User login
ROME – The use of coronary artery bypass graft surgery for revascularization in patients with multivessel CAD and comorbid diabetes plus chronic kidney disease was associated with a significantly lower risk of major cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events than was PCI with first-generation drug-eluting stents in a new secondary analysis from the landmark FREEDOM trial.
“The reason for this presentation is that even though chronic kidney disease is common in patients with diabetes, until now there has not been a large study of the efficacy and safety of coronary revascularization with drug-eluting stents versus CABG in this population in a randomized trial cohort,” explained Usman Baber, MD, who reported the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) randomized 1,900 diabetic patients with multivessel CAD to PCI or CABG. As previously reported, CABG proved superior to PCI, with a significantly lower rate of the composite primary endpoint composed of all-cause mortality, MI, or stroke (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
Dr. Baber presented a post hoc analysis of the 451 FREEDOM participants with baseline comorbid chronic kidney disease (CKD). Their mean SYNTAX score was 27, and their mean baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate was 44 mL/min per 1.73 m2, indicative of mild to moderate CKD.
“Only 28 patients in the FREEDOM trial had an estimated GFR below 30, therefore we can’t make any inferences about revascularization in that setting, which I think is a completely different population,” he noted.
The 5-year rate of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in patients with CKD was 26% in the CABG group, an absolute 9.4% less than the 35.6% rate in subjects randomized to PCI.
Roughly one-quarter of FREEDOM participants had CKD. They fared significantly worse than did those without CKD. The 5-year incidence of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events was 30.8% in patients with CKD and 20.1% in patients without renal impairment. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, gender, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and other potential confounders, the risk of all-cause mortality was twofold higher in the CKD group. Their risk of cardiac death was increased 1.8-fold, and they were at 1.9-fold increased risk for stroke. Interestingly, however, the acute MI risk did not differ between patients with or without CKD, Dr. Baber observed.
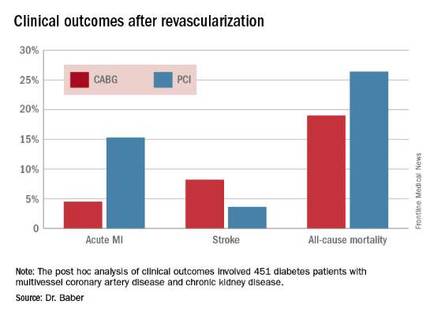
Drilling deeper into the data, the cardiologist reported that CABG was associated with significantly lower rates of MI and a nonsignificant trend for fewer deaths, but with a significantly higher stroke rate than PCI.
One audience member rose to complain that this information won’t be helpful in counseling his diabetic patients with CKD and multivessel CAD because the choices look so grim: a higher risk of MI with percutaneous therapy, and a greater risk of stroke with surgery.
Dr. Baber replied by pointing out that the 10.8% absolute reduction in the risk of MI with CABG compared with PCI was more than twice as large as the absolute 4.6% increase in stroke risk with surgery.
“Most people would say that a heart attack is an inconvenience, and a stroke is a life-changing experience for them and their family,” said session cochair Kim A. Williams, MD, professor of medicine and chairman of cardiology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
At that, Dr. Baber backtracked a bit, observing that since this was a post hoc analysis, the FREEDOM findings in patients with CKD must be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than definitive. And, of course, contemporary second-generation drug-eluting stents have a better risk/benefit profile than do those used in FREEDOM.
“The number needed to treat/number needed to harm ratio for CABG and PCI probably ends up being roughly equal. The pertinence of an analysis like this is if you look at real-world registry-based data, you find a therapeutic nihilism that’s highly prevalent in CKD patients, where many patients who might benefit are not provided with revascularization therapy. It’s clear that we as clinicians – either because we don’t know there is a benefit or we are too concerned about potential harm – deprive patients of a treatment that might be beneficial. This analysis makes clinicians who might be concerned feel somewhat comforted that there is not unacceptable harm and that there is benefit,” Dr. Baber said.
Follow-up of FREEDOM participants continues and will be the subject of future reports, he added.
The FREEDOM trial was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Baber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
ROME – The use of coronary artery bypass graft surgery for revascularization in patients with multivessel CAD and comorbid diabetes plus chronic kidney disease was associated with a significantly lower risk of major cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events than was PCI with first-generation drug-eluting stents in a new secondary analysis from the landmark FREEDOM trial.
“The reason for this presentation is that even though chronic kidney disease is common in patients with diabetes, until now there has not been a large study of the efficacy and safety of coronary revascularization with drug-eluting stents versus CABG in this population in a randomized trial cohort,” explained Usman Baber, MD, who reported the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) randomized 1,900 diabetic patients with multivessel CAD to PCI or CABG. As previously reported, CABG proved superior to PCI, with a significantly lower rate of the composite primary endpoint composed of all-cause mortality, MI, or stroke (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
Dr. Baber presented a post hoc analysis of the 451 FREEDOM participants with baseline comorbid chronic kidney disease (CKD). Their mean SYNTAX score was 27, and their mean baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate was 44 mL/min per 1.73 m2, indicative of mild to moderate CKD.
“Only 28 patients in the FREEDOM trial had an estimated GFR below 30, therefore we can’t make any inferences about revascularization in that setting, which I think is a completely different population,” he noted.
The 5-year rate of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in patients with CKD was 26% in the CABG group, an absolute 9.4% less than the 35.6% rate in subjects randomized to PCI.

Roughly one-quarter of FREEDOM participants had CKD. They fared significantly worse than did those without CKD. The 5-year incidence of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events was 30.8% in patients with CKD and 20.1% in patients without renal impairment. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, gender, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and other potential confounders, the risk of all-cause mortality was twofold higher in the CKD group. Their risk of cardiac death was increased 1.8-fold, and they were at 1.9-fold increased risk for stroke. Interestingly, however, the acute MI risk did not differ between patients with or without CKD, Dr. Baber observed.
Drilling deeper into the data, the cardiologist reported that CABG was associated with significantly lower rates of MI and a nonsignificant trend for fewer deaths, but with a significantly higher stroke rate than PCI.
One audience member rose to complain that this information won’t be helpful in counseling his diabetic patients with CKD and multivessel CAD because the choices look so grim: a higher risk of MI with percutaneous therapy, and a greater risk of stroke with surgery.
Dr. Baber replied by pointing out that the 10.8% absolute reduction in the risk of MI with CABG compared with PCI was more than twice as large as the absolute 4.6% increase in stroke risk with surgery.
“Most people would say that a heart attack is an inconvenience, and a stroke is a life-changing experience for them and their family,” said session cochair Kim A. Williams, MD, professor of medicine and chairman of cardiology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
At that, Dr. Baber backtracked a bit, observing that since this was a post hoc analysis, the FREEDOM findings in patients with CKD must be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than definitive. And, of course, contemporary second-generation drug-eluting stents have a better risk/benefit profile than do those used in FREEDOM.
“The number needed to treat/number needed to harm ratio for CABG and PCI probably ends up being roughly equal. The pertinence of an analysis like this is if you look at real-world registry-based data, you find a therapeutic nihilism that’s highly prevalent in CKD patients, where many patients who might benefit are not provided with revascularization therapy. It’s clear that we as clinicians – either because we don’t know there is a benefit or we are too concerned about potential harm – deprive patients of a treatment that might be beneficial. This analysis makes clinicians who might be concerned feel somewhat comforted that there is not unacceptable harm and that there is benefit,” Dr. Baber said.
Follow-up of FREEDOM participants continues and will be the subject of future reports, he added.
The FREEDOM trial was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Baber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
ROME – The use of coronary artery bypass graft surgery for revascularization in patients with multivessel CAD and comorbid diabetes plus chronic kidney disease was associated with a significantly lower risk of major cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events than was PCI with first-generation drug-eluting stents in a new secondary analysis from the landmark FREEDOM trial.
“The reason for this presentation is that even though chronic kidney disease is common in patients with diabetes, until now there has not been a large study of the efficacy and safety of coronary revascularization with drug-eluting stents versus CABG in this population in a randomized trial cohort,” explained Usman Baber, MD, who reported the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) randomized 1,900 diabetic patients with multivessel CAD to PCI or CABG. As previously reported, CABG proved superior to PCI, with a significantly lower rate of the composite primary endpoint composed of all-cause mortality, MI, or stroke (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
Dr. Baber presented a post hoc analysis of the 451 FREEDOM participants with baseline comorbid chronic kidney disease (CKD). Their mean SYNTAX score was 27, and their mean baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate was 44 mL/min per 1.73 m2, indicative of mild to moderate CKD.
“Only 28 patients in the FREEDOM trial had an estimated GFR below 30, therefore we can’t make any inferences about revascularization in that setting, which I think is a completely different population,” he noted.
The 5-year rate of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in patients with CKD was 26% in the CABG group, an absolute 9.4% less than the 35.6% rate in subjects randomized to PCI.

Roughly one-quarter of FREEDOM participants had CKD. They fared significantly worse than did those without CKD. The 5-year incidence of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events was 30.8% in patients with CKD and 20.1% in patients without renal impairment. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, gender, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and other potential confounders, the risk of all-cause mortality was twofold higher in the CKD group. Their risk of cardiac death was increased 1.8-fold, and they were at 1.9-fold increased risk for stroke. Interestingly, however, the acute MI risk did not differ between patients with or without CKD, Dr. Baber observed.
Drilling deeper into the data, the cardiologist reported that CABG was associated with significantly lower rates of MI and a nonsignificant trend for fewer deaths, but with a significantly higher stroke rate than PCI.
One audience member rose to complain that this information won’t be helpful in counseling his diabetic patients with CKD and multivessel CAD because the choices look so grim: a higher risk of MI with percutaneous therapy, and a greater risk of stroke with surgery.
Dr. Baber replied by pointing out that the 10.8% absolute reduction in the risk of MI with CABG compared with PCI was more than twice as large as the absolute 4.6% increase in stroke risk with surgery.
“Most people would say that a heart attack is an inconvenience, and a stroke is a life-changing experience for them and their family,” said session cochair Kim A. Williams, MD, professor of medicine and chairman of cardiology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
At that, Dr. Baber backtracked a bit, observing that since this was a post hoc analysis, the FREEDOM findings in patients with CKD must be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than definitive. And, of course, contemporary second-generation drug-eluting stents have a better risk/benefit profile than do those used in FREEDOM.
“The number needed to treat/number needed to harm ratio for CABG and PCI probably ends up being roughly equal. The pertinence of an analysis like this is if you look at real-world registry-based data, you find a therapeutic nihilism that’s highly prevalent in CKD patients, where many patients who might benefit are not provided with revascularization therapy. It’s clear that we as clinicians – either because we don’t know there is a benefit or we are too concerned about potential harm – deprive patients of a treatment that might be beneficial. This analysis makes clinicians who might be concerned feel somewhat comforted that there is not unacceptable harm and that there is benefit,” Dr. Baber said.
Follow-up of FREEDOM participants continues and will be the subject of future reports, he added.
The FREEDOM trial was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Baber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2016
Key clinical point: Coronary artery bypass graft surgery resulted in fewer myocardial infarctions but more strokes than did percutaneous coronary intervention at 5 years of follow-up in diabetic patients with multivessel coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease.
Major finding: The cumulative MI rates in patients randomized to CABG versus PCI were 4.5% and 15.3%, respectively, while the stroke rates were 8.2% versus 3.6%.
Data source: A post hoc analysis of clinical outcomes in 451 diabetic patients with multivessel CAD and chronic kidney disease who were randomized to CABG or PCI in the prospective multicenter FREEDOM trial.
Disclosures: The FREEDOM trial was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The presenter reported having no financial conflicts of interest.


