User login
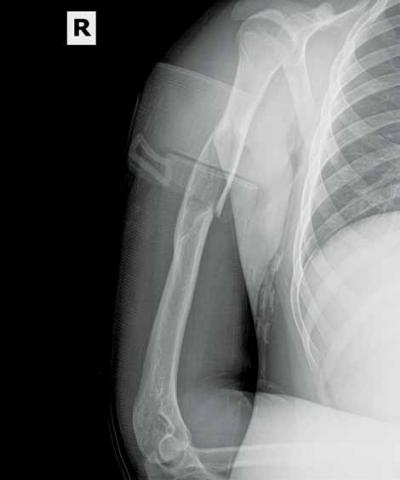
After playing football, an 18-year-old man presented to the ED with severe pain in his right arm. He stated that while throwing a pass, he felt a "snap" in his right arm and has been unable to move the arm since the injury. Radiographs were completed.
What is your interpretation of the radiographic image (Figure 1)?
Dr Patterson, editor of "Challenges in Sports Medicine and Orthopedics," is a sports medicine physician at Florida Sports Injury in Clermont, Florida. Dr Patterson is board certified in family medicine and spinal cord injury medicine, and is a member of the faculty of sports and exercise medicine of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
The radiograph (Figure 2) revealed a minimally displaced pathologic fracture (red arrow) through the midshaft of the humerus, which resulted from a space-occupying lesion (green arrow) in the humeral diaphysis. Since the radial nerve is commonly affected in this type of injury due to its close proximity to the humeral midshaft, careful neurologic assessment at the wrist and hand is essential. Injury to the nerve can occur during the fracture or reduction of the fracture, causing weakness in the extensors of the hand and numbness in the first dorsal web space. The incidence of radial nerve palsy in midshaft fractures of the humerus is 16%.1
In nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures of the humeral midshaft, conservative management with a U-shaped (sugar-tong) splint from axilla to shoulder with elasticized wrap and sling is recommended. Surgical management is indicated in comminuted, significantly displaced, nonreducible, pathologic cases or in fractures resulting in neurovascular compromise. The patient in this case was referred to an orthopedic surgeon for open treatment.
- Smith WR, Agudelo JF, Parekh AA, Shank, JR. Musculoskeletal trauma surgery. In: Skinner HB, ed. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics. 4th ed. McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2006:121.
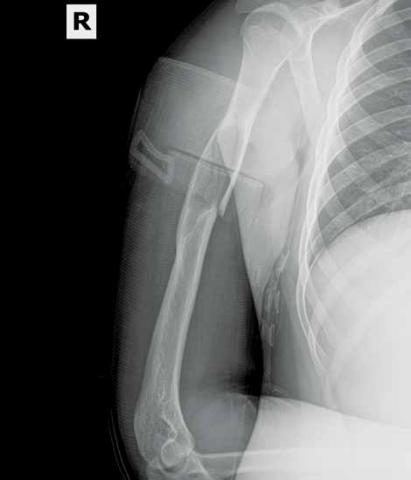
After playing football, an 18-year-old man presented to the ED with severe pain in his right arm. He stated that while throwing a pass, he felt a "snap" in his right arm and has been unable to move the arm since the injury. Radiographs were completed.
What is your interpretation of the radiographic image (Figure 1)?
Dr Patterson, editor of "Challenges in Sports Medicine and Orthopedics," is a sports medicine physician at Florida Sports Injury in Clermont, Florida. Dr Patterson is board certified in family medicine and spinal cord injury medicine, and is a member of the faculty of sports and exercise medicine of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
The radiograph (Figure 2) revealed a minimally displaced pathologic fracture (red arrow) through the midshaft of the humerus, which resulted from a space-occupying lesion (green arrow) in the humeral diaphysis. Since the radial nerve is commonly affected in this type of injury due to its close proximity to the humeral midshaft, careful neurologic assessment at the wrist and hand is essential. Injury to the nerve can occur during the fracture or reduction of the fracture, causing weakness in the extensors of the hand and numbness in the first dorsal web space. The incidence of radial nerve palsy in midshaft fractures of the humerus is 16%.1
In nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures of the humeral midshaft, conservative management with a U-shaped (sugar-tong) splint from axilla to shoulder with elasticized wrap and sling is recommended. Surgical management is indicated in comminuted, significantly displaced, nonreducible, pathologic cases or in fractures resulting in neurovascular compromise. The patient in this case was referred to an orthopedic surgeon for open treatment.
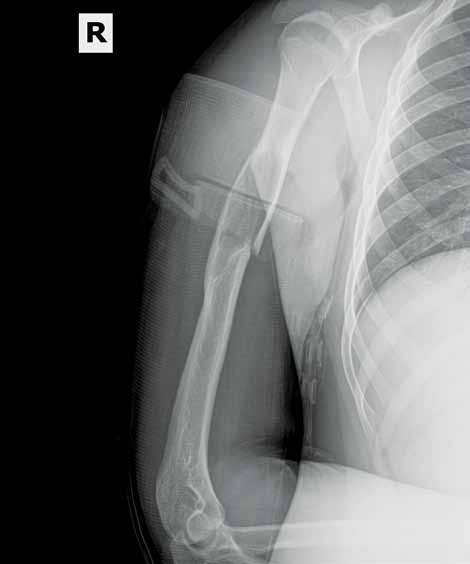
After playing football, an 18-year-old man presented to the ED with severe pain in his right arm. He stated that while throwing a pass, he felt a "snap" in his right arm and has been unable to move the arm since the injury. Radiographs were completed.
What is your interpretation of the radiographic image (Figure 1)?
Dr Patterson, editor of "Challenges in Sports Medicine and Orthopedics," is a sports medicine physician at Florida Sports Injury in Clermont, Florida. Dr Patterson is board certified in family medicine and spinal cord injury medicine, and is a member of the faculty of sports and exercise medicine of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
The radiograph (Figure 2) revealed a minimally displaced pathologic fracture (red arrow) through the midshaft of the humerus, which resulted from a space-occupying lesion (green arrow) in the humeral diaphysis. Since the radial nerve is commonly affected in this type of injury due to its close proximity to the humeral midshaft, careful neurologic assessment at the wrist and hand is essential. Injury to the nerve can occur during the fracture or reduction of the fracture, causing weakness in the extensors of the hand and numbness in the first dorsal web space. The incidence of radial nerve palsy in midshaft fractures of the humerus is 16%.1
In nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures of the humeral midshaft, conservative management with a U-shaped (sugar-tong) splint from axilla to shoulder with elasticized wrap and sling is recommended. Surgical management is indicated in comminuted, significantly displaced, nonreducible, pathologic cases or in fractures resulting in neurovascular compromise. The patient in this case was referred to an orthopedic surgeon for open treatment.
- Smith WR, Agudelo JF, Parekh AA, Shank, JR. Musculoskeletal trauma surgery. In: Skinner HB, ed. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics. 4th ed. McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2006:121.
- Smith WR, Agudelo JF, Parekh AA, Shank, JR. Musculoskeletal trauma surgery. In: Skinner HB, ed. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics. 4th ed. McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2006:121.