User login
Tumor vs. saxophone: The surgical grudge match
Brain surgery is a notoriously difficult task. There’s a reason we say, “Well, at least it’s not brain surgery” when we’re trying to convince someone that a task isn’t that tough. Make one wrong incision, cut the wrong neuron, and it’s goodbye higher cognitive function. And most people appreciate thinking. Crazy, right?
One would imagine that the act of brain surgery would become even more difficult when the patient brings his saxophone and plays it randomly throughout the operation. It’s a hospital, after all, not a jazz club. Patients don’t get to play musical instruments during other surgeries. Why should brain surgery patients get special treatment?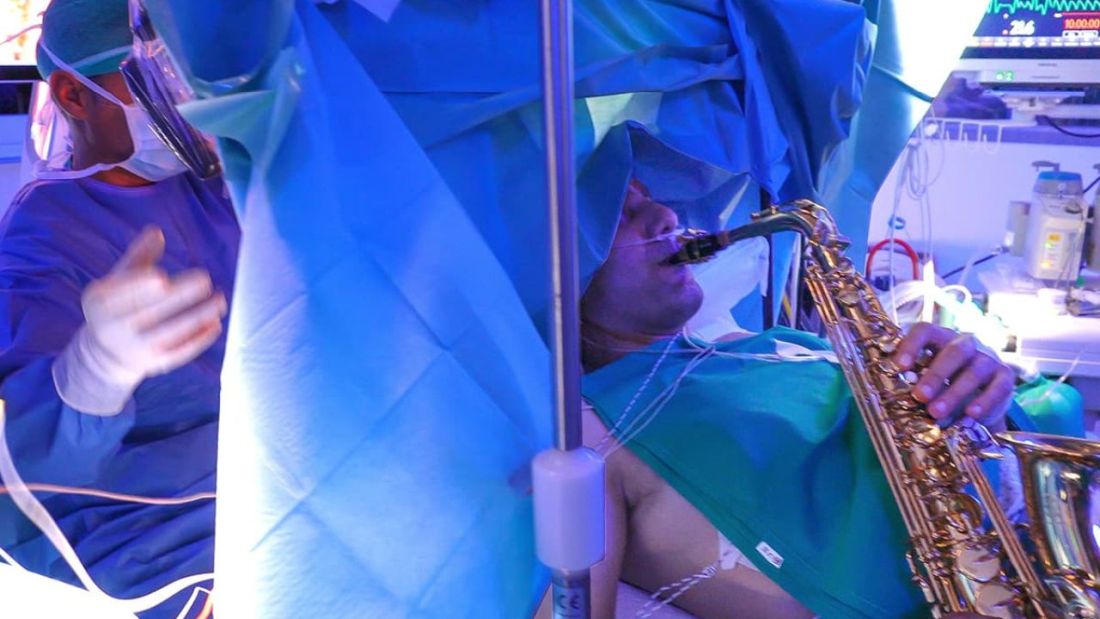
As it turns out, the musical performance was actually quite helpful. A man in Italy had a brain tumor in a particularly complex area, and he’s left-handed, which apparently makes the brain’s neural pathways much more complicated. Plus, he insisted that he retain his musical ability after the surgery. So he and his medical team had a crazy thought: Why not play the saxophone throughout the surgery? After all, according to head surgeon Christian Brogna, MD, playing an instrument means you understand music, which tests many higher cognitive functions such as coordination, mathematics, and memory.
And so, at various points throughout the 9-hour surgery, the patient played his saxophone for his doctors. Doing so allowed the surgeons to map the patient’s brain in a more complete and personalized fashion. With that extra knowledge, they were able to successfully remove the tumor while maintaining the patient’s musical ability, and the patient was discharged on Oct. 13, just 3 days after his operation.
While we’re happy the patient recovered, we do have to question his choice of music. During the surgery, he played the theme to the 1970 movie “Love Story” and the Italian national anthem. Perfectly fine pieces, no doubt, but the saxophone solo in “Jungleland” exists. And we could listen to that for 9 hours straight. In fact, we do that every Friday in the LOTME office.
Basketball has the Big Dance. Mosquitoes get the Big Sniff
In this week’s installment of our seemingly never-ending series, “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them,” we visit The Rockefeller University in New York, where the olfactory capabilities of Aedes Aegypti – the primary vector species for Zika, dengue, yellow fever, and chikungunya – became the subject of a round robin–style tournament.
First things first, though. If you’re going to test mosquito noses, you have to give them something to smell. The researchers enrolled eight humans who were willing to wear nylon stockings on their forearms for 6 hours a day for multiple days. “Over the next few years, the researchers tested the nylons against each other in all possible pairings,” Leslie B. Vosshall, PhD, and associates said in a statement from the university. In other words, mosquito March Madness.
Nylons from different participants were hooked up in pairs to an olfactometer assay consisting of a plexiglass chamber divided into two tubes, each ending in a box that held a stocking. The mosquitoes were placed in the main chamber and observed as they flew down the tubes toward one stocking or the other.
Eventually, the “winner” of the “tournament” was Subject 33. And no, we don’t know why there was a Subject 33 since the study involved only eight participants. We do know that the nylons worn by Subject 33 were “four times more attractive to the mosquitoes than the next most-attractive study participant, and an astonishing 100 times more appealing than the least attractive, Subject 19,” according to the written statement.
Chemical analysis identified 50 molecular compounds that were elevated in the sebum of the high-attracting participants, and eventually the investigators discovered that mosquito magnets produced carboxylic acids at much higher levels than the less-attractive volunteers.
We could go on about the research team genetically engineering mosquitoes without odor receptors, but we have to save something for later. Tune in again next week for another exciting episode of “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them.”
Are women better with words?
Men vs. Women is probably the oldest argument in the book, but there may now be movement. Researchers have been able not only to shift the advantage toward women, but also to use that knowledge to medical advantage.
When it comes to the matter of words and remembering them, women apparently have men beat. The margin is small, said lead author Marco Hirnstein, PhD, of the University of Bergen, Norway, but, after performing a meta-analysis of 168 published studies and PhD theses involving more than 350,000 participants, it’s pretty clear. The research supports women’s advantage over men in recall, verbal fluency (categorical and phonemic), and recognition.
So how is this information useful from a medical standpoint?
Dr. Hirnstein and colleagues suggested that this information can help in interpreting diagnostic assessment results. The example given was dementia diagnosis. Since women are underdiagnosed because their baseline exceeds average while men are overdiagnosed, taking gender and performance into account could clear up or catch cases that might otherwise slip through the cracks.
Now, let’s just put this part of the debate to rest and take this not only as a win for women but for science as well.
Tumor vs. saxophone: The surgical grudge match
Brain surgery is a notoriously difficult task. There’s a reason we say, “Well, at least it’s not brain surgery” when we’re trying to convince someone that a task isn’t that tough. Make one wrong incision, cut the wrong neuron, and it’s goodbye higher cognitive function. And most people appreciate thinking. Crazy, right?
One would imagine that the act of brain surgery would become even more difficult when the patient brings his saxophone and plays it randomly throughout the operation. It’s a hospital, after all, not a jazz club. Patients don’t get to play musical instruments during other surgeries. Why should brain surgery patients get special treatment?
As it turns out, the musical performance was actually quite helpful. A man in Italy had a brain tumor in a particularly complex area, and he’s left-handed, which apparently makes the brain’s neural pathways much more complicated. Plus, he insisted that he retain his musical ability after the surgery. So he and his medical team had a crazy thought: Why not play the saxophone throughout the surgery? After all, according to head surgeon Christian Brogna, MD, playing an instrument means you understand music, which tests many higher cognitive functions such as coordination, mathematics, and memory.
And so, at various points throughout the 9-hour surgery, the patient played his saxophone for his doctors. Doing so allowed the surgeons to map the patient’s brain in a more complete and personalized fashion. With that extra knowledge, they were able to successfully remove the tumor while maintaining the patient’s musical ability, and the patient was discharged on Oct. 13, just 3 days after his operation.
While we’re happy the patient recovered, we do have to question his choice of music. During the surgery, he played the theme to the 1970 movie “Love Story” and the Italian national anthem. Perfectly fine pieces, no doubt, but the saxophone solo in “Jungleland” exists. And we could listen to that for 9 hours straight. In fact, we do that every Friday in the LOTME office.
Basketball has the Big Dance. Mosquitoes get the Big Sniff
In this week’s installment of our seemingly never-ending series, “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them,” we visit The Rockefeller University in New York, where the olfactory capabilities of Aedes Aegypti – the primary vector species for Zika, dengue, yellow fever, and chikungunya – became the subject of a round robin–style tournament.
First things first, though. If you’re going to test mosquito noses, you have to give them something to smell. The researchers enrolled eight humans who were willing to wear nylon stockings on their forearms for 6 hours a day for multiple days. “Over the next few years, the researchers tested the nylons against each other in all possible pairings,” Leslie B. Vosshall, PhD, and associates said in a statement from the university. In other words, mosquito March Madness.
Nylons from different participants were hooked up in pairs to an olfactometer assay consisting of a plexiglass chamber divided into two tubes, each ending in a box that held a stocking. The mosquitoes were placed in the main chamber and observed as they flew down the tubes toward one stocking or the other.
Eventually, the “winner” of the “tournament” was Subject 33. And no, we don’t know why there was a Subject 33 since the study involved only eight participants. We do know that the nylons worn by Subject 33 were “four times more attractive to the mosquitoes than the next most-attractive study participant, and an astonishing 100 times more appealing than the least attractive, Subject 19,” according to the written statement.
Chemical analysis identified 50 molecular compounds that were elevated in the sebum of the high-attracting participants, and eventually the investigators discovered that mosquito magnets produced carboxylic acids at much higher levels than the less-attractive volunteers.
We could go on about the research team genetically engineering mosquitoes without odor receptors, but we have to save something for later. Tune in again next week for another exciting episode of “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them.”
Are women better with words?
Men vs. Women is probably the oldest argument in the book, but there may now be movement. Researchers have been able not only to shift the advantage toward women, but also to use that knowledge to medical advantage.
When it comes to the matter of words and remembering them, women apparently have men beat. The margin is small, said lead author Marco Hirnstein, PhD, of the University of Bergen, Norway, but, after performing a meta-analysis of 168 published studies and PhD theses involving more than 350,000 participants, it’s pretty clear. The research supports women’s advantage over men in recall, verbal fluency (categorical and phonemic), and recognition.
So how is this information useful from a medical standpoint?
Dr. Hirnstein and colleagues suggested that this information can help in interpreting diagnostic assessment results. The example given was dementia diagnosis. Since women are underdiagnosed because their baseline exceeds average while men are overdiagnosed, taking gender and performance into account could clear up or catch cases that might otherwise slip through the cracks.
Now, let’s just put this part of the debate to rest and take this not only as a win for women but for science as well.
Tumor vs. saxophone: The surgical grudge match
Brain surgery is a notoriously difficult task. There’s a reason we say, “Well, at least it’s not brain surgery” when we’re trying to convince someone that a task isn’t that tough. Make one wrong incision, cut the wrong neuron, and it’s goodbye higher cognitive function. And most people appreciate thinking. Crazy, right?
One would imagine that the act of brain surgery would become even more difficult when the patient brings his saxophone and plays it randomly throughout the operation. It’s a hospital, after all, not a jazz club. Patients don’t get to play musical instruments during other surgeries. Why should brain surgery patients get special treatment?
As it turns out, the musical performance was actually quite helpful. A man in Italy had a brain tumor in a particularly complex area, and he’s left-handed, which apparently makes the brain’s neural pathways much more complicated. Plus, he insisted that he retain his musical ability after the surgery. So he and his medical team had a crazy thought: Why not play the saxophone throughout the surgery? After all, according to head surgeon Christian Brogna, MD, playing an instrument means you understand music, which tests many higher cognitive functions such as coordination, mathematics, and memory.
And so, at various points throughout the 9-hour surgery, the patient played his saxophone for his doctors. Doing so allowed the surgeons to map the patient’s brain in a more complete and personalized fashion. With that extra knowledge, they were able to successfully remove the tumor while maintaining the patient’s musical ability, and the patient was discharged on Oct. 13, just 3 days after his operation.
While we’re happy the patient recovered, we do have to question his choice of music. During the surgery, he played the theme to the 1970 movie “Love Story” and the Italian national anthem. Perfectly fine pieces, no doubt, but the saxophone solo in “Jungleland” exists. And we could listen to that for 9 hours straight. In fact, we do that every Friday in the LOTME office.
Basketball has the Big Dance. Mosquitoes get the Big Sniff
In this week’s installment of our seemingly never-ending series, “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them,” we visit The Rockefeller University in New York, where the olfactory capabilities of Aedes Aegypti – the primary vector species for Zika, dengue, yellow fever, and chikungunya – became the subject of a round robin–style tournament.
First things first, though. If you’re going to test mosquito noses, you have to give them something to smell. The researchers enrolled eight humans who were willing to wear nylon stockings on their forearms for 6 hours a day for multiple days. “Over the next few years, the researchers tested the nylons against each other in all possible pairings,” Leslie B. Vosshall, PhD, and associates said in a statement from the university. In other words, mosquito March Madness.
Nylons from different participants were hooked up in pairs to an olfactometer assay consisting of a plexiglass chamber divided into two tubes, each ending in a box that held a stocking. The mosquitoes were placed in the main chamber and observed as they flew down the tubes toward one stocking or the other.
Eventually, the “winner” of the “tournament” was Subject 33. And no, we don’t know why there was a Subject 33 since the study involved only eight participants. We do know that the nylons worn by Subject 33 were “four times more attractive to the mosquitoes than the next most-attractive study participant, and an astonishing 100 times more appealing than the least attractive, Subject 19,” according to the written statement.
Chemical analysis identified 50 molecular compounds that were elevated in the sebum of the high-attracting participants, and eventually the investigators discovered that mosquito magnets produced carboxylic acids at much higher levels than the less-attractive volunteers.
We could go on about the research team genetically engineering mosquitoes without odor receptors, but we have to save something for later. Tune in again next week for another exciting episode of “Mosquitoes and the scientists who love them.”
Are women better with words?
Men vs. Women is probably the oldest argument in the book, but there may now be movement. Researchers have been able not only to shift the advantage toward women, but also to use that knowledge to medical advantage.
When it comes to the matter of words and remembering them, women apparently have men beat. The margin is small, said lead author Marco Hirnstein, PhD, of the University of Bergen, Norway, but, after performing a meta-analysis of 168 published studies and PhD theses involving more than 350,000 participants, it’s pretty clear. The research supports women’s advantage over men in recall, verbal fluency (categorical and phonemic), and recognition.
So how is this information useful from a medical standpoint?
Dr. Hirnstein and colleagues suggested that this information can help in interpreting diagnostic assessment results. The example given was dementia diagnosis. Since women are underdiagnosed because their baseline exceeds average while men are overdiagnosed, taking gender and performance into account could clear up or catch cases that might otherwise slip through the cracks.
Now, let’s just put this part of the debate to rest and take this not only as a win for women but for science as well.

