User login
SAN ANTONIO – Clinicians don’t appear to mind too much when their red blood cell orders are flagged for review by a best practice alert system, and alert fatigue doesn’t seem to hamper patient blood management efforts, investigators in a single-center study reported.
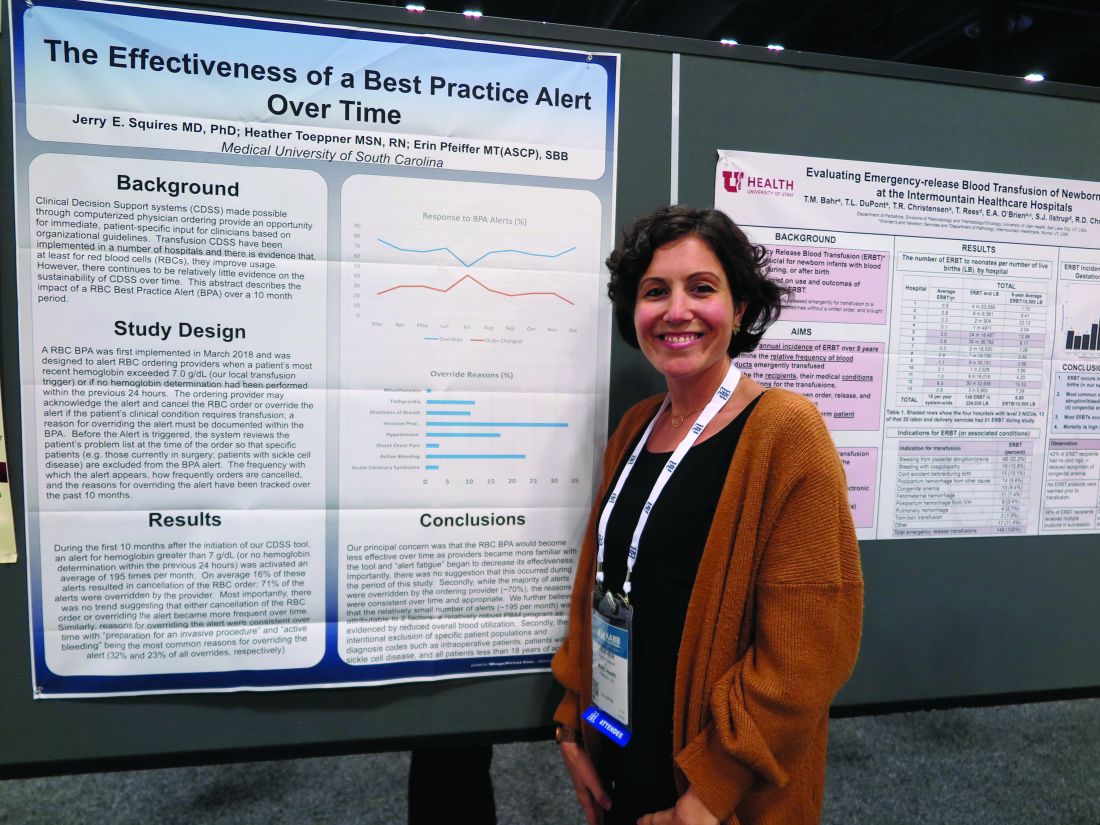
At the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (MUSC), if clinicians order RBC transfusions for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or for patients who did not have a hemoglobin determination over the past 24 hours, they receive a best practice alert. They must acknowledge it and cancel the order, or override it and document a reason in the medical record.
Although approximately 70% of alerts were overridden, the reasons for the overrides “were consistent over time and appropriate,” reported Jerry E. Squires, MD, PhD, and colleagues from MUSC in a poster presentation at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
The goal of the study was to find out if the effectiveness of the alert was wearing out after months of active use by clinicians. “Is it true that they’re clicking too much and they’re inundated with other [best practice alerts], and are they even paying attention?” said coauthor Heather Toeppner, RN, also from MUSC, in an interview. “All in all, we found that the alert is making a lasting impression in our institution,” she said.
Transfusion clinical decision support systems that produce automated alerts for clinicians can improve usage and reduce waste of RBCs, but whether the effect is sustained over time was unknown, Ms. Toeppner said, prompting the investigators to study the effect of the RBC best practice alert over 10 months.
As noted, the alert is triggered when providers order RBCs for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or when there is no record of a hemoglobin test in the chart within the past 24 hours. Before the alert is triggered, however, the system reviews the record and excludes alerts for patients with specific conditions, such as concurrent surgery or sickle cell disease.
The authors found that the alert was triggered an average of 195 times per month over the 10 months studied. On average, 16% of the alerts resulted in a cancellation of the RBC order, and 71% of alerts were overridden.
“Most importantly, there was no trend suggesting that either cancellation of the RBC order or overriding the alert became more frequent over time,” the investigators wrote. “Similarly, reasons for overriding the alert were consistent over time, with ‘preparation for an invasive procedure’ and ‘active bleeding’ being the most common reasons for overriding the alert (32% and 23% of all overrides, respectively).”
Other common reasons for overrides included tachycardia, shortness of breath, hypotension, onset of chest pain, and acute coronary syndrome.
Interestingly, but perhaps not surprisingly, they found that overrides dropped sharply and changed orders rose by the same magnitude in July, when new residents started their rotations.
The investigators wrote that the relatively small number of alerts may be attributable to their institution’s robust patient blood management program and the intentional exclusion of orders for patients with specific diagnostic codes, including intraoperative patients, those with sickle cell disease, and all patients aged younger than 18 years.
The study was internally funded. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SAN ANTONIO – Clinicians don’t appear to mind too much when their red blood cell orders are flagged for review by a best practice alert system, and alert fatigue doesn’t seem to hamper patient blood management efforts, investigators in a single-center study reported.
At the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (MUSC), if clinicians order RBC transfusions for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or for patients who did not have a hemoglobin determination over the past 24 hours, they receive a best practice alert. They must acknowledge it and cancel the order, or override it and document a reason in the medical record.
Although approximately 70% of alerts were overridden, the reasons for the overrides “were consistent over time and appropriate,” reported Jerry E. Squires, MD, PhD, and colleagues from MUSC in a poster presentation at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
The goal of the study was to find out if the effectiveness of the alert was wearing out after months of active use by clinicians. “Is it true that they’re clicking too much and they’re inundated with other [best practice alerts], and are they even paying attention?” said coauthor Heather Toeppner, RN, also from MUSC, in an interview. “All in all, we found that the alert is making a lasting impression in our institution,” she said.
Transfusion clinical decision support systems that produce automated alerts for clinicians can improve usage and reduce waste of RBCs, but whether the effect is sustained over time was unknown, Ms. Toeppner said, prompting the investigators to study the effect of the RBC best practice alert over 10 months.
As noted, the alert is triggered when providers order RBCs for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or when there is no record of a hemoglobin test in the chart within the past 24 hours. Before the alert is triggered, however, the system reviews the record and excludes alerts for patients with specific conditions, such as concurrent surgery or sickle cell disease.
The authors found that the alert was triggered an average of 195 times per month over the 10 months studied. On average, 16% of the alerts resulted in a cancellation of the RBC order, and 71% of alerts were overridden.
“Most importantly, there was no trend suggesting that either cancellation of the RBC order or overriding the alert became more frequent over time,” the investigators wrote. “Similarly, reasons for overriding the alert were consistent over time, with ‘preparation for an invasive procedure’ and ‘active bleeding’ being the most common reasons for overriding the alert (32% and 23% of all overrides, respectively).”
Other common reasons for overrides included tachycardia, shortness of breath, hypotension, onset of chest pain, and acute coronary syndrome.
Interestingly, but perhaps not surprisingly, they found that overrides dropped sharply and changed orders rose by the same magnitude in July, when new residents started their rotations.
The investigators wrote that the relatively small number of alerts may be attributable to their institution’s robust patient blood management program and the intentional exclusion of orders for patients with specific diagnostic codes, including intraoperative patients, those with sickle cell disease, and all patients aged younger than 18 years.
The study was internally funded. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SAN ANTONIO – Clinicians don’t appear to mind too much when their red blood cell orders are flagged for review by a best practice alert system, and alert fatigue doesn’t seem to hamper patient blood management efforts, investigators in a single-center study reported.
At the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (MUSC), if clinicians order RBC transfusions for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or for patients who did not have a hemoglobin determination over the past 24 hours, they receive a best practice alert. They must acknowledge it and cancel the order, or override it and document a reason in the medical record.
Although approximately 70% of alerts were overridden, the reasons for the overrides “were consistent over time and appropriate,” reported Jerry E. Squires, MD, PhD, and colleagues from MUSC in a poster presentation at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
The goal of the study was to find out if the effectiveness of the alert was wearing out after months of active use by clinicians. “Is it true that they’re clicking too much and they’re inundated with other [best practice alerts], and are they even paying attention?” said coauthor Heather Toeppner, RN, also from MUSC, in an interview. “All in all, we found that the alert is making a lasting impression in our institution,” she said.
Transfusion clinical decision support systems that produce automated alerts for clinicians can improve usage and reduce waste of RBCs, but whether the effect is sustained over time was unknown, Ms. Toeppner said, prompting the investigators to study the effect of the RBC best practice alert over 10 months.
As noted, the alert is triggered when providers order RBCs for patients with hemoglobin levels over 7.0 g/dL or when there is no record of a hemoglobin test in the chart within the past 24 hours. Before the alert is triggered, however, the system reviews the record and excludes alerts for patients with specific conditions, such as concurrent surgery or sickle cell disease.
The authors found that the alert was triggered an average of 195 times per month over the 10 months studied. On average, 16% of the alerts resulted in a cancellation of the RBC order, and 71% of alerts were overridden.
“Most importantly, there was no trend suggesting that either cancellation of the RBC order or overriding the alert became more frequent over time,” the investigators wrote. “Similarly, reasons for overriding the alert were consistent over time, with ‘preparation for an invasive procedure’ and ‘active bleeding’ being the most common reasons for overriding the alert (32% and 23% of all overrides, respectively).”
Other common reasons for overrides included tachycardia, shortness of breath, hypotension, onset of chest pain, and acute coronary syndrome.
Interestingly, but perhaps not surprisingly, they found that overrides dropped sharply and changed orders rose by the same magnitude in July, when new residents started their rotations.
The investigators wrote that the relatively small number of alerts may be attributable to their institution’s robust patient blood management program and the intentional exclusion of orders for patients with specific diagnostic codes, including intraoperative patients, those with sickle cell disease, and all patients aged younger than 18 years.
The study was internally funded. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM AABB 2019