User login
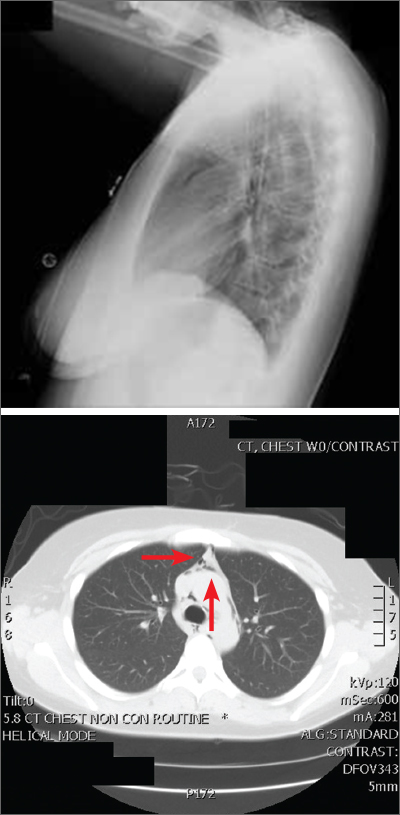
The posteroanterior (PA) and lateral view CXRs, as well as the CT scan, revealed the presence of retrosternal air and confirmed the patient’s diagnosis of pneumomediastinum.
Pneumomediastinum—the presence of free air in the mediastinum—can develop spontaneously (as was the case with our patient) or in response to trauma. Common causes include respiratory diseases such as asthma, and trauma to the esophagus secondary to mechanical ventilation, endoscopy, and excessive vomiting.1 Other possible causes include respiratory infections, foreign body aspiration, recent dental extraction, diabetic ketoacidosis, esophageal perforation, barotrauma (due to activities such as flying or scuba diving), and use of illicit drugs.1
Patients with pneumomediastinum often complain of retrosternal, pleuritic pain that radiates to their back, shoulders, and arms. They may also have difficulty swallowing (globus pharyngeus), a nasal voice, and/or dyspnea. Physical findings can include subcutaneous emphysema in the neck and supraclavicular fossa as manifested by the Hamman sign (a precordial “crunching” sound heard during systole), a fever, and distended neck veins.1
Diagnosis is made by CXR and/or chest CT. On a CXR, retrosternal air is best seen in the lateral projection. Small amounts of air can appear as linear lucencies outlining mediastinal contours. This air can be seen under the skin, surrounding the pericardium, around the pulmonary and/or aortic vasculature, and/or between the parietal pleura and diaphragm.2 A pleural effusion—particularly on the patient’s left side—should raise concern for esophageal perforation.
Pneumomediastinum is generally a self-limiting condition. Thus, patients who don’t have severe symptoms, such as respiratory distress or signs of inflammation, should be observed for 2 days, managed with rest and pain control, and discharged home. If severe symptoms or inflammatory signs are present, a Gastrografin swallow study is recommended to rule out esophageal perforation.3 If the result of this test is abnormal, a follow-up study with barium is recommended.3
The patient underwent both swallow studies, and they were negative. This patient received subsequent serial CXRs that showed improvement in the pneumomediastinum. Once the patient’s pain was well controlled with oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, she was discharged (after a 3-day hospitalization) with close follow-up. One week later, her pain had almost entirely resolved.
This case was adapted from: Gawrys B, Shaha D. Pleuritic chest pain and globus pharyngeus. J Fam Pract. 2015;64:305-307.
1. Park DE, Vallieres E. Pneumomediastinum and mediastinitis. In: Mason R, Broaddus V, Murray J, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 4th ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2005:2039-2068.
2. Zylak CM, Standen JR, Barnes GR, et al. Pneumomediastinum revisited. Radiographics. 2000;20:1043-1057. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.20.4.g00jl13104
3. Takada K, Matsumoto S, Hiramatsu T, et al. Management of spontaneous pneumomediastinum based on clinical experience of 25 cases. Respir Med. 2008;102:1329-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.03.023
The posteroanterior (PA) and lateral view CXRs, as well as the CT scan, revealed the presence of retrosternal air and confirmed the patient’s diagnosis of pneumomediastinum.
Pneumomediastinum—the presence of free air in the mediastinum—can develop spontaneously (as was the case with our patient) or in response to trauma. Common causes include respiratory diseases such as asthma, and trauma to the esophagus secondary to mechanical ventilation, endoscopy, and excessive vomiting.1 Other possible causes include respiratory infections, foreign body aspiration, recent dental extraction, diabetic ketoacidosis, esophageal perforation, barotrauma (due to activities such as flying or scuba diving), and use of illicit drugs.1
Patients with pneumomediastinum often complain of retrosternal, pleuritic pain that radiates to their back, shoulders, and arms. They may also have difficulty swallowing (globus pharyngeus), a nasal voice, and/or dyspnea. Physical findings can include subcutaneous emphysema in the neck and supraclavicular fossa as manifested by the Hamman sign (a precordial “crunching” sound heard during systole), a fever, and distended neck veins.1
Diagnosis is made by CXR and/or chest CT. On a CXR, retrosternal air is best seen in the lateral projection. Small amounts of air can appear as linear lucencies outlining mediastinal contours. This air can be seen under the skin, surrounding the pericardium, around the pulmonary and/or aortic vasculature, and/or between the parietal pleura and diaphragm.2 A pleural effusion—particularly on the patient’s left side—should raise concern for esophageal perforation.
Pneumomediastinum is generally a self-limiting condition. Thus, patients who don’t have severe symptoms, such as respiratory distress or signs of inflammation, should be observed for 2 days, managed with rest and pain control, and discharged home. If severe symptoms or inflammatory signs are present, a Gastrografin swallow study is recommended to rule out esophageal perforation.3 If the result of this test is abnormal, a follow-up study with barium is recommended.3
The patient underwent both swallow studies, and they were negative. This patient received subsequent serial CXRs that showed improvement in the pneumomediastinum. Once the patient’s pain was well controlled with oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, she was discharged (after a 3-day hospitalization) with close follow-up. One week later, her pain had almost entirely resolved.
This case was adapted from: Gawrys B, Shaha D. Pleuritic chest pain and globus pharyngeus. J Fam Pract. 2015;64:305-307.
The posteroanterior (PA) and lateral view CXRs, as well as the CT scan, revealed the presence of retrosternal air and confirmed the patient’s diagnosis of pneumomediastinum.
Pneumomediastinum—the presence of free air in the mediastinum—can develop spontaneously (as was the case with our patient) or in response to trauma. Common causes include respiratory diseases such as asthma, and trauma to the esophagus secondary to mechanical ventilation, endoscopy, and excessive vomiting.1 Other possible causes include respiratory infections, foreign body aspiration, recent dental extraction, diabetic ketoacidosis, esophageal perforation, barotrauma (due to activities such as flying or scuba diving), and use of illicit drugs.1
Patients with pneumomediastinum often complain of retrosternal, pleuritic pain that radiates to their back, shoulders, and arms. They may also have difficulty swallowing (globus pharyngeus), a nasal voice, and/or dyspnea. Physical findings can include subcutaneous emphysema in the neck and supraclavicular fossa as manifested by the Hamman sign (a precordial “crunching” sound heard during systole), a fever, and distended neck veins.1
Diagnosis is made by CXR and/or chest CT. On a CXR, retrosternal air is best seen in the lateral projection. Small amounts of air can appear as linear lucencies outlining mediastinal contours. This air can be seen under the skin, surrounding the pericardium, around the pulmonary and/or aortic vasculature, and/or between the parietal pleura and diaphragm.2 A pleural effusion—particularly on the patient’s left side—should raise concern for esophageal perforation.
Pneumomediastinum is generally a self-limiting condition. Thus, patients who don’t have severe symptoms, such as respiratory distress or signs of inflammation, should be observed for 2 days, managed with rest and pain control, and discharged home. If severe symptoms or inflammatory signs are present, a Gastrografin swallow study is recommended to rule out esophageal perforation.3 If the result of this test is abnormal, a follow-up study with barium is recommended.3
The patient underwent both swallow studies, and they were negative. This patient received subsequent serial CXRs that showed improvement in the pneumomediastinum. Once the patient’s pain was well controlled with oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, she was discharged (after a 3-day hospitalization) with close follow-up. One week later, her pain had almost entirely resolved.
This case was adapted from: Gawrys B, Shaha D. Pleuritic chest pain and globus pharyngeus. J Fam Pract. 2015;64:305-307.
1. Park DE, Vallieres E. Pneumomediastinum and mediastinitis. In: Mason R, Broaddus V, Murray J, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 4th ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2005:2039-2068.
2. Zylak CM, Standen JR, Barnes GR, et al. Pneumomediastinum revisited. Radiographics. 2000;20:1043-1057. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.20.4.g00jl13104
3. Takada K, Matsumoto S, Hiramatsu T, et al. Management of spontaneous pneumomediastinum based on clinical experience of 25 cases. Respir Med. 2008;102:1329-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.03.023
1. Park DE, Vallieres E. Pneumomediastinum and mediastinitis. In: Mason R, Broaddus V, Murray J, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 4th ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2005:2039-2068.
2. Zylak CM, Standen JR, Barnes GR, et al. Pneumomediastinum revisited. Radiographics. 2000;20:1043-1057. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.20.4.g00jl13104
3. Takada K, Matsumoto S, Hiramatsu T, et al. Management of spontaneous pneumomediastinum based on clinical experience of 25 cases. Respir Med. 2008;102:1329-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.03.023