers produced minimal damage. Increased power was more likely to produce collateral damage and blisters, Dr. Blome-Eberwein said.
Any results were persistent and additive. Because penetration of these lasers is limited, multiple treatments are needed for thick scars, she noted.
Based on these findings and her experience at the burn center, Dr. Blome-Eberwein recommended treating scars that seem to turn hypertrophic early (within 4 weeks of wound healing) and frequently (every 3 weeks) with a nonablative fractional erbium glass laser or pulsed dye laser. The erbium glass laser does seem to prevent "some degree of hypertrophy early on," she said. Either of these early treatments may decrease hypertrophic activity and prevent hypertrophy with no dermal damage.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein said she treats hypertrophic scars 3-12 months after healing with fractional CO2 laser. Treating scar pigment remains a challenge, she added.
"In the future, there will be handheld devices" to treat scars at home "because a lot of people are affected by this problem," she said.
Most of the scars in the studies were from burns, with a few from trauma.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein reported having no financial disclosures.
On Twitter @sherryboschert
PHOENIX – A fractional carbon dioxide laser at 10,600 nm was the only one of three laser treatments for hypertrophic scars that produced significant overall improvements in a comparison of data on 141 scars in 66 patients.
Less successful were treatments using a vascular KTP laser at 532 nm or a 1,550-nm nonablative fractional erbium glass laser.
"The only one that showed significant improvement compared with the control scar, adjusted for the baseline scar, was the fractional CO2 laser," Dr. Sigrid Blome-Eberwein said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
The data came from three prospective controlled studies at one institution. The patients were burn survivors who had at least two scars of similar appearance and physiologic function in the same body area that were at least 6 months from wound healing. Patients underwent a series of at least three treatments at 4-week intervals on one or more scars, with a similar scar left untreated as the control scar.
Subjective assessments of the scars showed statistically significant improvements in scores on the Vancouver Scar Scale with all three treatments compared with control scars, but fewer changes were seen in objective measurements of scar qualities. "Measurements of these improvements are really difficult to tackle. We tried to add some objective measurement instruments to our evaluations," reported Dr. Blome-Eberwein of Lehigh Valley Regional Burn Center, Allentown, Pa.
None of the treatments produced significant changes in elasticity as measured by the Cutometer device. "It’s really a complete mix of results in this value," she said.
The fractional erbium laser produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars, in thickness as measured by high-resolution ultrasound used to assess scar thickness (so that patients could avoid biopsies). The KTP laser also produced one statistically significant improvement, compared with control scars: improved sensation as assessed by Semmes Weinstein monofilaments.
The CO2 laser, however, produced greater improvements in scar thickness and sensation, as well as significant improvements in erythema and pigment (both measured by spectrometry), compared with control scars. Measurements of pain and pruritus did not differ significantly between treated and control scars in any of the studies; pain levels tended to improve in both the treated and control areas and pruritus tended to remain steady.
The KTP laser caused blisters in some patients. The fractional CO2 and fractional erbium lasers produced minimal damage. Increased power was more likely to produce collateral damage and blisters, Dr. Blome-Eberwein said.
Any results were persistent and additive. Because penetration of these lasers is limited, multiple treatments are needed for thick scars, she noted.
Based on these findings and her experience at the burn center, Dr. Blome-Eberwein recommended treating scars that seem to turn hypertrophic early (within 4 weeks of wound healing) and frequently (every 3 weeks) with a nonablative fractional erbium glass laser or pulsed dye laser. The erbium glass laser does seem to prevent "some degree of hypertrophy early on," she said. Either of these early treatments may decrease hypertrophic activity and prevent hypertrophy with no dermal damage.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein said she treats hypertrophic scars 3-12 months after healing with fractional CO2 laser. Treating scar pigment remains a challenge, she added.
"In the future, there will be handheld devices" to treat scars at home "because a lot of people are affected by this problem," she said.
Most of the scars in the studies were from burns, with a few from trauma.
Dr. Blome-Eberwein reported having no financial disclosures.
On Twitter @sherryboschert
AT LASER 2014
Major finding: The fractional CO2 laser significantly improved scar thickness, sensation, erythema, and pigment, compared with untreated scars. The KTP laser improved sensation and the erbium glass laser improved thickness in treated scars, compared with control scars.
Data source: An analysis of data from three prospective controlled studies of laser treatments in 66 patients with 141 scars.
Disclosures: Dr. Blome-Eberwein reported having no financial disclosures.