User login
, according to a recent cross-sectional study.
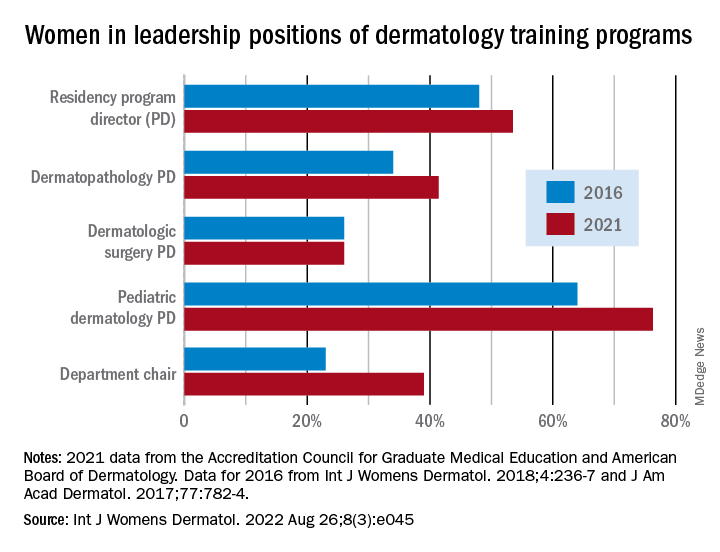
Although women made up more than half of the dermatology residency program directors (53.5%), associate directors (62.6%), and assistant directors (58.3%) in 2021, those numbers fall short of women’s majority (65% in 2018) among the trainees themselves, Yasmine Abushukur of Oakland University in Rochester, Mich., and associates said in a research letter.
Advancements were “made in gender diversity within academic dermatology from 2016 to 2021, [but] women remain underrepresented, particularly in leadership of dermatopathology and dermatologic surgery fellowships,” the investigators wrote.
Data gathered from 142 dermatology residency programs accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education show that progress has been made since 2016, at least among program directors (PDs), of whom 48% were women, according to a previous study. Data on associate and assistant PDs from 2016 were not available to Ms. Abushukur and associates.
At the fellowship program level, women made gains as PDs in dermatopathology (34% in 2016 and 41% in 2021) and pediatric dermatology (64% in 2016 and 76% in 2021), but not in dermatologic surgery, where the proportion held at 26% over the study period. “This disparity is reflective of the general trend in surgery and pathology leadership nationally,” the researchers noted.
Taking a couple of steps up the ladder of authority shows that 39% of dermatology chairs were women in 2021, compared with 23% in 2016. A study published in 2016 demonstrated decreased diversity among academic faculty members as faculty rank increased, and “our data mirror this sentiment by demonstrating a majority of women in assistant and associate PD positions, with a minority of women chairs,” they wrote.
The investigators said that they had no conflicts of interest and no outside funding. Ms. Abushukur’s coauthors were from the departments of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, and Wayne State University, Dearborn, Mich.
, according to a recent cross-sectional study.

Although women made up more than half of the dermatology residency program directors (53.5%), associate directors (62.6%), and assistant directors (58.3%) in 2021, those numbers fall short of women’s majority (65% in 2018) among the trainees themselves, Yasmine Abushukur of Oakland University in Rochester, Mich., and associates said in a research letter.
Advancements were “made in gender diversity within academic dermatology from 2016 to 2021, [but] women remain underrepresented, particularly in leadership of dermatopathology and dermatologic surgery fellowships,” the investigators wrote.
Data gathered from 142 dermatology residency programs accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education show that progress has been made since 2016, at least among program directors (PDs), of whom 48% were women, according to a previous study. Data on associate and assistant PDs from 2016 were not available to Ms. Abushukur and associates.
At the fellowship program level, women made gains as PDs in dermatopathology (34% in 2016 and 41% in 2021) and pediatric dermatology (64% in 2016 and 76% in 2021), but not in dermatologic surgery, where the proportion held at 26% over the study period. “This disparity is reflective of the general trend in surgery and pathology leadership nationally,” the researchers noted.
Taking a couple of steps up the ladder of authority shows that 39% of dermatology chairs were women in 2021, compared with 23% in 2016. A study published in 2016 demonstrated decreased diversity among academic faculty members as faculty rank increased, and “our data mirror this sentiment by demonstrating a majority of women in assistant and associate PD positions, with a minority of women chairs,” they wrote.
The investigators said that they had no conflicts of interest and no outside funding. Ms. Abushukur’s coauthors were from the departments of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, and Wayne State University, Dearborn, Mich.
, according to a recent cross-sectional study.

Although women made up more than half of the dermatology residency program directors (53.5%), associate directors (62.6%), and assistant directors (58.3%) in 2021, those numbers fall short of women’s majority (65% in 2018) among the trainees themselves, Yasmine Abushukur of Oakland University in Rochester, Mich., and associates said in a research letter.
Advancements were “made in gender diversity within academic dermatology from 2016 to 2021, [but] women remain underrepresented, particularly in leadership of dermatopathology and dermatologic surgery fellowships,” the investigators wrote.
Data gathered from 142 dermatology residency programs accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education show that progress has been made since 2016, at least among program directors (PDs), of whom 48% were women, according to a previous study. Data on associate and assistant PDs from 2016 were not available to Ms. Abushukur and associates.
At the fellowship program level, women made gains as PDs in dermatopathology (34% in 2016 and 41% in 2021) and pediatric dermatology (64% in 2016 and 76% in 2021), but not in dermatologic surgery, where the proportion held at 26% over the study period. “This disparity is reflective of the general trend in surgery and pathology leadership nationally,” the researchers noted.
Taking a couple of steps up the ladder of authority shows that 39% of dermatology chairs were women in 2021, compared with 23% in 2016. A study published in 2016 demonstrated decreased diversity among academic faculty members as faculty rank increased, and “our data mirror this sentiment by demonstrating a majority of women in assistant and associate PD positions, with a minority of women chairs,” they wrote.
The investigators said that they had no conflicts of interest and no outside funding. Ms. Abushukur’s coauthors were from the departments of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, and Wayne State University, Dearborn, Mich.
FROM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN’S DERMATOLOGY