User login
To the Editor:
Raynaud phenomenon (RP) is an episodic vasospasm of the digits that can lead to ulceration, gangrene, and autoamputation with prolonged ischemia. OnabotulinumtoxinA has been implemented as a treatment of intractable RP by paralyzing the muscles of the digital arteries. We report a case of a woman with severe RP secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who was treated with onabotulinumtoxinA injections after multiple treatment modalities failed to improve her condition. We describe the dosage and injection technique used to produce clinical improvement in our patient and compare it to prior reports in the literature.
A 33-year-old woman presented to the emergency department for worsening foot pain of 5 days' duration with dusky purple color changes concerning for impending Raynaud crisis related to RP. The patient had a history of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) and SLE with overlapping symptoms of polymyositis and scleroderma. She had been hospitalized for RP multiple times prior to the current admission. She was medically managed with nifedipine, sildenafil, losartan potassium, aspirin, alprostadil, and prostaglandin infusions, and was surgically managed with a right-hand sympathectomy and right ulnar artery bypass graft that had subsequently thrombosed. At the current presentation, she had painful dusky toes on both feet though more pronounced on the left foot. She endorsed foot pain while walking and tenderness to palpation of the fingers, which were minimally improved with intravenous prostaglandins.
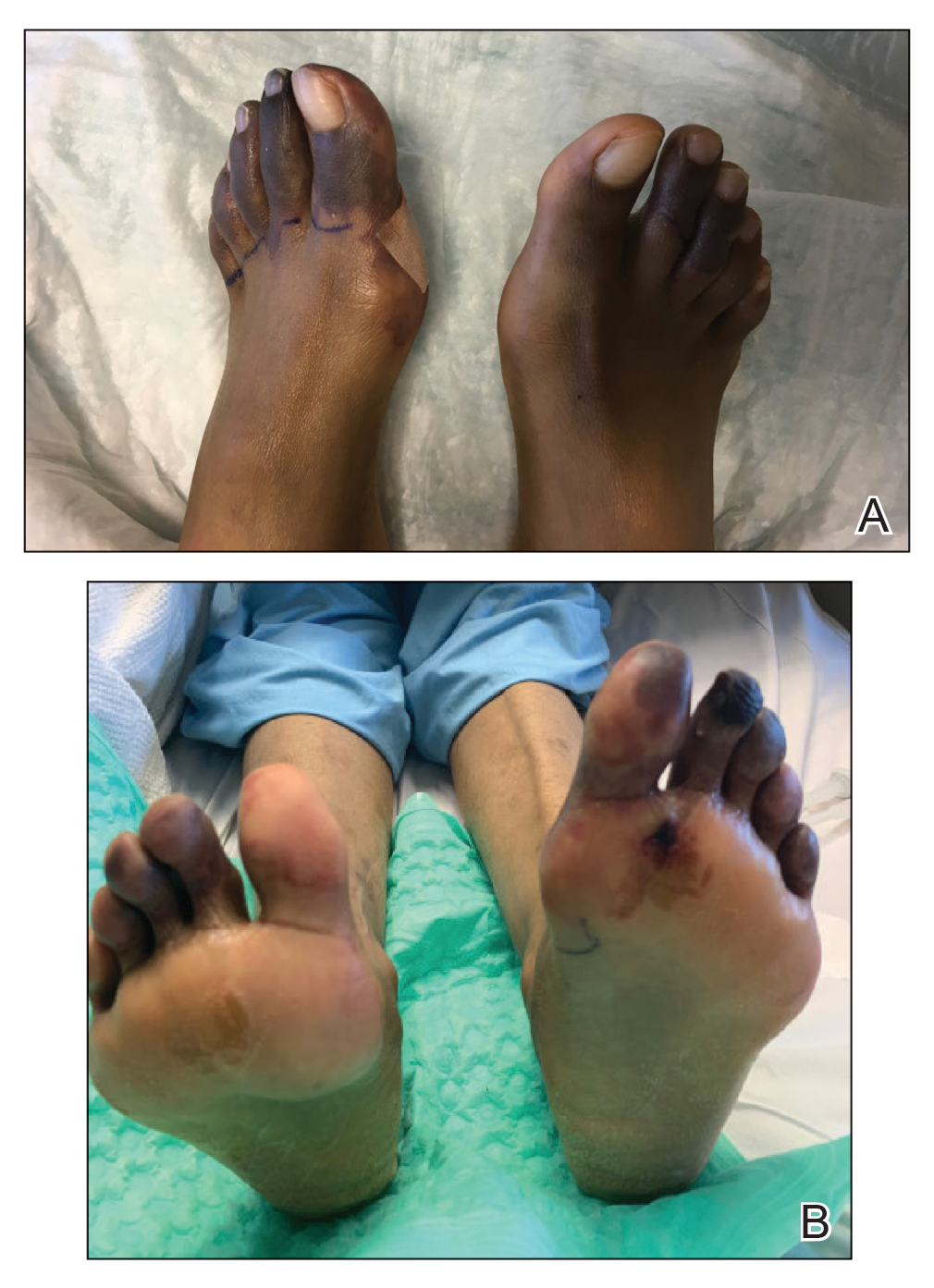
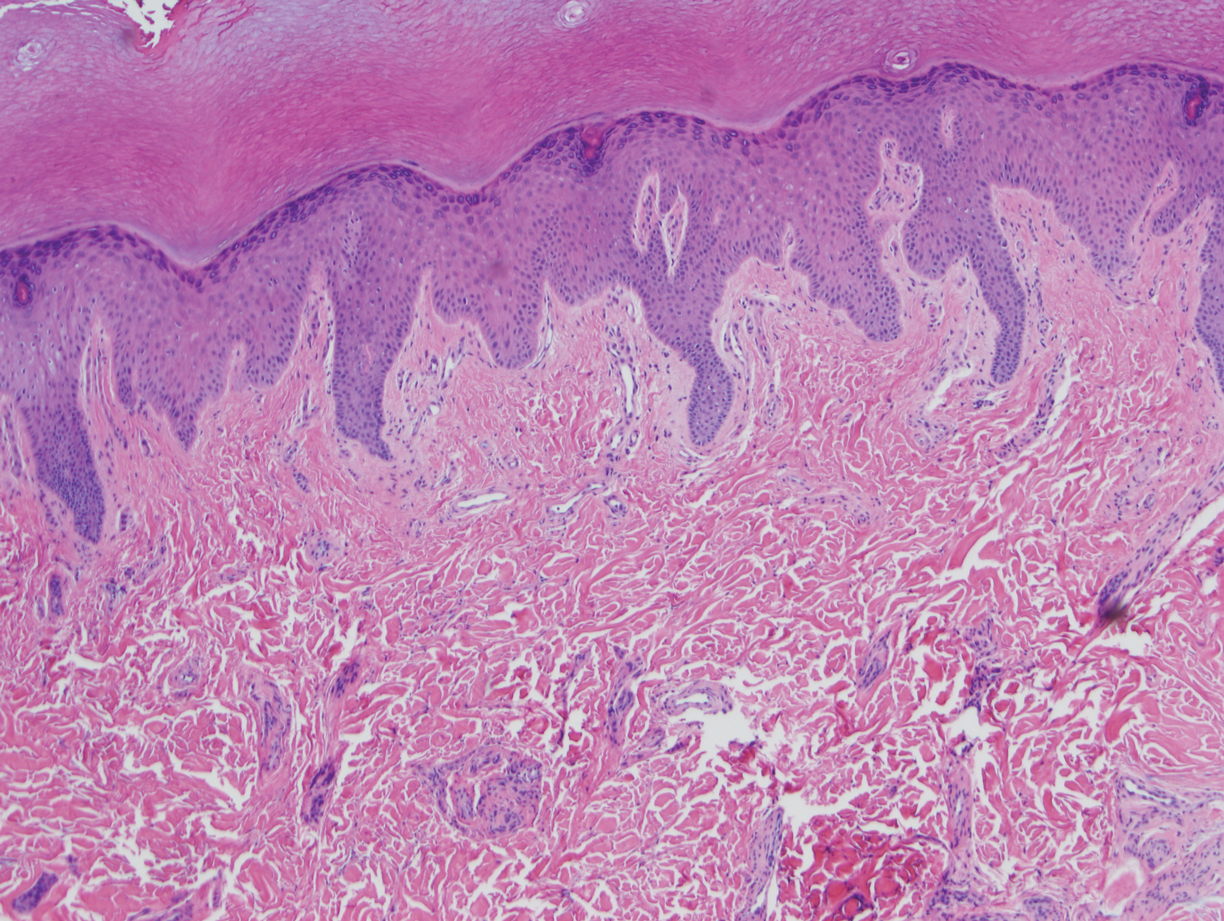
Physical examination revealed blanching of the digits in both hands with pits in the right fourth and left first digits. Dusky patches overlaid all the toes as well as the superior plantar aspects of the feet (Figure 1). Given the history of APS, a punch biopsy was performed on the left medial plantar foot and results showed no histologic evidence of vasculitis or vasculopathy. Necrotic foci were present on the left and right second metatarsal bones, which were not reperfusable (Figure 2). The clinical findings and punch biopsy results favored RP as opposed to vasculopathy from APS.
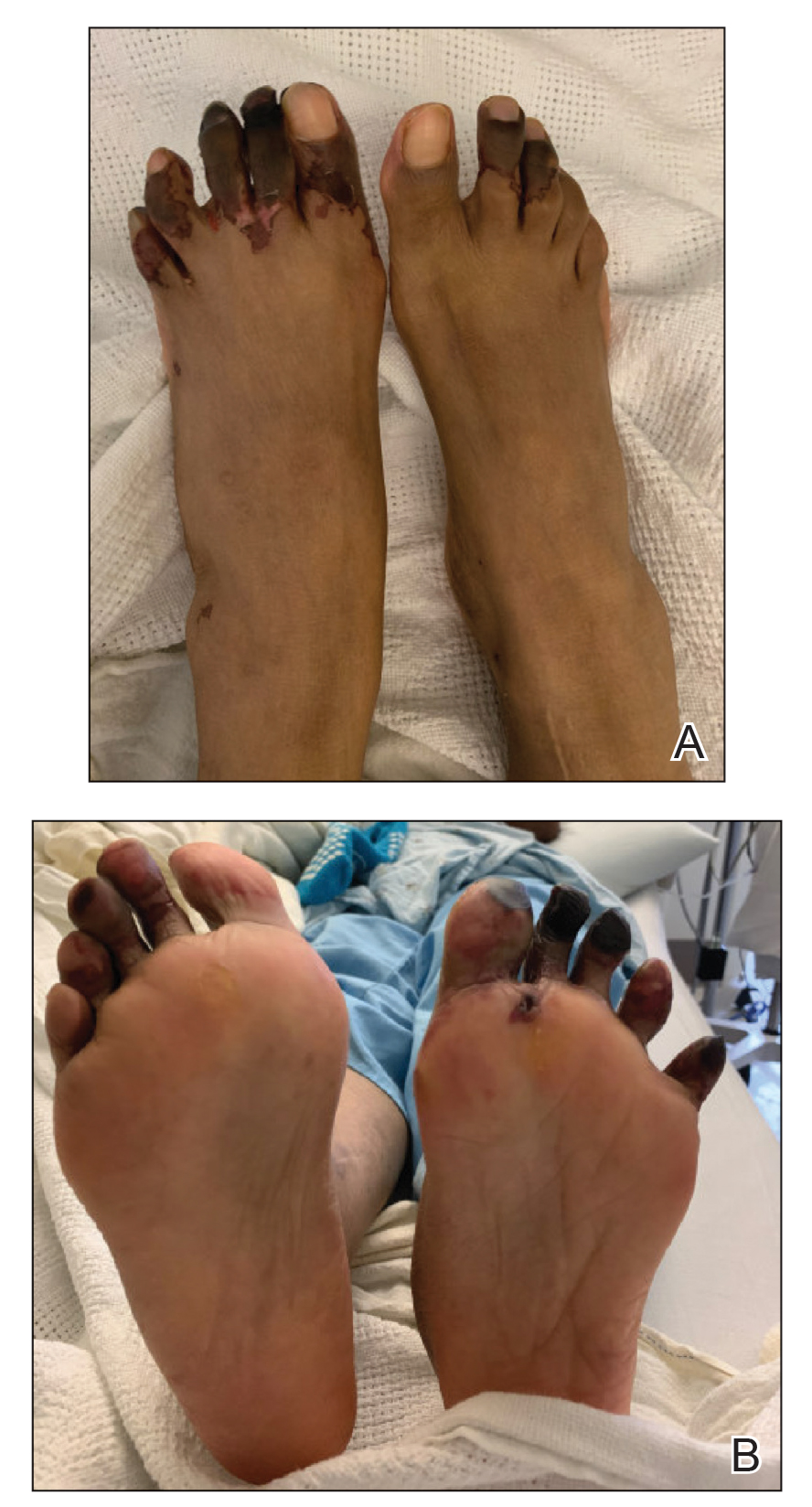
Several interventions were attempted, and after 4 days with no response, the patient agreed to receive treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. OnabotulinumtoxinA (5 U) was injected into the subcutaneous tissue of the medial and lateral aspects of each of the first and second toes near the proximal phalanges (40 U total). However, treatment could not be completed due to severe pain caused by the injections despite preprocedure regional nerve blocks to both lower extremities, preinjection icing, and lorazepam. Two days later, the patient tolerated onabotulinumtoxinA injections of all remaining digits of both feet (60 U total). She noted slight clinical improvement soon thereafter. One week after treatment of all 10 toes, she reported decreased pain and reduced duskiness of both feet (Figure 3).
One month later, the patient endorsed recurring pain in the hands and feet. Physical examination revealed reticular cyanosis and increased violaceous patches of the hands; the feet were overall unchanged from the prior hospitalization. At 4-month follow-up, there was gangrene on the left second, third, and fifth toe in addition to areas of induration noted on the fingers. She was repeatedly hospitalized over the next 6 months for pain management and gangrene of the toes, and finally underwent an amputation of the left and right second toe at the proximal and middle phalanx, respectively. She currently is continuing extensive medical management for pain and gangrene of the digits; she has not received additional onabotulinumtoxinA injections.
Raynaud phenomenon is a vascular disorder characterized by intermittent arteriolar vasospasm of the digits, often due to cold temperature or stress. Approximately 90% of RP cases are primarily idiopathic, with the remaining cases secondary to other diseases, typically systemic sclerosis, SLE, or mixed connective tissue disease.1 Symptoms present with characteristic changing of hands from white (ischemia) to blue (hypoxia) to red (reperfusion). Episodic attacks of vasospasm and ischemia can be painful and lead to digital ulcerations and necrosis of the digits or hands. Other complications including digital tuft pits, pterygium inversum unguis, or torturous nail fold capillaries with capillary dropout also may be seen.2
Although the etiology is multifactorial, the pathophysiology primarily is due to an imbalance of vasodilation and vasoconstriction. Perturbed levels of vasodilatory mediators include nitric oxide, prostacyclin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide.3 Meanwhile, abnormal neural sympathetic control of α-adrenergic receptors located on smooth muscle vasculature and subsequent endothelial hyperproliferation may contribute to inappropriate vasoconstriction.4
The first-line therapy for mild to moderate disease refractory to conservative management includes monotherapy with dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. For severe disease, combination therapy involves addition of other classes of medications including phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, topical nitrates, angiotensin receptor blockers, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Intravenous prostacyclin, endothelin receptor blockers, and onabotulinumtoxinA injections may be added as third-line therapy. Finally, surgical management including sympathectomy with continued pharmacologic therapy may be needed for disease recalcitrant to the aforementioned options.2
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The toxin’s mechanism of action involves inhibition of the release of presynaptic acetylcholine-containing vesicles at the neuromuscular junction through cleavage of sensory nerve action potential receptor proteins. In addition, it inhibits smooth muscle vasoconstriction and pain by blocking α2-adrenergic receptors on blood vessels and chronic pain-transmitting C fibers in nerves, respectively.3,5
Only recently has onabotulinumtoxinA been used for treatment of RP. Botulinum toxin is approved for the treatment of spastic and dystonic diseases such as blepharospasm, headaches in patients with chronic migraines, upper limb spasticity, cervical dystonia, torticollis, ocular strabismus, and hyperhidrosis.3 However, the versatility of its therapeutic effects is evident in its broad off-label clinical applications, including achalasia; carpal tunnel syndrome; and spasticity relating to stroke, paraplegia, and cerebral palsy, among many others.5
Few studies have analyzed the use of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of RP.3,6 There is no consensus yet regarding dose, dilution, or injection sites. One vial of onabotulinumtoxinA contains 100 U and is reconstituted in 20 mL of normal saline to produce 5 U/mL. The simplest technique involves the injection of 5 U into the medial and lateral aspects of each finger at its base, at the level of or just proximal to the A1 pulley, for a total of 50 U per hand.7 In the foot, injection can be made at the base of each toe near the proximal phalanges. A regimen of 50 to 100 U per hand was used by Neumeister et al5 on 19 patients, who subsequently standardized it to 10 U on each neurovascular bundle in a follow-up study,7 giving a total volume of 2 mL per injection. Associated pain or a burning sensation initially may be experienced, which may be mitigated by a lidocaine hydrochloride wrist block prior to injection.7 This technique produced immediate and lasting pain relief, increased tissue perfusion, and resolved digital ulcers in 28 of 33 patients. Most patients reported immediate relief, and a few noted gradual reduction in pain and resolution of chronic ulcers within 2 months. Of the 33 patients, 7 (21.2%) required repeat injections for recurrent pain, but the majority were pain free up to 6 years later with a single injection schedule.7
Injection into the palmar region, wrists, and/or fingers also may be performed. Effects of using different injection sites (eg, neurovascular bundle, distal palm, proximal hand) have been explored and were not notably different between these locations.8 Lastly, the frequency of injections may be attenuated according to the spectrum and severity of the patient’s symptoms. In a report of 11 patients who received a total of 100 U of onabotulinumtoxinA per hand, 5 required repeat injections within 3 to 8 months.9
Studies have reported onabotulinumtoxinA to be a promising option for the treatment of intractable symptoms. Likewise, our patient had a notable reduction in pain with signs of clinical improvement within 24 to 48 hours after injection. The need for amputation 6 months later likely was because the patient’s toes were already necrosing prior to treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. Thus, the timing of intervention may play a critical role in response to onabotulinumtoxinA injections, particularly because the severity of our patient’s presentation was comparable to other cases reported in the literature. Even in reports using a smaller dose—2 U injected into each toe as opposed to 10 U per toe, as in our case—follow-up showed favorable results.10 In other reports, response can be perceived within days to a week, with remarkable improvement of numbness, pain, digit color, and wound resolution, in addition to decreased frequency and severity of attacks. Moreover, greater vasodilation and subsequent tissue perfusion have been evidenced by objective measures including digital transcutaneous oxygen saturation and Doppler sonography.7,8 Side effects, which are minimal and temporary, include local pain triggering a vasospastic attack and intrinsic muscle weakness; more rarely, dysesthesia and thenar eminence atrophy have been reported.11
Available studies have shown onabotulinumtoxinA to produce favorable results in the treatment of vasospastic disease. We suspect that an earlier intervention for our patient—before necrosis of the toes developed—would have led to a more positive outcome, consistent with other reports. Treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA is an approach to consider when the standard-of-care treatments for RP have been exhausted, as timely intervention may prevent the need for surgery. The indications and appropriate dosing protocol remain to be defined, in addition to more thorough evaluation of its efficacy relative to other medical and surgical options.
- Neumeister MW. The role of botulinum toxin in vasospastic disorders of the hand. Hand Clin. 2015;31:23-37. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2014.09.003
- Bakst R, Merola JF, Franks AG, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon: pathogenesis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:633-653. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.004
- Iorio ML, Masden DL, Higgins JP. Botulinum toxin a treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.006
- Wigley FM, Flavahan NA. Raynaud’s phenomenon. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:556-565. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1507638
- Neumeister MW, Chambers CB, Herron MS, et al. Botox therapy for ischemic digits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:191-200. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a80576
- Sycha T, Graninger M, Auff E, et al. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a pilot study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:312-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.029
- Neumeister MW. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35:2085-2092. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.09.019
- Fregene A, Ditmars D, Siddiqui A. Botulinum toxin type A: a treatment option for digital ischemia in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34:446-452. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.11.026
- Van Beek AL, Lim PK, Gear AJL, et al. Management of vasospastic disorders with botulinum toxin A. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:217-226. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000244860.00674.57
- Dhaliwal K, Griffin M, Denton CP, et al. The novel use of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon in the toes. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018:2017-2019. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-219348
- Eickhoff JC, Smith JK, Landau ME, et al. Iatrogenic thenar eminence atrophy after Botox A injection for secondary Raynaud phenomenon. J Clin Rheumatol. 2016;22:395-396. doi:10.1097/RHU.0000000000000450
To the Editor:
Raynaud phenomenon (RP) is an episodic vasospasm of the digits that can lead to ulceration, gangrene, and autoamputation with prolonged ischemia. OnabotulinumtoxinA has been implemented as a treatment of intractable RP by paralyzing the muscles of the digital arteries. We report a case of a woman with severe RP secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who was treated with onabotulinumtoxinA injections after multiple treatment modalities failed to improve her condition. We describe the dosage and injection technique used to produce clinical improvement in our patient and compare it to prior reports in the literature.
A 33-year-old woman presented to the emergency department for worsening foot pain of 5 days' duration with dusky purple color changes concerning for impending Raynaud crisis related to RP. The patient had a history of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) and SLE with overlapping symptoms of polymyositis and scleroderma. She had been hospitalized for RP multiple times prior to the current admission. She was medically managed with nifedipine, sildenafil, losartan potassium, aspirin, alprostadil, and prostaglandin infusions, and was surgically managed with a right-hand sympathectomy and right ulnar artery bypass graft that had subsequently thrombosed. At the current presentation, she had painful dusky toes on both feet though more pronounced on the left foot. She endorsed foot pain while walking and tenderness to palpation of the fingers, which were minimally improved with intravenous prostaglandins.
Physical examination revealed blanching of the digits in both hands with pits in the right fourth and left first digits. Dusky patches overlaid all the toes as well as the superior plantar aspects of the feet (Figure 1). Given the history of APS, a punch biopsy was performed on the left medial plantar foot and results showed no histologic evidence of vasculitis or vasculopathy. Necrotic foci were present on the left and right second metatarsal bones, which were not reperfusable (Figure 2). The clinical findings and punch biopsy results favored RP as opposed to vasculopathy from APS.
Several interventions were attempted, and after 4 days with no response, the patient agreed to receive treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. OnabotulinumtoxinA (5 U) was injected into the subcutaneous tissue of the medial and lateral aspects of each of the first and second toes near the proximal phalanges (40 U total). However, treatment could not be completed due to severe pain caused by the injections despite preprocedure regional nerve blocks to both lower extremities, preinjection icing, and lorazepam. Two days later, the patient tolerated onabotulinumtoxinA injections of all remaining digits of both feet (60 U total). She noted slight clinical improvement soon thereafter. One week after treatment of all 10 toes, she reported decreased pain and reduced duskiness of both feet (Figure 3).
One month later, the patient endorsed recurring pain in the hands and feet. Physical examination revealed reticular cyanosis and increased violaceous patches of the hands; the feet were overall unchanged from the prior hospitalization. At 4-month follow-up, there was gangrene on the left second, third, and fifth toe in addition to areas of induration noted on the fingers. She was repeatedly hospitalized over the next 6 months for pain management and gangrene of the toes, and finally underwent an amputation of the left and right second toe at the proximal and middle phalanx, respectively. She currently is continuing extensive medical management for pain and gangrene of the digits; she has not received additional onabotulinumtoxinA injections.
Raynaud phenomenon is a vascular disorder characterized by intermittent arteriolar vasospasm of the digits, often due to cold temperature or stress. Approximately 90% of RP cases are primarily idiopathic, with the remaining cases secondary to other diseases, typically systemic sclerosis, SLE, or mixed connective tissue disease.1 Symptoms present with characteristic changing of hands from white (ischemia) to blue (hypoxia) to red (reperfusion). Episodic attacks of vasospasm and ischemia can be painful and lead to digital ulcerations and necrosis of the digits or hands. Other complications including digital tuft pits, pterygium inversum unguis, or torturous nail fold capillaries with capillary dropout also may be seen.2
Although the etiology is multifactorial, the pathophysiology primarily is due to an imbalance of vasodilation and vasoconstriction. Perturbed levels of vasodilatory mediators include nitric oxide, prostacyclin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide.3 Meanwhile, abnormal neural sympathetic control of α-adrenergic receptors located on smooth muscle vasculature and subsequent endothelial hyperproliferation may contribute to inappropriate vasoconstriction.4
The first-line therapy for mild to moderate disease refractory to conservative management includes monotherapy with dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. For severe disease, combination therapy involves addition of other classes of medications including phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, topical nitrates, angiotensin receptor blockers, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Intravenous prostacyclin, endothelin receptor blockers, and onabotulinumtoxinA injections may be added as third-line therapy. Finally, surgical management including sympathectomy with continued pharmacologic therapy may be needed for disease recalcitrant to the aforementioned options.2
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The toxin’s mechanism of action involves inhibition of the release of presynaptic acetylcholine-containing vesicles at the neuromuscular junction through cleavage of sensory nerve action potential receptor proteins. In addition, it inhibits smooth muscle vasoconstriction and pain by blocking α2-adrenergic receptors on blood vessels and chronic pain-transmitting C fibers in nerves, respectively.3,5
Only recently has onabotulinumtoxinA been used for treatment of RP. Botulinum toxin is approved for the treatment of spastic and dystonic diseases such as blepharospasm, headaches in patients with chronic migraines, upper limb spasticity, cervical dystonia, torticollis, ocular strabismus, and hyperhidrosis.3 However, the versatility of its therapeutic effects is evident in its broad off-label clinical applications, including achalasia; carpal tunnel syndrome; and spasticity relating to stroke, paraplegia, and cerebral palsy, among many others.5
Few studies have analyzed the use of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of RP.3,6 There is no consensus yet regarding dose, dilution, or injection sites. One vial of onabotulinumtoxinA contains 100 U and is reconstituted in 20 mL of normal saline to produce 5 U/mL. The simplest technique involves the injection of 5 U into the medial and lateral aspects of each finger at its base, at the level of or just proximal to the A1 pulley, for a total of 50 U per hand.7 In the foot, injection can be made at the base of each toe near the proximal phalanges. A regimen of 50 to 100 U per hand was used by Neumeister et al5 on 19 patients, who subsequently standardized it to 10 U on each neurovascular bundle in a follow-up study,7 giving a total volume of 2 mL per injection. Associated pain or a burning sensation initially may be experienced, which may be mitigated by a lidocaine hydrochloride wrist block prior to injection.7 This technique produced immediate and lasting pain relief, increased tissue perfusion, and resolved digital ulcers in 28 of 33 patients. Most patients reported immediate relief, and a few noted gradual reduction in pain and resolution of chronic ulcers within 2 months. Of the 33 patients, 7 (21.2%) required repeat injections for recurrent pain, but the majority were pain free up to 6 years later with a single injection schedule.7
Injection into the palmar region, wrists, and/or fingers also may be performed. Effects of using different injection sites (eg, neurovascular bundle, distal palm, proximal hand) have been explored and were not notably different between these locations.8 Lastly, the frequency of injections may be attenuated according to the spectrum and severity of the patient’s symptoms. In a report of 11 patients who received a total of 100 U of onabotulinumtoxinA per hand, 5 required repeat injections within 3 to 8 months.9
Studies have reported onabotulinumtoxinA to be a promising option for the treatment of intractable symptoms. Likewise, our patient had a notable reduction in pain with signs of clinical improvement within 24 to 48 hours after injection. The need for amputation 6 months later likely was because the patient’s toes were already necrosing prior to treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. Thus, the timing of intervention may play a critical role in response to onabotulinumtoxinA injections, particularly because the severity of our patient’s presentation was comparable to other cases reported in the literature. Even in reports using a smaller dose—2 U injected into each toe as opposed to 10 U per toe, as in our case—follow-up showed favorable results.10 In other reports, response can be perceived within days to a week, with remarkable improvement of numbness, pain, digit color, and wound resolution, in addition to decreased frequency and severity of attacks. Moreover, greater vasodilation and subsequent tissue perfusion have been evidenced by objective measures including digital transcutaneous oxygen saturation and Doppler sonography.7,8 Side effects, which are minimal and temporary, include local pain triggering a vasospastic attack and intrinsic muscle weakness; more rarely, dysesthesia and thenar eminence atrophy have been reported.11
Available studies have shown onabotulinumtoxinA to produce favorable results in the treatment of vasospastic disease. We suspect that an earlier intervention for our patient—before necrosis of the toes developed—would have led to a more positive outcome, consistent with other reports. Treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA is an approach to consider when the standard-of-care treatments for RP have been exhausted, as timely intervention may prevent the need for surgery. The indications and appropriate dosing protocol remain to be defined, in addition to more thorough evaluation of its efficacy relative to other medical and surgical options.
To the Editor:
Raynaud phenomenon (RP) is an episodic vasospasm of the digits that can lead to ulceration, gangrene, and autoamputation with prolonged ischemia. OnabotulinumtoxinA has been implemented as a treatment of intractable RP by paralyzing the muscles of the digital arteries. We report a case of a woman with severe RP secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who was treated with onabotulinumtoxinA injections after multiple treatment modalities failed to improve her condition. We describe the dosage and injection technique used to produce clinical improvement in our patient and compare it to prior reports in the literature.
A 33-year-old woman presented to the emergency department for worsening foot pain of 5 days' duration with dusky purple color changes concerning for impending Raynaud crisis related to RP. The patient had a history of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) and SLE with overlapping symptoms of polymyositis and scleroderma. She had been hospitalized for RP multiple times prior to the current admission. She was medically managed with nifedipine, sildenafil, losartan potassium, aspirin, alprostadil, and prostaglandin infusions, and was surgically managed with a right-hand sympathectomy and right ulnar artery bypass graft that had subsequently thrombosed. At the current presentation, she had painful dusky toes on both feet though more pronounced on the left foot. She endorsed foot pain while walking and tenderness to palpation of the fingers, which were minimally improved with intravenous prostaglandins.
Physical examination revealed blanching of the digits in both hands with pits in the right fourth and left first digits. Dusky patches overlaid all the toes as well as the superior plantar aspects of the feet (Figure 1). Given the history of APS, a punch biopsy was performed on the left medial plantar foot and results showed no histologic evidence of vasculitis or vasculopathy. Necrotic foci were present on the left and right second metatarsal bones, which were not reperfusable (Figure 2). The clinical findings and punch biopsy results favored RP as opposed to vasculopathy from APS.
Several interventions were attempted, and after 4 days with no response, the patient agreed to receive treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. OnabotulinumtoxinA (5 U) was injected into the subcutaneous tissue of the medial and lateral aspects of each of the first and second toes near the proximal phalanges (40 U total). However, treatment could not be completed due to severe pain caused by the injections despite preprocedure regional nerve blocks to both lower extremities, preinjection icing, and lorazepam. Two days later, the patient tolerated onabotulinumtoxinA injections of all remaining digits of both feet (60 U total). She noted slight clinical improvement soon thereafter. One week after treatment of all 10 toes, she reported decreased pain and reduced duskiness of both feet (Figure 3).
One month later, the patient endorsed recurring pain in the hands and feet. Physical examination revealed reticular cyanosis and increased violaceous patches of the hands; the feet were overall unchanged from the prior hospitalization. At 4-month follow-up, there was gangrene on the left second, third, and fifth toe in addition to areas of induration noted on the fingers. She was repeatedly hospitalized over the next 6 months for pain management and gangrene of the toes, and finally underwent an amputation of the left and right second toe at the proximal and middle phalanx, respectively. She currently is continuing extensive medical management for pain and gangrene of the digits; she has not received additional onabotulinumtoxinA injections.
Raynaud phenomenon is a vascular disorder characterized by intermittent arteriolar vasospasm of the digits, often due to cold temperature or stress. Approximately 90% of RP cases are primarily idiopathic, with the remaining cases secondary to other diseases, typically systemic sclerosis, SLE, or mixed connective tissue disease.1 Symptoms present with characteristic changing of hands from white (ischemia) to blue (hypoxia) to red (reperfusion). Episodic attacks of vasospasm and ischemia can be painful and lead to digital ulcerations and necrosis of the digits or hands. Other complications including digital tuft pits, pterygium inversum unguis, or torturous nail fold capillaries with capillary dropout also may be seen.2
Although the etiology is multifactorial, the pathophysiology primarily is due to an imbalance of vasodilation and vasoconstriction. Perturbed levels of vasodilatory mediators include nitric oxide, prostacyclin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide.3 Meanwhile, abnormal neural sympathetic control of α-adrenergic receptors located on smooth muscle vasculature and subsequent endothelial hyperproliferation may contribute to inappropriate vasoconstriction.4
The first-line therapy for mild to moderate disease refractory to conservative management includes monotherapy with dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. For severe disease, combination therapy involves addition of other classes of medications including phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, topical nitrates, angiotensin receptor blockers, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Intravenous prostacyclin, endothelin receptor blockers, and onabotulinumtoxinA injections may be added as third-line therapy. Finally, surgical management including sympathectomy with continued pharmacologic therapy may be needed for disease recalcitrant to the aforementioned options.2
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The toxin’s mechanism of action involves inhibition of the release of presynaptic acetylcholine-containing vesicles at the neuromuscular junction through cleavage of sensory nerve action potential receptor proteins. In addition, it inhibits smooth muscle vasoconstriction and pain by blocking α2-adrenergic receptors on blood vessels and chronic pain-transmitting C fibers in nerves, respectively.3,5
Only recently has onabotulinumtoxinA been used for treatment of RP. Botulinum toxin is approved for the treatment of spastic and dystonic diseases such as blepharospasm, headaches in patients with chronic migraines, upper limb spasticity, cervical dystonia, torticollis, ocular strabismus, and hyperhidrosis.3 However, the versatility of its therapeutic effects is evident in its broad off-label clinical applications, including achalasia; carpal tunnel syndrome; and spasticity relating to stroke, paraplegia, and cerebral palsy, among many others.5
Few studies have analyzed the use of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of RP.3,6 There is no consensus yet regarding dose, dilution, or injection sites. One vial of onabotulinumtoxinA contains 100 U and is reconstituted in 20 mL of normal saline to produce 5 U/mL. The simplest technique involves the injection of 5 U into the medial and lateral aspects of each finger at its base, at the level of or just proximal to the A1 pulley, for a total of 50 U per hand.7 In the foot, injection can be made at the base of each toe near the proximal phalanges. A regimen of 50 to 100 U per hand was used by Neumeister et al5 on 19 patients, who subsequently standardized it to 10 U on each neurovascular bundle in a follow-up study,7 giving a total volume of 2 mL per injection. Associated pain or a burning sensation initially may be experienced, which may be mitigated by a lidocaine hydrochloride wrist block prior to injection.7 This technique produced immediate and lasting pain relief, increased tissue perfusion, and resolved digital ulcers in 28 of 33 patients. Most patients reported immediate relief, and a few noted gradual reduction in pain and resolution of chronic ulcers within 2 months. Of the 33 patients, 7 (21.2%) required repeat injections for recurrent pain, but the majority were pain free up to 6 years later with a single injection schedule.7
Injection into the palmar region, wrists, and/or fingers also may be performed. Effects of using different injection sites (eg, neurovascular bundle, distal palm, proximal hand) have been explored and were not notably different between these locations.8 Lastly, the frequency of injections may be attenuated according to the spectrum and severity of the patient’s symptoms. In a report of 11 patients who received a total of 100 U of onabotulinumtoxinA per hand, 5 required repeat injections within 3 to 8 months.9
Studies have reported onabotulinumtoxinA to be a promising option for the treatment of intractable symptoms. Likewise, our patient had a notable reduction in pain with signs of clinical improvement within 24 to 48 hours after injection. The need for amputation 6 months later likely was because the patient’s toes were already necrosing prior to treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA. Thus, the timing of intervention may play a critical role in response to onabotulinumtoxinA injections, particularly because the severity of our patient’s presentation was comparable to other cases reported in the literature. Even in reports using a smaller dose—2 U injected into each toe as opposed to 10 U per toe, as in our case—follow-up showed favorable results.10 In other reports, response can be perceived within days to a week, with remarkable improvement of numbness, pain, digit color, and wound resolution, in addition to decreased frequency and severity of attacks. Moreover, greater vasodilation and subsequent tissue perfusion have been evidenced by objective measures including digital transcutaneous oxygen saturation and Doppler sonography.7,8 Side effects, which are minimal and temporary, include local pain triggering a vasospastic attack and intrinsic muscle weakness; more rarely, dysesthesia and thenar eminence atrophy have been reported.11
Available studies have shown onabotulinumtoxinA to produce favorable results in the treatment of vasospastic disease. We suspect that an earlier intervention for our patient—before necrosis of the toes developed—would have led to a more positive outcome, consistent with other reports. Treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA is an approach to consider when the standard-of-care treatments for RP have been exhausted, as timely intervention may prevent the need for surgery. The indications and appropriate dosing protocol remain to be defined, in addition to more thorough evaluation of its efficacy relative to other medical and surgical options.
- Neumeister MW. The role of botulinum toxin in vasospastic disorders of the hand. Hand Clin. 2015;31:23-37. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2014.09.003
- Bakst R, Merola JF, Franks AG, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon: pathogenesis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:633-653. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.004
- Iorio ML, Masden DL, Higgins JP. Botulinum toxin a treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.006
- Wigley FM, Flavahan NA. Raynaud’s phenomenon. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:556-565. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1507638
- Neumeister MW, Chambers CB, Herron MS, et al. Botox therapy for ischemic digits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:191-200. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a80576
- Sycha T, Graninger M, Auff E, et al. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a pilot study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:312-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.029
- Neumeister MW. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35:2085-2092. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.09.019
- Fregene A, Ditmars D, Siddiqui A. Botulinum toxin type A: a treatment option for digital ischemia in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34:446-452. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.11.026
- Van Beek AL, Lim PK, Gear AJL, et al. Management of vasospastic disorders with botulinum toxin A. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:217-226. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000244860.00674.57
- Dhaliwal K, Griffin M, Denton CP, et al. The novel use of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon in the toes. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018:2017-2019. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-219348
- Eickhoff JC, Smith JK, Landau ME, et al. Iatrogenic thenar eminence atrophy after Botox A injection for secondary Raynaud phenomenon. J Clin Rheumatol. 2016;22:395-396. doi:10.1097/RHU.0000000000000450
- Neumeister MW. The role of botulinum toxin in vasospastic disorders of the hand. Hand Clin. 2015;31:23-37. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2014.09.003
- Bakst R, Merola JF, Franks AG, et al. Raynaud’s phenomenon: pathogenesis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:633-653. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.004
- Iorio ML, Masden DL, Higgins JP. Botulinum toxin a treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.006
- Wigley FM, Flavahan NA. Raynaud’s phenomenon. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:556-565. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1507638
- Neumeister MW, Chambers CB, Herron MS, et al. Botox therapy for ischemic digits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:191-200. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a80576
- Sycha T, Graninger M, Auff E, et al. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon: a pilot study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:312-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.029
- Neumeister MW. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35:2085-2092. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.09.019
- Fregene A, Ditmars D, Siddiqui A. Botulinum toxin type A: a treatment option for digital ischemia in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34:446-452. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.11.026
- Van Beek AL, Lim PK, Gear AJL, et al. Management of vasospastic disorders with botulinum toxin A. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:217-226. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000244860.00674.57
- Dhaliwal K, Griffin M, Denton CP, et al. The novel use of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon in the toes. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018:2017-2019. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-219348
- Eickhoff JC, Smith JK, Landau ME, et al. Iatrogenic thenar eminence atrophy after Botox A injection for secondary Raynaud phenomenon. J Clin Rheumatol. 2016;22:395-396. doi:10.1097/RHU.0000000000000450
Practice Points
- Raynaud phenomenon (RP) is a vascular disorder characterized by episodic vasospasms of the digits often due to cold temperature or stress.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA has been implemented as a treatment of intractable RP after failure with traditional treatments, such as calcium channel blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, prostaglandins, endothelin receptor blockers, and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors.
- A standard technique of delivery of onabotulinumtoxinA involves injection of 5 U/mL into the medial and lateral aspects of each finger at its base (near the metacarpal head) for a total of 50 U per hand or foot.