User login
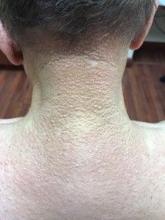
Scleromyxedema
area, characteristically involving the glabella and ears. In some patients, the skin may be intensely pruritic, but this is not a universal finding and varies considerably among patients. In addition to affecting the skin, scleromyxedema has variable multisystem effects on the gastrointestinal tract, and musculoskeletal, pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, and central nervous systems. The most common symptoms are proximal muscle weakness, dysphagia, and dyspnea on exertion. Scleromyxedema can also be associated with a paraproteinemia, mainly immunoglobulin G-lambda type.
Scleromyxedema shares some features with other cutaneous diseases, and the main differential diagnosis includes localized scleromyxedema, also known as lichen myxedematosus. Lichen myxedematosus presents with waxy, firm papules and plaques. Systemic involvement and monoclonal gammopathy are characteristically absent. Scleroderma differs given the increase in fibrosis of cutaneous lesions, a higher percentage of Raynaud’s phenomenon, prominent lung disease, and autoantibodies.
On histopathologic review, scleromyxedema is associated with papular and mucin deposition, and increased fibroblast proliferation. The punch biopsy of the exhibited patient demonstrated a dome-shaped dermal nodule composed of fibroblasts in an edematous stroma. An Alcian blue stain highlighted increased mucin in the dermis and S-100 staining highlighted rare cells in the dermis.
The treatment of choice for scleromyxedema varies but includes intravenous immunoglobulins, systemic glucocorticosteroids, thalidomide, or immunosuppressant medications. In this patient, an IgG paraproteinemia was found on serum protein electrophoresis. The patient was evaluated by hematology-oncology, and no underlying myeloproliferative or dysplastic disease was found. The patient was started on intravenous immunoglobulin infusions with near complete resolution of his eruption and arthritic symptoms.
This case and photo were submitted by Jennifer Maldonado, a medical student at Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla., and Kate Oberlin, MD, and Brian Morrison, MD, of the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of Miami; and Michelle Demory Beckler, PhD, of the College of Osteopathic Medicine and the department of microbiology, College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
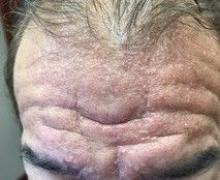
Scleromyxedema
area, characteristically involving the glabella and ears. In some patients, the skin may be intensely pruritic, but this is not a universal finding and varies considerably among patients. In addition to affecting the skin, scleromyxedema has variable multisystem effects on the gastrointestinal tract, and musculoskeletal, pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, and central nervous systems. The most common symptoms are proximal muscle weakness, dysphagia, and dyspnea on exertion. Scleromyxedema can also be associated with a paraproteinemia, mainly immunoglobulin G-lambda type.
Scleromyxedema shares some features with other cutaneous diseases, and the main differential diagnosis includes localized scleromyxedema, also known as lichen myxedematosus. Lichen myxedematosus presents with waxy, firm papules and plaques. Systemic involvement and monoclonal gammopathy are characteristically absent. Scleroderma differs given the increase in fibrosis of cutaneous lesions, a higher percentage of Raynaud’s phenomenon, prominent lung disease, and autoantibodies.
On histopathologic review, scleromyxedema is associated with papular and mucin deposition, and increased fibroblast proliferation. The punch biopsy of the exhibited patient demonstrated a dome-shaped dermal nodule composed of fibroblasts in an edematous stroma. An Alcian blue stain highlighted increased mucin in the dermis and S-100 staining highlighted rare cells in the dermis.
The treatment of choice for scleromyxedema varies but includes intravenous immunoglobulins, systemic glucocorticosteroids, thalidomide, or immunosuppressant medications. In this patient, an IgG paraproteinemia was found on serum protein electrophoresis. The patient was evaluated by hematology-oncology, and no underlying myeloproliferative or dysplastic disease was found. The patient was started on intravenous immunoglobulin infusions with near complete resolution of his eruption and arthritic symptoms.
This case and photo were submitted by Jennifer Maldonado, a medical student at Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla., and Kate Oberlin, MD, and Brian Morrison, MD, of the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of Miami; and Michelle Demory Beckler, PhD, of the College of Osteopathic Medicine and the department of microbiology, College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
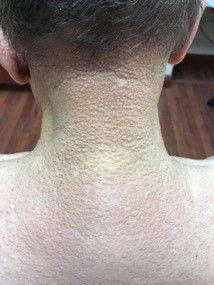
Scleromyxedema
area, characteristically involving the glabella and ears. In some patients, the skin may be intensely pruritic, but this is not a universal finding and varies considerably among patients. In addition to affecting the skin, scleromyxedema has variable multisystem effects on the gastrointestinal tract, and musculoskeletal, pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, and central nervous systems. The most common symptoms are proximal muscle weakness, dysphagia, and dyspnea on exertion. Scleromyxedema can also be associated with a paraproteinemia, mainly immunoglobulin G-lambda type.
Scleromyxedema shares some features with other cutaneous diseases, and the main differential diagnosis includes localized scleromyxedema, also known as lichen myxedematosus. Lichen myxedematosus presents with waxy, firm papules and plaques. Systemic involvement and monoclonal gammopathy are characteristically absent. Scleroderma differs given the increase in fibrosis of cutaneous lesions, a higher percentage of Raynaud’s phenomenon, prominent lung disease, and autoantibodies.
On histopathologic review, scleromyxedema is associated with papular and mucin deposition, and increased fibroblast proliferation. The punch biopsy of the exhibited patient demonstrated a dome-shaped dermal nodule composed of fibroblasts in an edematous stroma. An Alcian blue stain highlighted increased mucin in the dermis and S-100 staining highlighted rare cells in the dermis.
The treatment of choice for scleromyxedema varies but includes intravenous immunoglobulins, systemic glucocorticosteroids, thalidomide, or immunosuppressant medications. In this patient, an IgG paraproteinemia was found on serum protein electrophoresis. The patient was evaluated by hematology-oncology, and no underlying myeloproliferative or dysplastic disease was found. The patient was started on intravenous immunoglobulin infusions with near complete resolution of his eruption and arthritic symptoms.
This case and photo were submitted by Jennifer Maldonado, a medical student at Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla., and Kate Oberlin, MD, and Brian Morrison, MD, of the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of Miami; and Michelle Demory Beckler, PhD, of the College of Osteopathic Medicine and the department of microbiology, College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.