User login
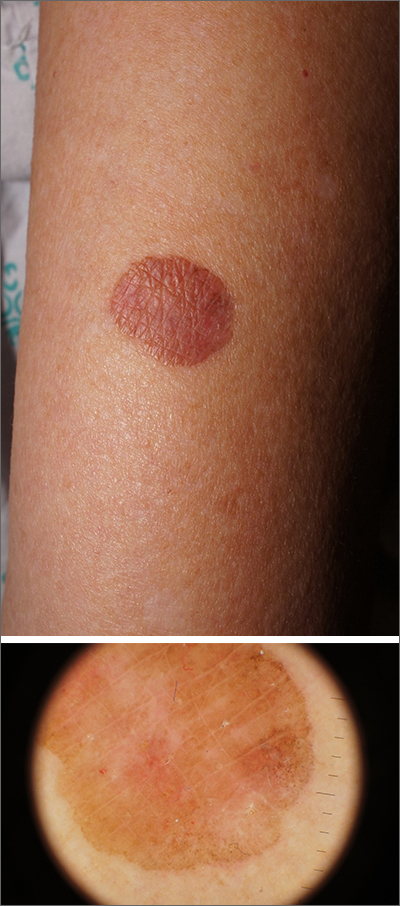
Due to its size, 2 shave biopsies targeting the most concerning portions of the lesion were performed; the results were consistent with a lichenoid keratosis (LK), also known as lichen planus-like keratosis.
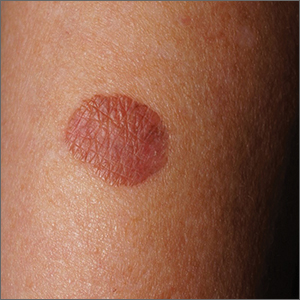
LK is a benign solitary lesion that mimics basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and superficial spreading or amelanotic melanoma.1 One theory suggests that LK is a solar lentigo or actinic keratosis undergoing attack from the immune system. Lesions most often manifest as a pink, gray, or brown macule to thin papule on the trunk or extremities. Itching or mild pain may be present. Dermoscopy can help distinguish an LK from malignancy but overlapping features of fine dark regression structures (called peppering, as seen in this case) should prompt further evaluation.
LKs are great mimics and biopsy is key to distinguishing them from cancer. In this case, shave biopsies were performed in the thickest and most characteristic portions of the lesion. Punch or incisional biopsies also would have been appropriate, but any result would have been a partial result. If the result had come back as an atypical melanocytic lesion, a complete excision would have been necessary to make sure the pathology reflected the entirety of the lesion.
Armed with the knowledge that the LK was benign, the patient in this case was scheduled for a follow-up visit for cryotherapy to remove the residual lesion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178
Due to its size, 2 shave biopsies targeting the most concerning portions of the lesion were performed; the results were consistent with a lichenoid keratosis (LK), also known as lichen planus-like keratosis.
LK is a benign solitary lesion that mimics basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and superficial spreading or amelanotic melanoma.1 One theory suggests that LK is a solar lentigo or actinic keratosis undergoing attack from the immune system. Lesions most often manifest as a pink, gray, or brown macule to thin papule on the trunk or extremities. Itching or mild pain may be present. Dermoscopy can help distinguish an LK from malignancy but overlapping features of fine dark regression structures (called peppering, as seen in this case) should prompt further evaluation.
LKs are great mimics and biopsy is key to distinguishing them from cancer. In this case, shave biopsies were performed in the thickest and most characteristic portions of the lesion. Punch or incisional biopsies also would have been appropriate, but any result would have been a partial result. If the result had come back as an atypical melanocytic lesion, a complete excision would have been necessary to make sure the pathology reflected the entirety of the lesion.
Armed with the knowledge that the LK was benign, the patient in this case was scheduled for a follow-up visit for cryotherapy to remove the residual lesion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
Due to its size, 2 shave biopsies targeting the most concerning portions of the lesion were performed; the results were consistent with a lichenoid keratosis (LK), also known as lichen planus-like keratosis.
LK is a benign solitary lesion that mimics basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and superficial spreading or amelanotic melanoma.1 One theory suggests that LK is a solar lentigo or actinic keratosis undergoing attack from the immune system. Lesions most often manifest as a pink, gray, or brown macule to thin papule on the trunk or extremities. Itching or mild pain may be present. Dermoscopy can help distinguish an LK from malignancy but overlapping features of fine dark regression structures (called peppering, as seen in this case) should prompt further evaluation.
LKs are great mimics and biopsy is key to distinguishing them from cancer. In this case, shave biopsies were performed in the thickest and most characteristic portions of the lesion. Punch or incisional biopsies also would have been appropriate, but any result would have been a partial result. If the result had come back as an atypical melanocytic lesion, a complete excision would have been necessary to make sure the pathology reflected the entirety of the lesion.
Armed with the knowledge that the LK was benign, the patient in this case was scheduled for a follow-up visit for cryotherapy to remove the residual lesion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178