User login
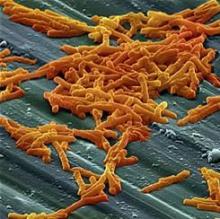
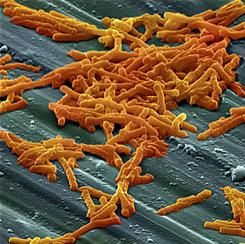
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
AGA offers patient education materials on C. diff that can help your patients better understand the infection. Learn more at http://www.gastro.org/patient-care/conditions-diseases/clostridium-difficile-infection.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @eaztweets
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
AGA offers patient education materials on C. diff that can help your patients better understand the infection. Learn more at http://www.gastro.org/patient-care/conditions-diseases/clostridium-difficile-infection.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @eaztweets
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
AGA offers patient education materials on C. diff that can help your patients better understand the infection. Learn more at http://www.gastro.org/patient-care/conditions-diseases/clostridium-difficile-infection.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES